Первый слайд презентации
Direct and reported speech 1 Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Answers 1/2 Grammar Review
Слайд 2
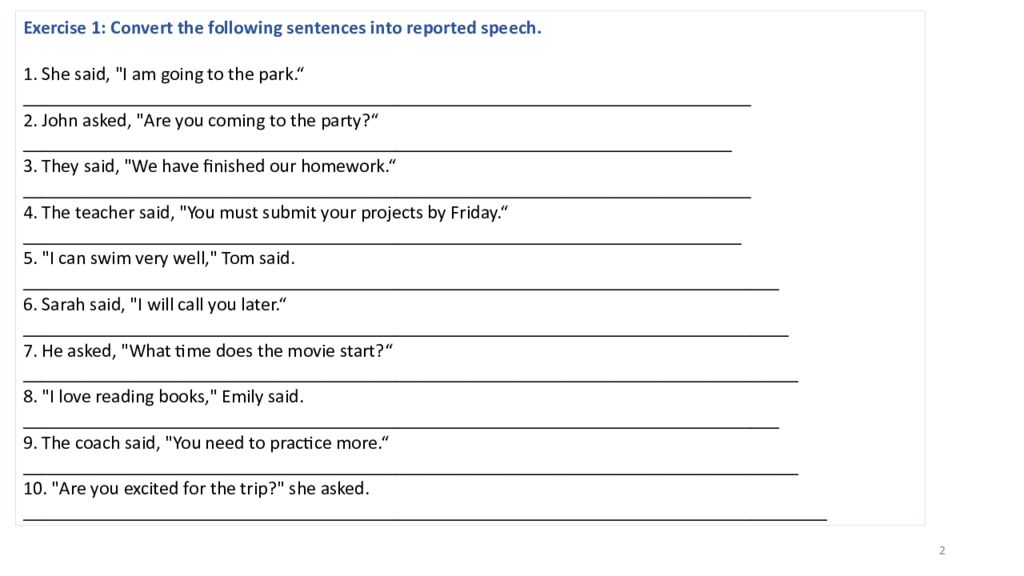
Exercise 1: Convert the following sentences into reported speech. 1. She said, "I am going to the park.“ ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. John asked, "Are you coming to the party?“ __________________________________________________________________________ 3. They said, "We have finished our homework.“ ____________________________________________________________________________ 4. The teacher said, "You must submit your projects by Friday.“ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. "I can swim very well," Tom said. _______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Sarah said, "I will call you later.“ ________________________________________________________________________________ 7. He asked, "What time does the movie start?“ _________________________________________________________________________________ 8. "I love reading books," Emily said. _______________________________________________________________________________ 9. The coach said, "You need to practice more.“ _________________________________________________________________________________ 10. "Are you excited for the trip?" she asked. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2
Слайд 3
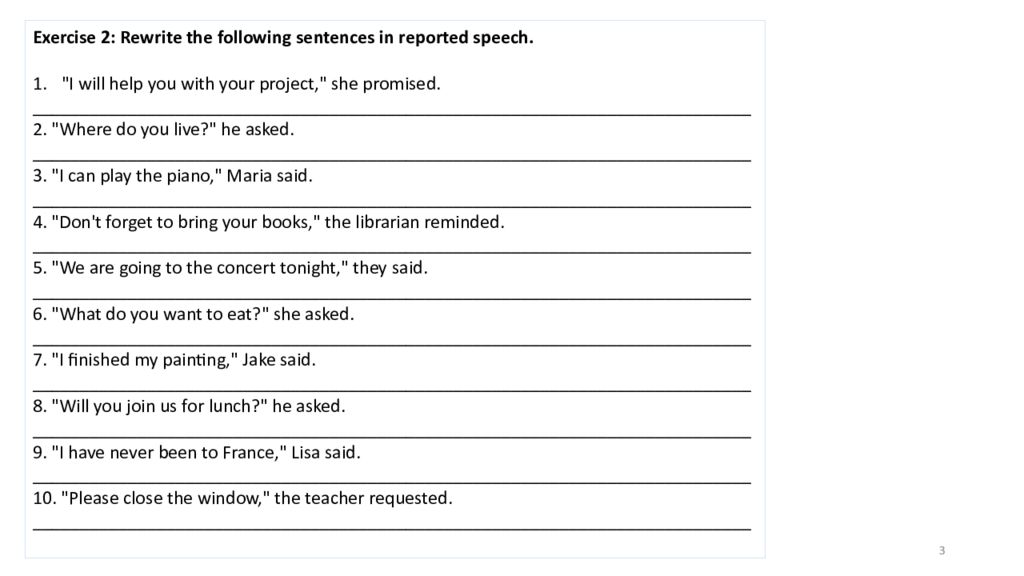
Exercise 2: Rewrite the following sentences in reported speech. "I will help you with your project," she promised. ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. "Where do you live?" he asked. ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. "I can play the piano," Maria said. ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. "Don't forget to bring your books," the librarian reminded. ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. "We are going to the concert tonight," they said. ___________________________________________________________________________ 6. "What do you want to eat?" she asked. ___________________________________________________________________________ 7. "I finished my painting," Jake said. ___________________________________________________________________________ 8. "Will you join us for lunch?" he asked. ___________________________________________________________________________ 9. "I have never been to France," Lisa said. ___________________________________________________________________________ 10. "Please close the window," the teacher requested. ___________________________________________________________________________ 3
Слайд 5
Answers for Exercise 1: She said that she was going to the park. John asked if I was coming to the party. They said that they had finished their homework. The teacher said that we must submit our projects by Friday. Tom said that he could swim very well. Sarah said that she would call me later. He asked what time the movie started. Emily said that she loved reading books. The coach said that we needed to practice more. She asked if I was excited for the trip. Answers for Exercise 2: She promised that she would help me with my project. He asked where I lived. Maria said that she could play the piano. The librarian reminded me not to forget to bring my books. They said that they were going to the concert that night. She asked what I wanted to eat. Jake said that he had finished his painting. He asked if I would join them for lunch. Lisa said that she had never been to France. The teacher requested me to close the window. 5
Слайд 6
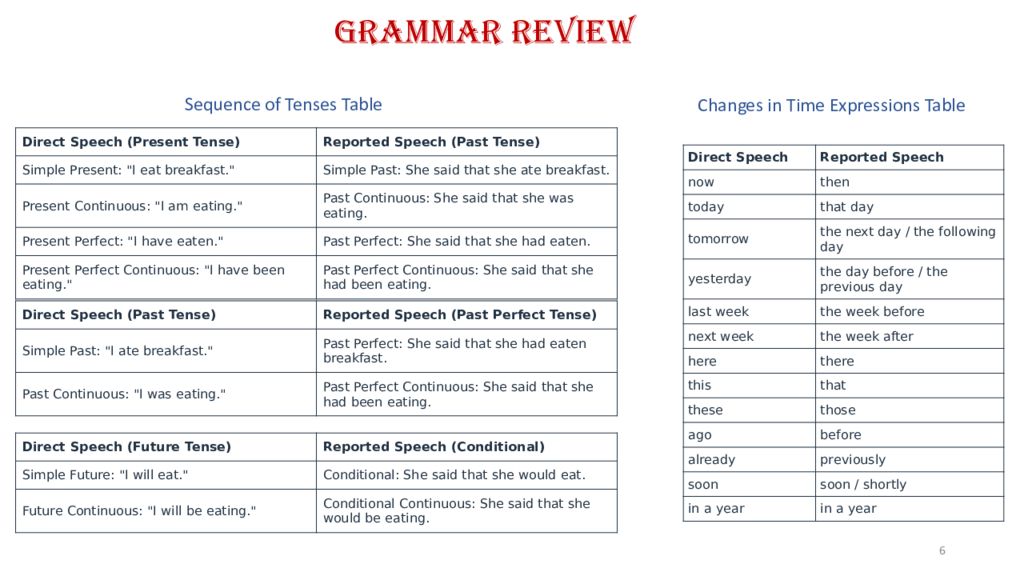
6 Sequence of Tenses Table Direct Speech (Present Tense) Reported Speech (Past Tense) Simple Present: "I eat breakfast." Simple Past: She said that she ate breakfast. Present Continuous: "I am eating." Past Continuous: She said that she was eating. Present Perfect: "I have eaten." Past Perfect: She said that she had eaten. Present Perfect Continuous: "I have been eating." Past Perfect Continuous: She said that she had been eating. Direct Speech (Past Tense) Reported Speech (Past Perfect Tense) Simple Past: "I ate breakfast." Past Perfect: She said that she had eaten breakfast. Past Continuous: "I was eating." Past Perfect Continuous: She said that she had been eating. Direct Speech (Future Tense) Reported Speech (Conditional) Simple Future: "I will eat." Conditional: She said that she would eat. Future Continuous: "I will be eating." Conditional Continuous: She said that she would be eating. Changes in Time Expressions Table Direct Speech Reported Speech now then today that day tomorrow the next day / the following day yesterday the day before / the previous day last week the week before next week the week after here there this that these those ago before already previously soon soon / shortly in a year in a year Grammar review
Слайд 7
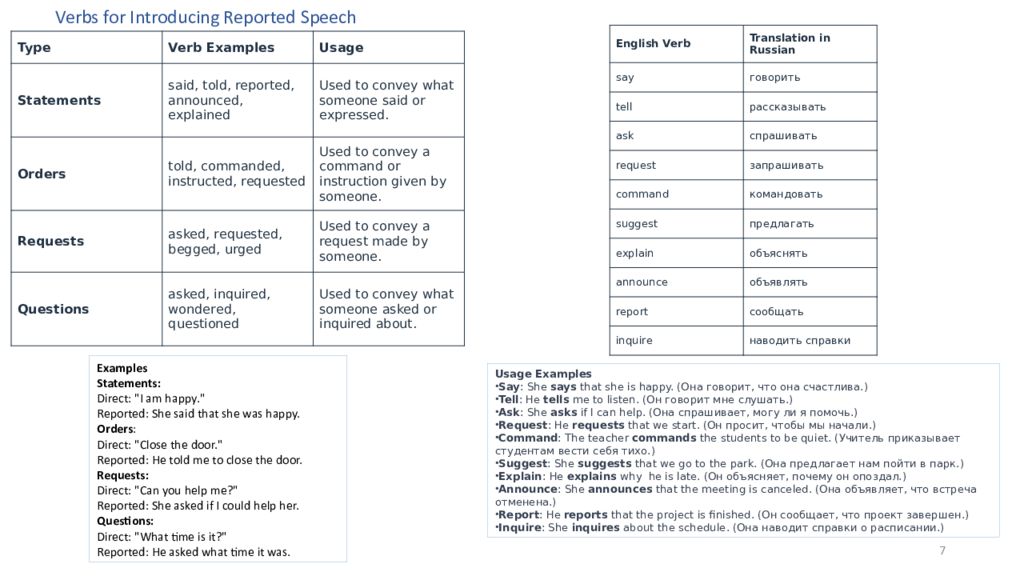
7 Verbs for Introducing Reported Speech Type Verb Examples Usage Statements said, told, reported, announced, explained Used to convey what someone said or expressed. Orders told, commanded, instructed, requested Used to convey a command or instruction given by someone. Requests asked, requested, begged, urged Used to convey a request made by someone. Questions asked, inquired, wondered, questioned Used to convey what someone asked or inquired about. English Verb Translation in Russian say говорить tell рассказывать ask спрашивать request запрашивать command командовать suggest предлагать explain объяснять announce объявлять report сообщать inquire наводить справки Examples Statements: Direct: "I am happy." Reported: She said that she was happy. Orders : Direct: "Close the door." Reported: He told me to close the door. Requests: Direct: "Can you help me?" Reported: She asked if I could help her. Questions: Direct: "What time is it?" Reported: He asked what time it was. Usage Examples Say : She says that she is happy. ( Она говорит, что она счастлива.) Tell : He tells me to listen. ( Он говорит мне слушать.) Ask : She asks if I can help. ( Она спрашивает, могу ли я помочь.) Request : He requests that we start. ( Он просит, чтобы мы начали.) Command : The teacher commands the students to be quiet. ( Учитель приказывает студентам вести себя тихо.) Suggest : She suggests that we go to the park. ( Она предлагает нам пойти в парк.) Explain : He explains why he is late. ( Он объясняет, почему он опоздал.) Announce : She announces that the meeting is canceled. ( Она объявляет, что встреча отменена.) Report : He reports that the project is finished. ( Он сообщает, что проект завершен.) Inquire : She inquires about the schedule. ( Она наводит справки о расписании.)
Последний слайд презентации: Direct and reported speech 1 Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Answers 1/2 Grammar Review
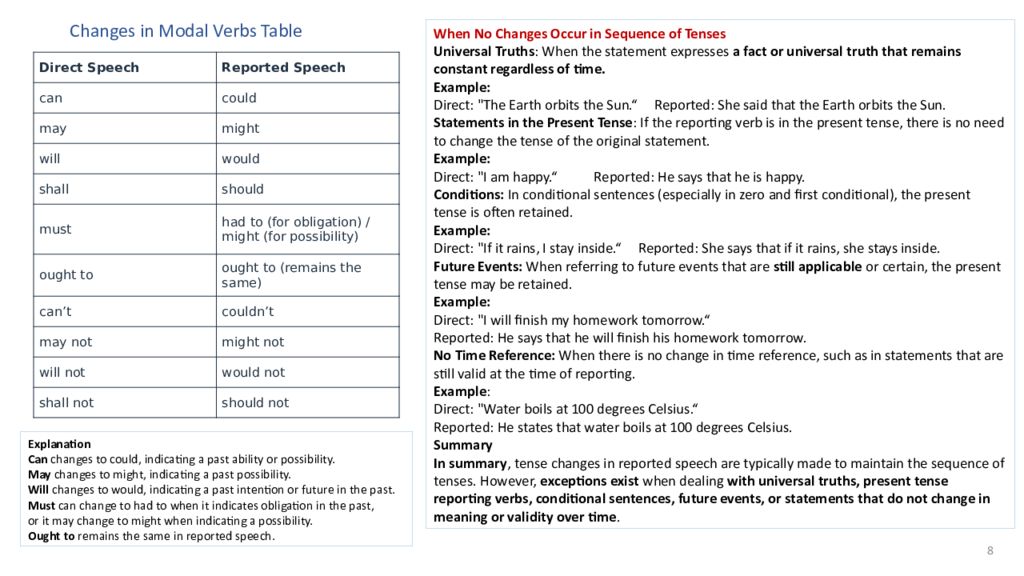
8 Changes in Modal Verbs Table Direct Speech Reported Speech can could may might will would shall should must had to (for obligation) / might (for possibility) ought to ought to (remains the same) can’t couldn’t may not might not will not would not shall not should not Explanation Can changes to could, indicating a past ability or possibility. May changes to might, indicating a past possibility. Will changes to would, indicating a past intention or future in the past. Must can change to had to when it indicates obligation in the past, or it may change to might when indicating a possibility. Ought to remains the same in reported speech. When No Changes Occur in Sequence of Tenses Universal Truths : When the statement expresses a fact or universal truth that remains constant regardless of time. Example: Direct: "The Earth orbits the Sun.“ Reported: She said that the Earth orbits the Sun. Statements in the Present Tense : If the reporting verb is in the present tense, there is no need to change the tense of the original statement. Example: Direct: "I am happy.“ Reported: He says that he is happy. Conditions: In conditional sentences (especially in zero and first conditional), the present tense is often retained. Example: Direct: "If it rains, I stay inside.“ Reported: She says that if it rains, she stays inside. Future Events: When referring to future events that are still applicable or certain, the present tense may be retained. Example: Direct: "I will finish my homework tomorrow.“ Reported: He says that he will finish his homework tomorrow. No Time Reference: When there is no change in time reference, such as in statements that are still valid at the time of reporting. Example : Direct: "Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.“ Reported: He states that water boils at 100 degrees Celsius. Summary In summary, tense changes in reported speech are typically made to maintain the sequence of tenses. However, exceptions exist when dealing with universal truths, present tense reporting verbs, conditional sentences, future events, or statements that do not change in meaning or validity over time.