Первый слайд презентации: high and low context cultures. WHAT IS ABOUT INDIA?
Подготовил: Симакова Я.А., МЕМ-201 ФГБОУ ВО «Челябинский государственный университет» Факультет Евразии и Востока Кафедра зарубежного регионоведения, политологии и восточной философии
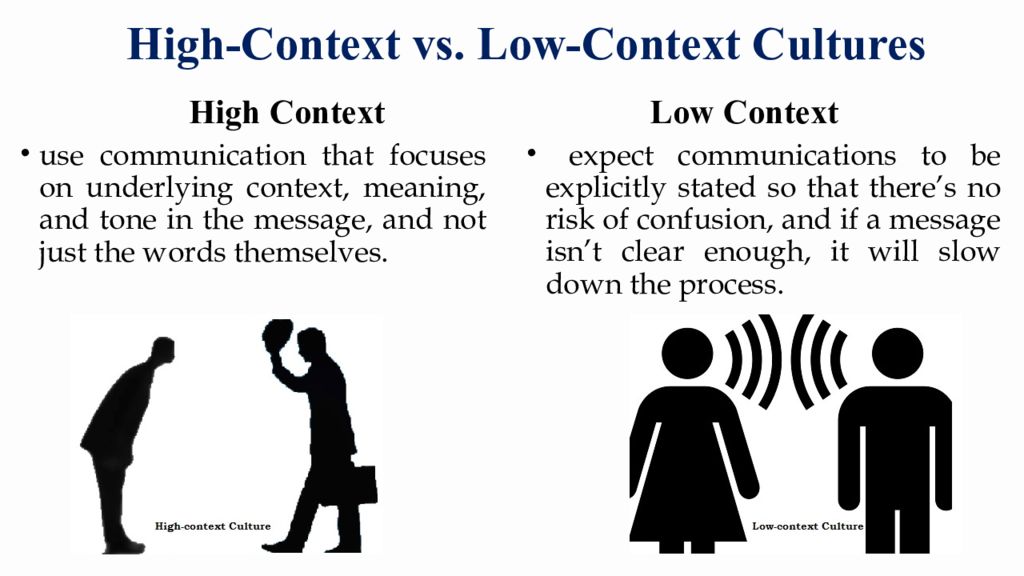
Слайд 2: High-Context vs. Low-Context Cultures
High Context use communication that focuses on underlying context, meaning, and tone in the message, and not just the words themselves. Low Context expect communications to be explicitly stated so that there’s no risk of confusion, and if a message isn’t clear enough, it will slow down the process.
Слайд 3: १. Perception of Time
There is one interesting saying in India: « In three days something can happen that has not happened in three years » Due to cultural and religious feature s, time is not perceived as something linear in India. This is not a set of intervals, each of which is designed for a specific purpose. Time is cyclical here, each stage or epoch repeats itself many times. Therefore, to arrive on time in India is to some extent even impolite. It is considered normal to be late for an appointment by one or two hours. The exception will be visit of a doctor: here it is allowed to come later for 15-20 minutes.
Слайд 4: १. Perception of Time
Thus, time is not given much importance in India. Haste and fast decisions are not acceptable here. High Context vs. Low Context 1 :0
Слайд 5: २. The Distance B etween the Interlocutors
It is necessary to keep a distance between unfamiliar people. On first meeting, it is acceptable for men to shake hands with each other. Women are greeted with a nod of the head or a traditional gesture (the palms of the hands are folded together in front of the chest). High Context vs. Low Context 2 :0
Слайд 6: ३. Features of the Indian Language
In Hindi, the main official language of India, there are three levels of politeness. It is necessary to treat parents and the elderly, seniors and strangers with respect. Simple communication is allowed between peers or younger in age. High Context vs. Low Context 3:0
Слайд 7: ४. Features of Verbal C ommunication
In everyday life, Indians tend to be very talkative and proactive. It is customary to start a conversation only with pleasant news or happy events. In the negotiation process, on the contrary, the members of the Indian delegation use only the necessary minimum of words, the rest of the time they prefer to listen to the interlocutor. High Context vs. Low Context 3:1
Слайд 8: ५. Features of Speech
According to research, the pace of speech in India is on average slower than the generally accepted in the world. It is customary to take short pauses here to think about what has been said and prepare the correct answer. Indians often use silence to draw attention to important facts and emphasize the meaning of expressions. The interlocutors must be addressed by status, using the words “Miss", “ M r.", “Professor" and so on, after which the last name is called. High Context vs. Low Context 4 :1
Слайд 9: ६. The Structure of Society
India is characterized by a culture of collectivism. It is not customary to express your individuality here. An important role is played by the hierarchy. A uthorities of parents, older, more experienced and high-status colleagues, superiors are of p rimary importance here. It is also not customary to openly express one's opinion during the negotiation process, all important and final decisions are made by the head of the delegation. High Context vs. Low Context 5:1
Слайд 10: ७. The Role of Non-verbal C ommunication
Gestures, facial expressions and body postures are of paramount importance in Indian culture. Sometimes it can completely replace words. For example, in traditional dance, an Indian can tell a lot more with the help of sacred body positions and gestures (mudras). During international negotiations, members of the Indian delegation carefully monitor the facial expressions and gestures of the interlocutors, as well as their own. High Context vs. Low Context 6 :1
Слайд 11: ८. Preferred Way of Communication
In formal communication, Indian businessmen prefer only face-to-face meetings. Written communication or phone conversations do not allow to see the other person's face and body language. Also it is often impossible to establish close and friendly relations at a distance. Therefore, Indians prefer to negotiate in several stages, using long pauses for reflection. High Context vs. Low Context 7:1
Слайд 12: ९. Attitude to Conflicts and Refusals
The members of the Indian delegation never give a direct negative answer. They avoid conflicts, trying to find a solution that will suit all parties to the negotiations. However, the absence of a refusal does not mean consent! If a person says that there are no problems, then most often there are, but no one will say so directly. On the other hand, Indians demand flexibility and openness from foreigners. They are suspicious of ambiguous and undefined words. High Context vs. Low Context 8 :1
Слайд 13: १०. The Importance of Traditions in Communication
At the heart of Indian business culture is the importance of trust and personal relationships. Making connections often begins with getting to know business matchmakers. In India, they are called "intermediaries of trust ". Indians consider the first meeting as an introductory one and most often do not discuss business issues at it. During business communication Indians will ask a lot of personal questions about one’s health or family. This is not just curiosity: in India, it is considered good form to inquire about a partner's personal life. High Context vs. Low Context 9 :1
Слайд 14: So What C ontext D oes Indian Culture B elong T o?
Like in many Eastern countries, Indian culture is high - context. Traditions, non-verbal communication and the hidden meaning of expressions play an important role here. Religion and philosophy have had a great influence on Indian culture. It help to preserve and pass on traditions through generations.