Слайд 2
“Motivation is the art of getting people to do what you want them to do because they want to do it ” D. Dwight → helping people see the connection between effort & reward
Слайд 3: What about you?
List five criteria (pay, recognition, challenging work, friendships, status, the opportunity to do new things, the opportunity to travel, etc.) that would be most important to you in a job. Rank them by order of importance.
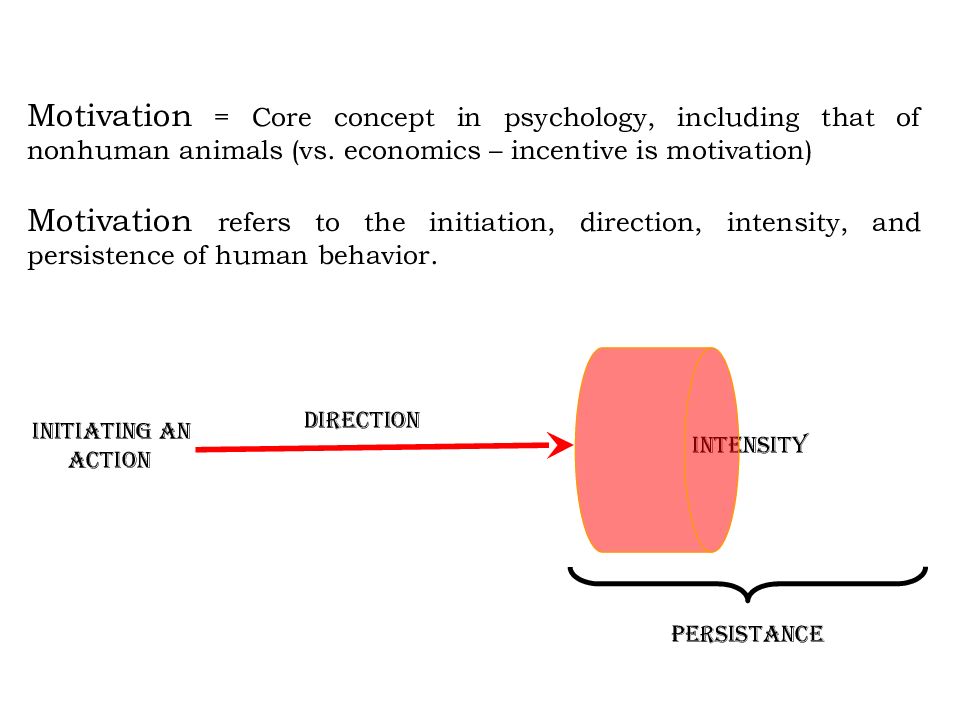
Слайд 4: Motivation = Core concept in psychology, including that of nonhuman animals (vs. economics – incentive is motivation)
Motivation refers to the initiation, direction, intensity, and persistence of human behavior. Initiating an action direction intensity persistance
Слайд 5: Extrinsic motivation = a certain behavior is performed with the purpose of obtaining external rewards. Intrinsic motivation = a certain behavior is performed for its own sake. * Intrinsic motivation ≠ T asks that intrinsically motivate
Слайд 6
Work Motivation = Psychological processes that direct, energize, and maintain action towards a job, goal, task, role, or project Important in the workplace? Determinants of Individual Performance: Ability—the capability to do the job Motivation—the desire to do the job Opportunity—the resources needed and the possibility of doing the job
Слайд 7: Content perspectives
Focus on needs and deficiencies of individuals Approaches to motivation that try to answer the question, “What factors in the workplace motivate people?” Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory McClelland’s Achievement, Power, and Affiliation Needs
Слайд 8: Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs
Self- actualization Esteem Belongingness Security Physiology Food Achievement Status Friendship Stability Job Friends Pension Base NEEDS General Examples Organizational Examples job Challenging title at work plan salary Source: Adapted from Abraham H. Maslow, “ A Theory of Human Motivation,” Psychology Review, 1943, Vol. 50, pp. 370-396.
Слайд 9
Weaknesses of Maslow’s theory Five levels of need are not always present. Ordering or importance of needs is not always the same. Cultural differences.
Слайд 10: The Two-Factor Theory (Herzberg)
People’s satisfaction and dissatisfaction are influenced by two independent sets of factors -motivation factors and hygiene factors. Theory assumes that job satisfaction and job dissatisfaction are on two distinct continuums: Motivational factors (work content) are on a continuum that ranges from satisfaction to no satisfaction. Hygiene factors (work environment) are on a separate continuum that ranges from dissatisfaction to no dissatisfaction.
Слайд 11
Satisfaction No satisfaction Motivation Factors • Achievement • Recognition • The work itself • Responsibility • Advancement and growth Dissatisfaction No dissatisfaction Hygiene Factors • Supervisors • Working conditions • Interpersonal relations • Pay and security • Company policies and administration
Слайд 12
Criticisms of the Two-Factor Theory Interview findings are subject to different explanations. Sample population was not representative. Subsequent research has not upheld theory.
Слайд 13: Individual Human Needs (McClelland)
The need for achievement The desire to accomplish a goal or task more effectively than in the past. The need for affiliation The desire for human companionship and acceptance. The need for power The desire to be influential in a group and to be in control of one’s environment.
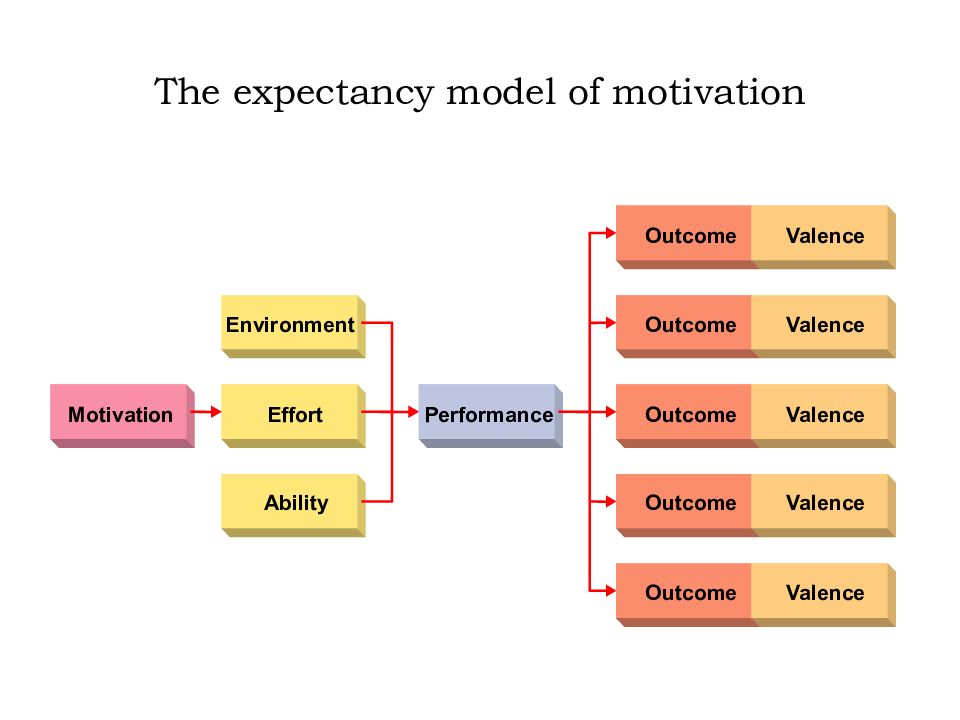
Слайд 16: The expectancy model of motivation
Environment Motivation Effort Performance Ability Outcome Outcome Outcome Valence Outcome Valence Outcome Valence Valence Valence
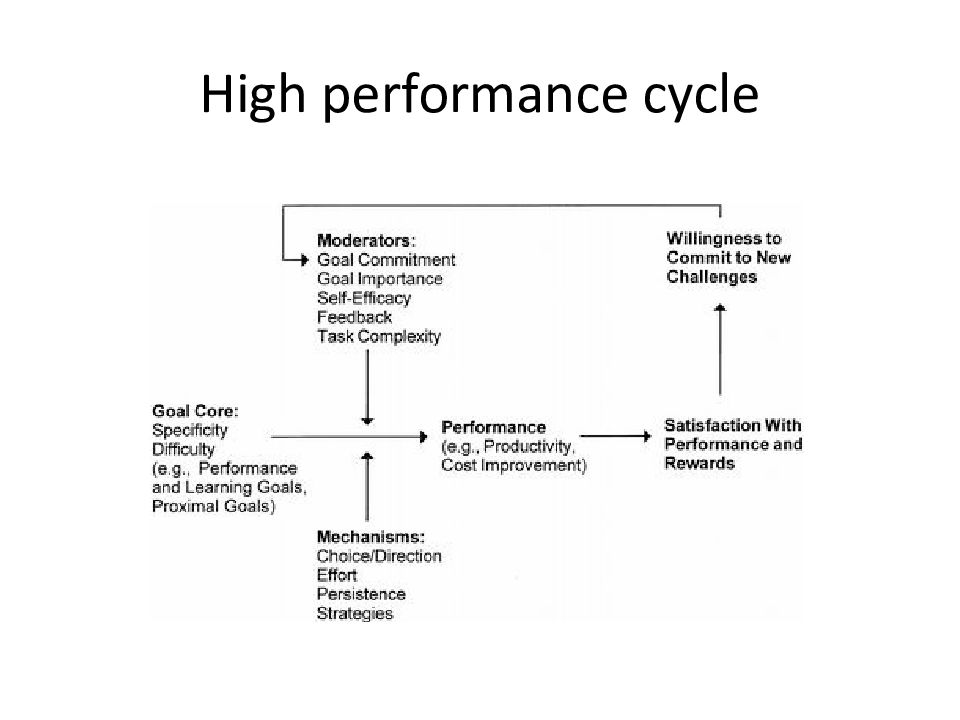
Слайд 17: Goal-Setting Theory
Assumptions Behavior is a result of conscious goals and intentions. Setting goals influences the behavior of people in organizations. Q: What is a goal?
Слайд 18
Specific and Difficult Goals, With Feedback lead to higher performance then “do your best”
Слайд 19: Why?
Expectancy theory would state the opposite: difficult goals, lower expectancy Difficulty: why not attainable goals rather than difficult?
Слайд 20
Because… difficult goals enhance Focus (ward off distractions) Effort (energizing to meet challenge) Persistence (not necessarily time spent) Discovery of strategies Task interest, discovering pleasurable aspects of an activity Self-efficacy
Слайд 21: Moderators of goal setting – performance relation
Commitment Feedback Task complexity
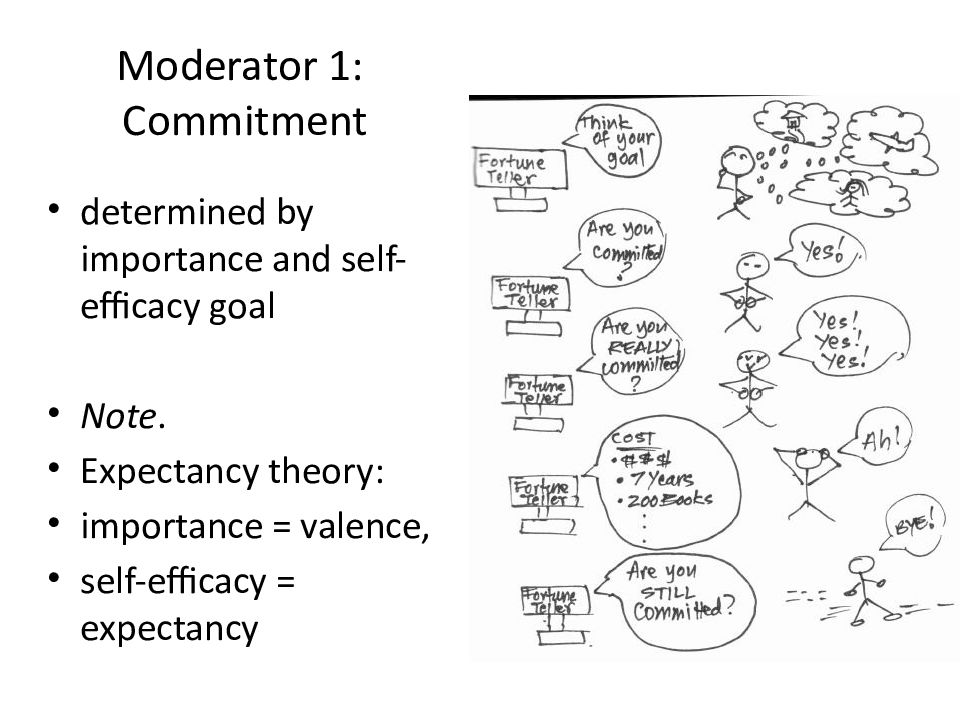
Слайд 22: Moderator 1: Commitment
determined by importance and self-efficacy goal Note. Expectancy theory : importance = valence, self-efficacy = expectancy
Слайд 23: Moderator 2: Feedback
Feedback “revealing progress in relation to goal” May lead to adapting goal, increasing effort, or coming up with new strategies Feedback vs. feedforward control: Discrepancy reduction vs. discrepancy production
Слайд 24: Moderator 3: Task Complexity
The more complex a task, the more variation in solutions. Performance dependent on ability to find appropriate strategies Instead of performance goal: Proximal goal: setting subgoals Learning goal: incremental rather than fixed idea of capability Creativity goal: output should be novel and appropriate.
Слайд 25: Practical applications of goal setting
Management by objectives Productivity enhancement Performance appraisal In selection interview Personal development plan
Слайд 27: Self-determination theory
Intrinsic – a desire to act based on interest and enjoyment of the work itself - vs. extrinsic motivation Intrinsic associated with higher performance, persistence, productivity
Слайд 28
“For the sake of doing it” Autonomy—need to determine, control, and organize one’s own behavior and goals Competence—need to effectively learn and master challenging tasks Relatedness—need to feel attached to others Note. Where is fun and enjoym ent?
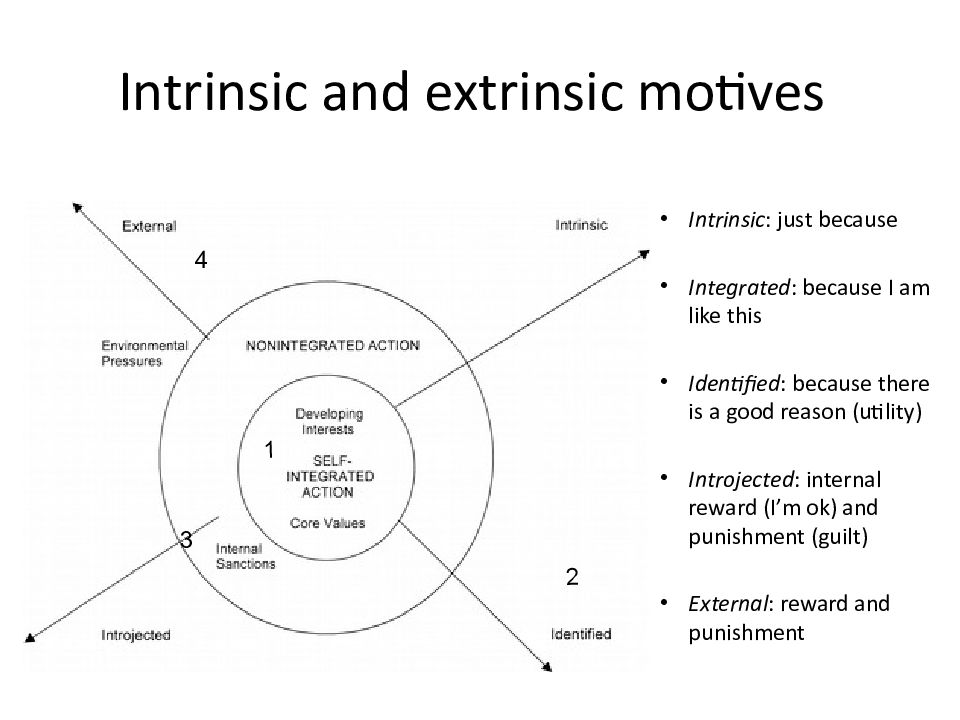
Слайд 29: Intrinsic and extrinsic motives
Intrinsic : just because Integrated : because I am like this Identified : because there is a good reason (utility) Introjected : internal reward (I’m ok) and punishment (guilt) External : reward and punishment 2 3 4 1
Слайд 30: At work
Internalize extrinsic goals More motivating when autonomy, competence, relatedness not threatened (controlling vs. supporting)
Слайд 31: Self-determination theory, still controversial ?
Is distinction intrinsic / extrinsic useful? (individual differences, p. 18 Grant & Shin) When does extrinsic detract from intrinsic? (crowding out)
Слайд 32: Feedback intervention theory
Feedback intervention: “Actions taken by (an) external agent(s ) to provide information regarding some aspect(s) of one’s task performance” (p.255) Cf. 360 degree feedback in organizations
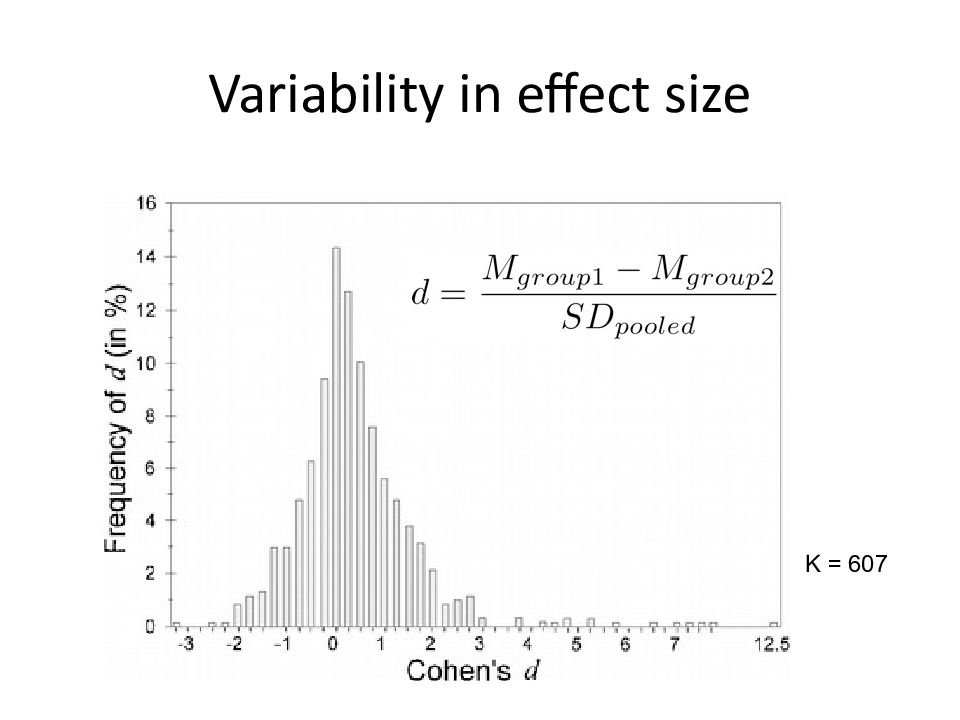
Слайд 33: Feedback does not uniformly improve performance”
Based upon inconsistent effects of feedback in previous studies, variability quantified. F ive propositions examined in preliminary test
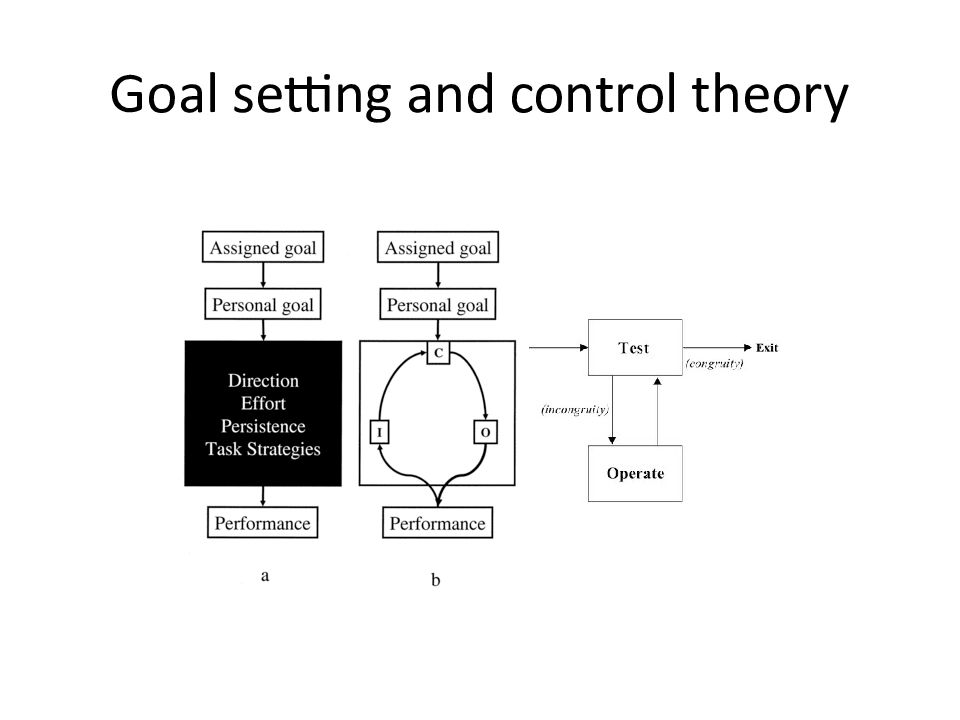
Слайд 35: Proposed mechanisms
Behavior regulated by comparison feedback to goals (control theory ) Goals are organized hierarchically Attention is limited ; only gaps receive attention Attention normally at moderate level of hierarchy FIs change level of attention to affect behavior
Слайд 37: Four strategies to eliminate negative feedback-goal gap
Increase effort ( motivation ) Abandon goal ( giving up, learned helplessness ) Change goal Reject feedback message
Слайд 38: Discrepancy reduction idea is too simple
What about: Multiple standards used? Detrimental effects of any feedback on learning? Affect induced by FI (arousal, pleasantness), does it affect performance?
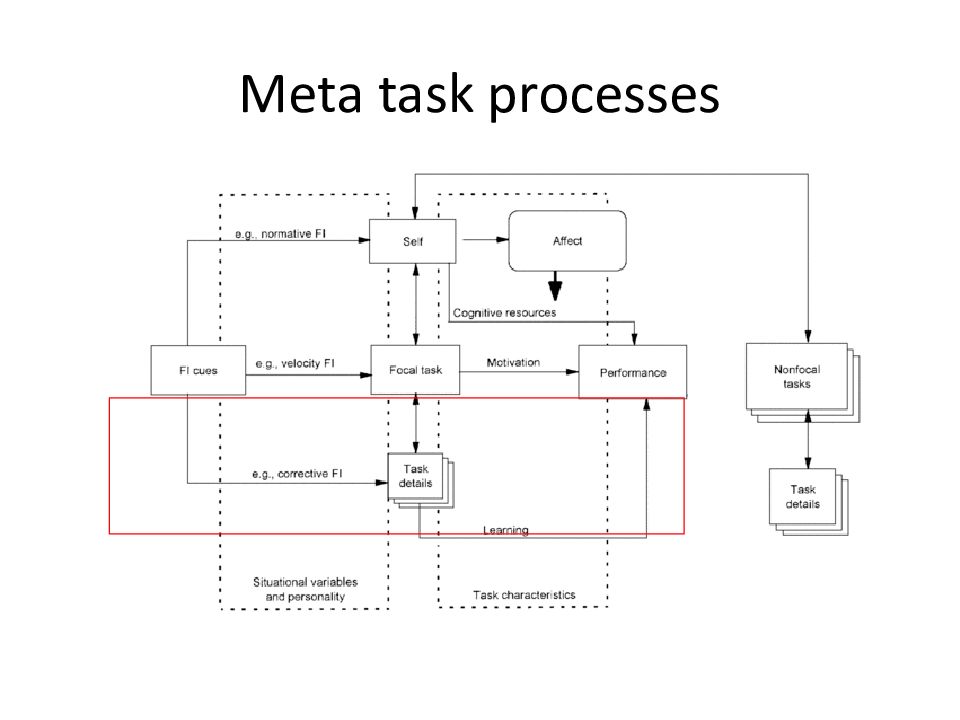
Слайд 39: Hierarchy of goals
Meta task processes: self Task motivation processes: focal task Task learning processes: task details Higher levels control lower processes
Слайд 40: Attention
Only loops that receive attention are acted on Normally at moderate level of hierarchy FI attracts attention
Слайд 42: Update on tasks (Van Dijk & Kluger, 2010)
Positive feedback on promotion task : positive effect on performance ( tasks requiring creativity-approach) Positive feedback on prevention task : negative effect on performance ( tasks requiring vigilance and attention to detail)
Слайд 43: Feedback intervention summary
People seek feedback, but do not always use it to improve performance Instead they assess progress of goals of the self, which may even deteriorate performance FI most useful when : Familiar task, cues that contain learning, attracting attention at task level, no cues on meta- task level