Первый слайд презентации: Model–View–Controller (MVC) Architecture
MVC is an architectural design pattern that divides an application into three interconnected components: Model, View, and Controller. It helps organize the code, making it structured, maintainable, and scalable.
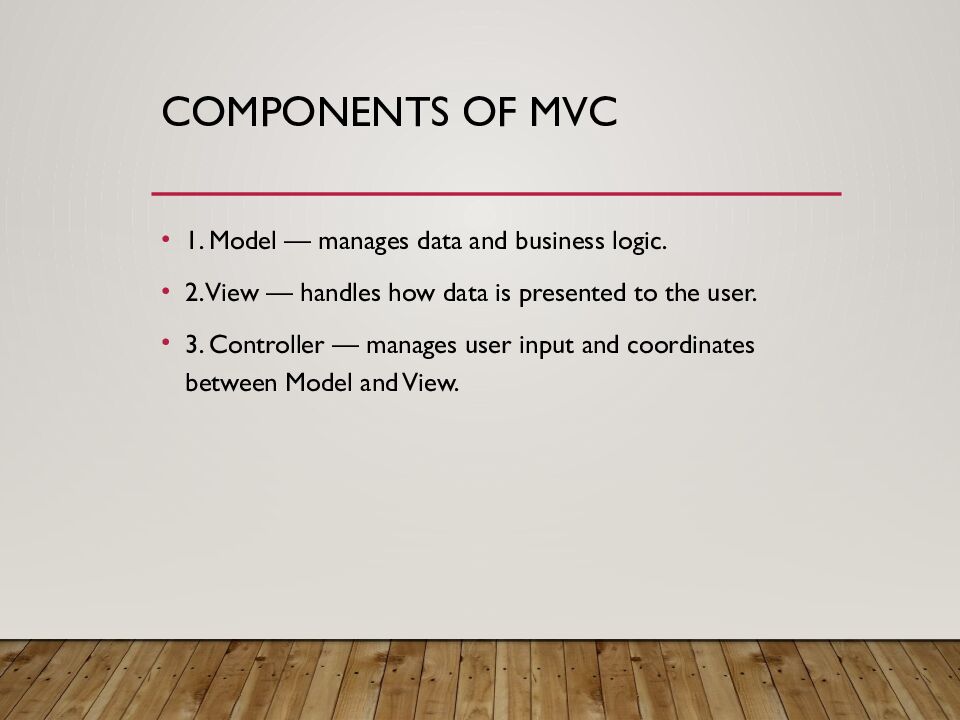
Слайд 2: Components of MVC
1. Model — manages data and business logic. 2. View — handles how data is presented to the user. 3. Controller — manages user input and coordinates between Model and View.
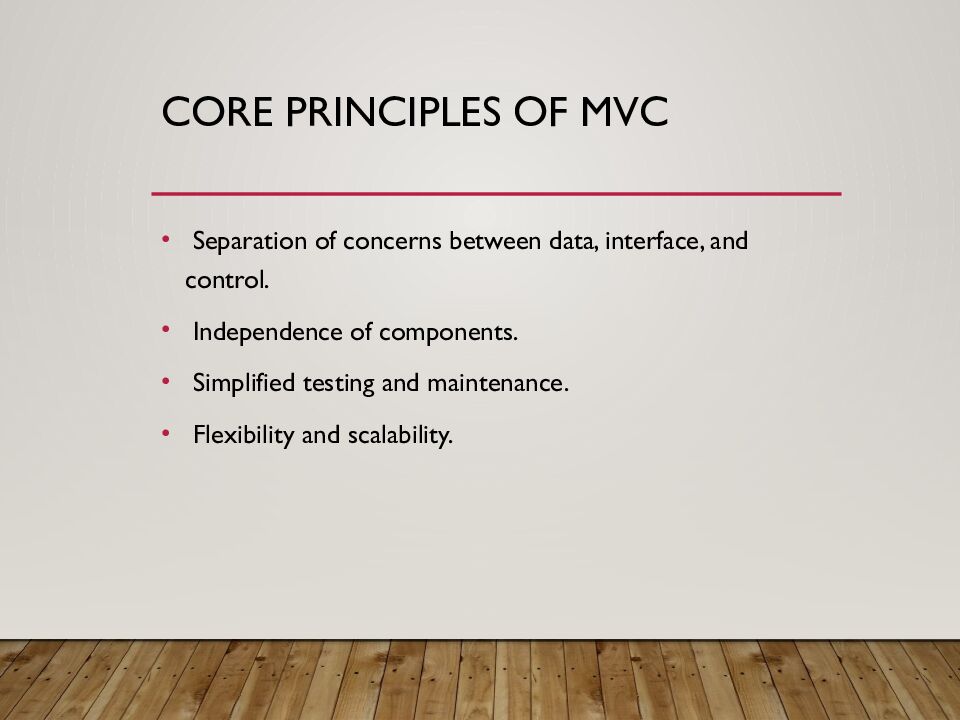
Слайд 3: Core Principles of MVC
Separation of concerns between data, interface, and control. Independence of components. Simplified testing and maintenance. Flexibility and scalability.
Слайд 4: Advantages of MVC
Clear and readable code structure. Enables teamwork and parallel development. Easier testing and debugging. Reusable and modular components.
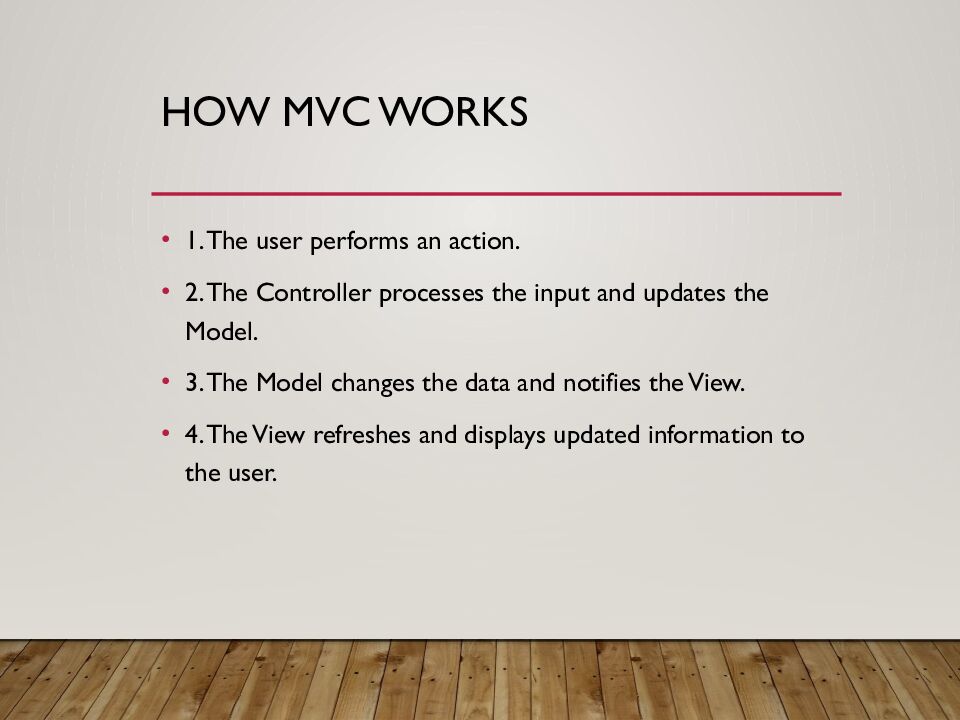
Слайд 5: How MVC Works
1. The user performs an action. 2. The Controller processes the input and updates the Model. 3. The Model changes the data and notifies the View. 4. The View refreshes and displays updated information to the user.
Слайд 6: Where MVC Is Used
Web development (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Angular). Mobile applications (Android, iOS). Desktop software (.NET, Qt, Electron). Game engines and user interface systems.
Слайд 7: Limitations of MVC
• May be too complex for small projects. • Requires understanding of interactions between components. • Increases the number of files and logical layers.