Слайд 2
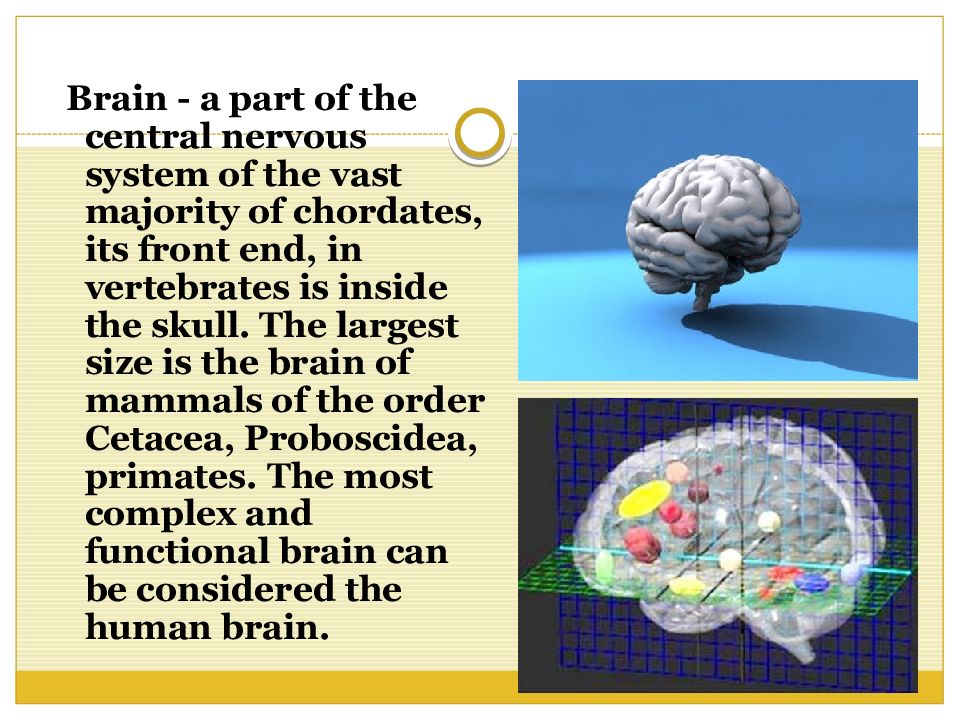
Brain - a part of the central nervous system of the vast majority of chordates, its front end, in vertebrates is inside the skull. The largest size is the brain of mammals of the order Cetacea, Proboscidea, primates. The most complex and functional brain can be considered the human brain.
Слайд 3: Fore Brain
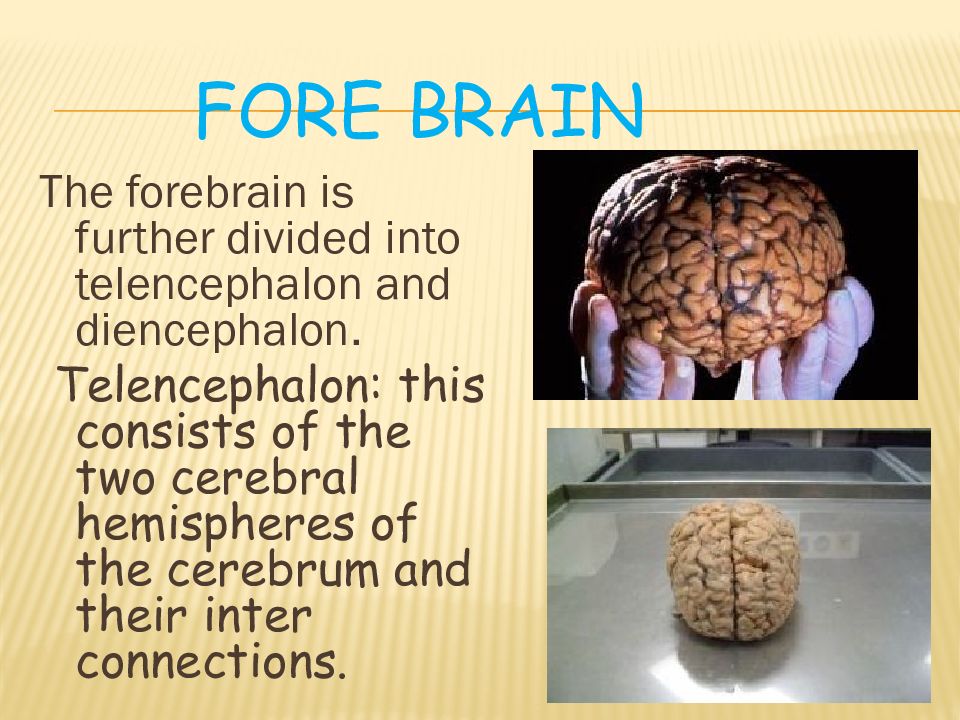
The forebrain is further divided into telencephalon and diencephalon. Telencephalon : this consists of the two cerebral hemispheres of the cerebrum and their inter connections.
Слайд 5: Frontal lobe
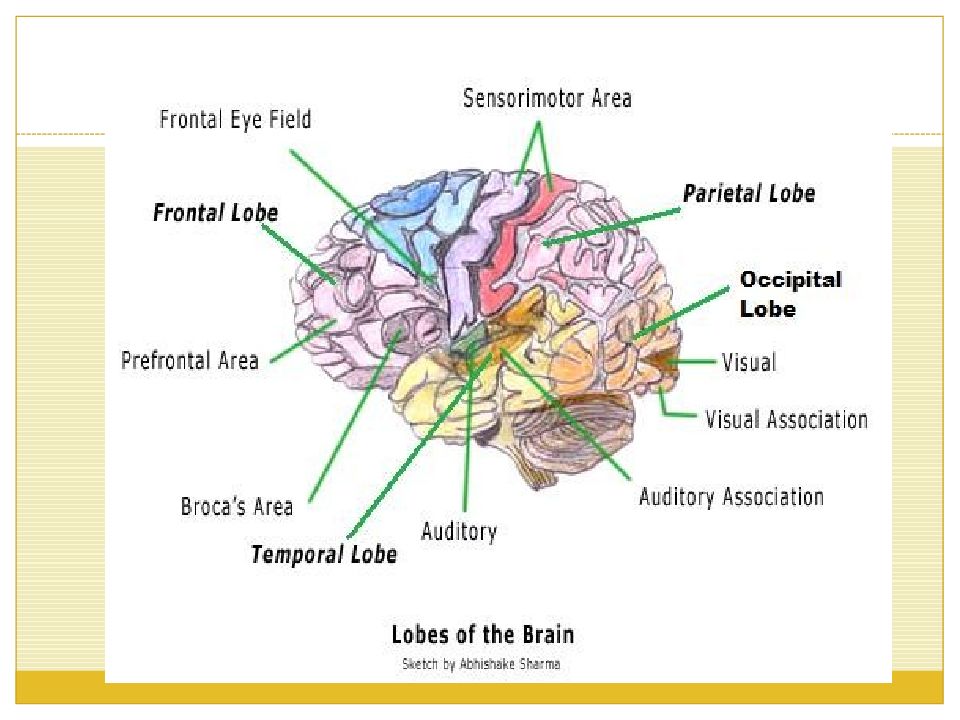
This is the part of the celebrum that lies directly below the frontal bone. It is the part that is present directly behind the forehead. It is separated from the parietal lobe by the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by the lateral sulcus. The frontal lobe is divided into a lateral, polar, orbital and medial part. The frontal lobe is seen in the above given diagram of the brain; and its functions are described below.
Слайд 6: Parietal lobe
T he parietal lobe is that lobe of the brain, that is present superior to the occipital lobe and posterior to the frontal lobe. It is enclosed by the parietal bone of the skull. The parietal lobe is separated from the frontal lobe by the central sulcus, while the lateral sulcus separates the parietal lobe from the temporal lobe.
Слайд 7: Temporal Lobe
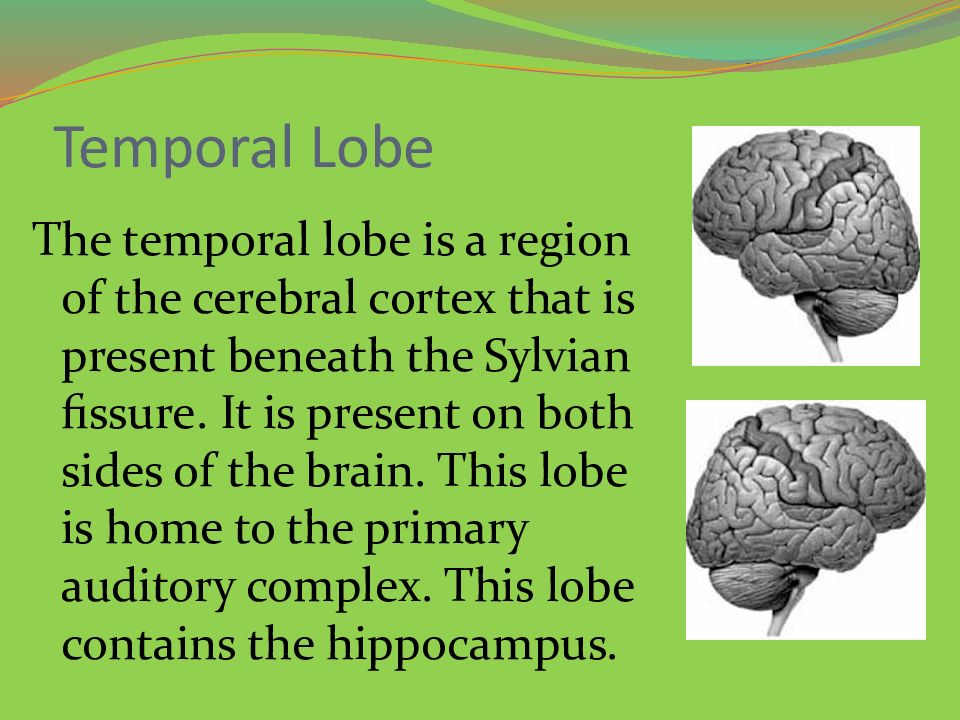
T he temporal lobe is a region of the cerebral cortex that is present beneath the Sylvian fissure. It is present on both sides of the brain. This lobe is home to the primary auditory complex. This lobe contains the hippocampus.
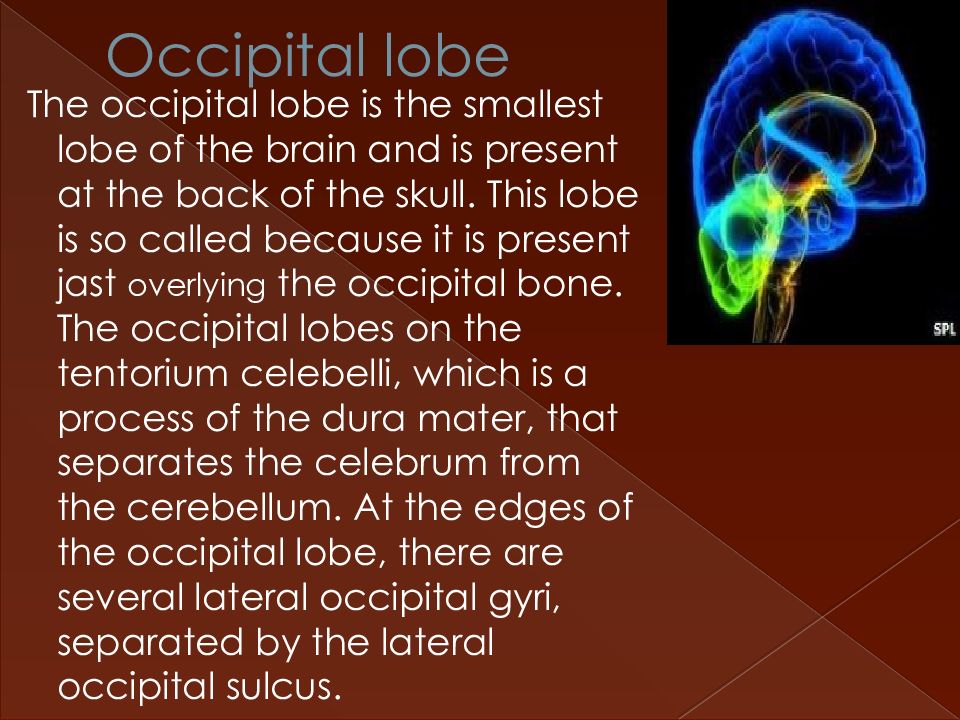
Слайд 8: Occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is the smallest lobe of the brain and is present at the back of the skull. This lobe is so called because it is present jast overlying the occipital bone. The occipital lobes on the tentorium celebelli, which is a process of the dura mater, that separates the celebrum from the cerebellum. At the edges of the occipital lobe, there are several lateral occipital gyri, separated by the lateral occipital sulcus.
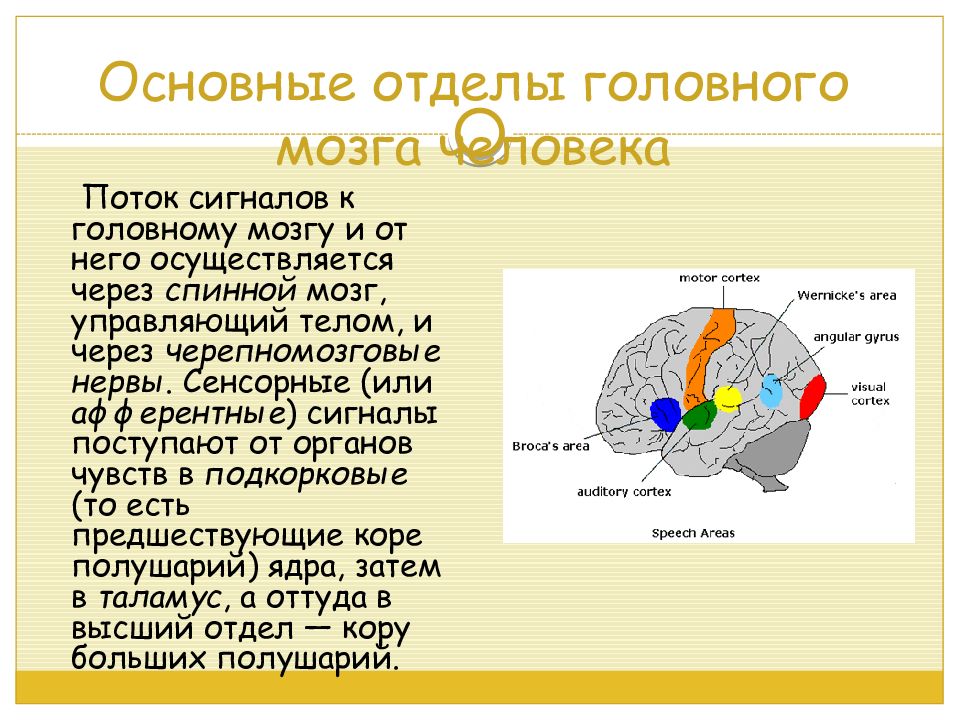
Слайд 9: Основные отделы головного мозга человека
Поток сигналов к головному мозгу и от него осуществляется через спинной мозг, управляющий телом, и через черепномозговые нервы. Сенсорные (или афферентные ) сигналы поступают от органов чувств в подкорковые (то есть предшествующие коре полушарий) ядра, затем в таламус, а оттуда в высший отдел — кору больших полушарий.
Слайд 10: Visual pathway
Visual input follow a slighty complex rule - the optic nerves from the two eyes come together at a point called the optic chiasm, and here, half the fibers of each nerve split off to join other. Thus, impulses received from the left half of the retina in both eyes go to the left side of the brain, while the impulses from the right half of the retina go to the right brain.
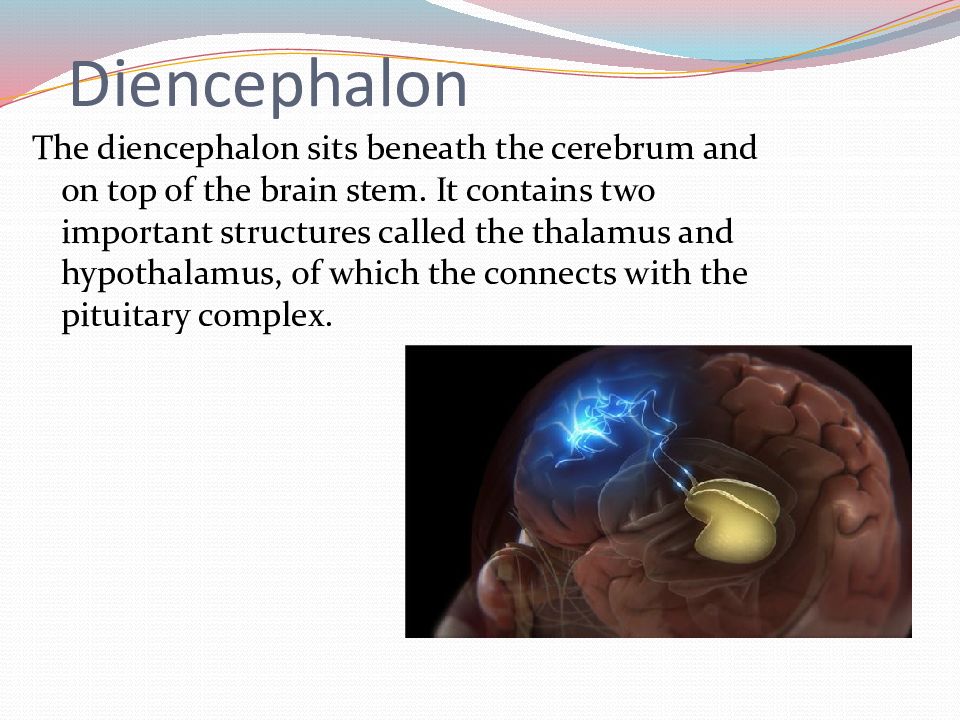
Слайд 11: Diencephalon
The diencephalon sits beneath the cerebrum and on top of the brain stem. It contains two important structures called the thalamus and hypothalamus, of which the connects with the pituitary complex.
Слайд 12: Thalamus
the thalamus is a paired structure that is a part of the diencephalon. Each thalamus is a large, egg-shaped cluster of nuclei (gray matter ).The two thalami lie close together, and are joined across mid-line by a mass of gray matter called massa intermiedia. Basically, it is responsible for letting the brain get information on what is happening outside the body.
Слайд 13: Hypothalamus
This is a small structure present in the diencephalon that plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis, that is, a state of equilibrium within the body. The thalamus keeps conditions in the body constant, preventing any sudden change from occurring. It regulates various sensations, such as hunger, thirst, temperature, libido among other things. It is also responsible for the circadian rhythm, which is exerted in the body (the daily sleep and awake cycle). It also plays a vital role in emotions, autonomic functions and motor functions. It tries to maintain homeostasis by exerting control on the pituitary gland.
Слайд 14: Pituitary gland
The pituitary gland, or the hypophysis, is a small pea-sized gland, that is present in the skull, resting in a cavity of the skull called the sella turcica. It is an endocrine gland that is involved with secreting various hormones, and thus, establishing hormonal balance in the body.
Слайд 15: Midbrain
The mid brain is divided into two past b y the Aqueduct of Sylvius, which in the duct that connects the III vetricle in the mid the IV ventricle in the pons and medulla oblongata. The ventral part of it is called the cerebral peduncle, which is chiefly made up of white matter and it unites the pons with the thalamic region of the cerebrum. The dorsal part is called the testum, which consists of two elevations, the superior and inferior colliculi.
Слайд 16: Hind brain
The mid brain, pons and medulla oblongata are often together termed as the brain stem (sometimes only the pons and medulla oblongata are referred to as the brain stem). All cranial nerves are situated in the brain stem. The hind brain is made up of the brain stem and the cerebellum.
Слайд 17: Pons
The world ‘ pons ’ literally means bridge. This is the structure that helps connect the two parts of the medulla oblongata and is often seen as a slight bulge present just above the medulla oblongata. The pons has a role in the level of arousal or consciousness and sleep. It also helps in relaying sensory impulses to, and from the brain. Furthermore, it is involved in controlling autonomic body functions.
Слайд 18: Medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata forms the lower half of the brain stem. It is an extremely important part of the brain, as it deals with vital and basic activities of the human body, as it contains the cardiac, respiratory and vasomotor centers.
Последний слайд презентации: Presentation "Brain": Cerebellum
The world ‘cerebellum’ literally means little brain. It is the second largest part of the brain, and is located at the back, below the occipital lobe, beneath the cerebrum and behind the brain stem. It contains an outer gray cortex and an inner white medulla, and has horizontal furrows, which makes it look different from the rest the of the brain. Cerebellum