Первый слайд презентации: OLD ENGLISH ALPHABET AND PRONUNCIATION
Apart from the runic alphabet, which had been used in earlier Germanic society for inscriptions on all kinds of objects, from weapons to standing stones, the earliest speakers of English were pagan and illiterate.
Слайд 2
The coming of Christianity in 597 AD introduced Latin literacy to England, which was followed by attempts to render the English language in the letters of the Latin alphabet.
Слайд 3
Old English forms of the Latin letters were very different from modern printed forms and in addition OE used some letters no longer found in English: D – eth, Z – yogh (it is printed as g in modern editions). These two letters were derived from Irish Latin.
Слайд 4
P thorn P wynn (printed as w in modern editions) x ash (Latin digraph) Thorn and eth are equivalent to “ th ” in the Modern spelling system.
Слайд 5
The letters v and z were not normally used in OE texts, and their roles were filled by f and s. The letters f and s stand for voiced fricatives between vowels / a vowel and a voiced consonant. e.g. ofer [ ' Ovqr ], risan [' rJzan ] The same with p and D: oDer [' LDqr ], wyrpe [' wyrDq ]
Слайд 6
By comparison with Modern English, OE was written relatively “phonetically”. So when reading, each letter is individually sounded even double consonants and in the initial position as in hring, hlaford, writan, cniht Vowels had a similar value to those in Latin.
Слайд 7: Ways of Reading Letter Z
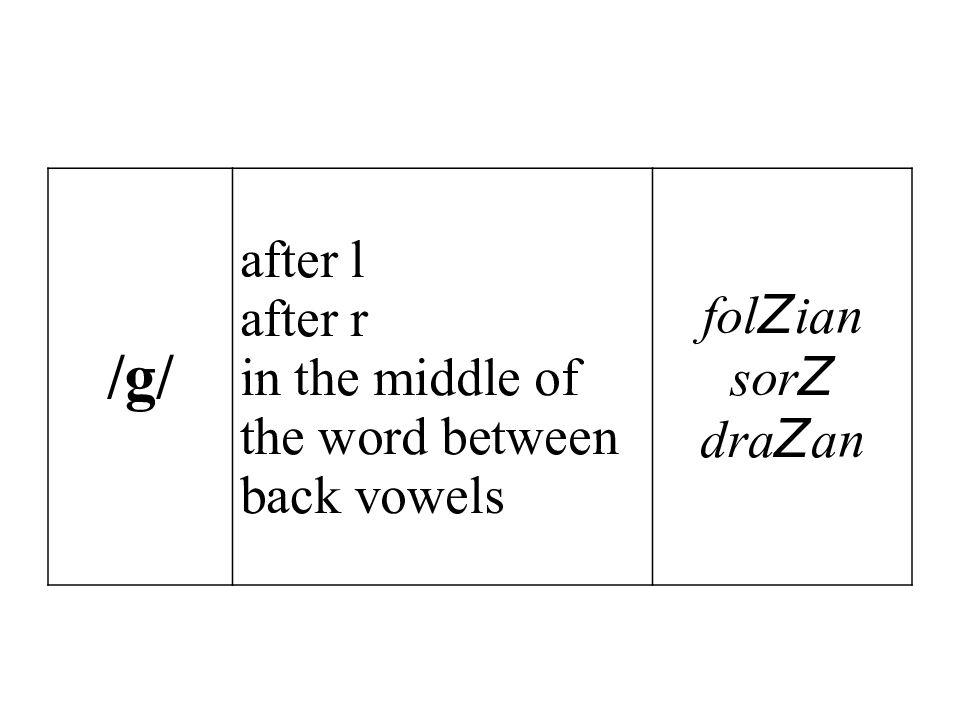
/g/ before consonants before back vowels in the middle of the word after n Z reat Z uma sin Z an
Слайд 8
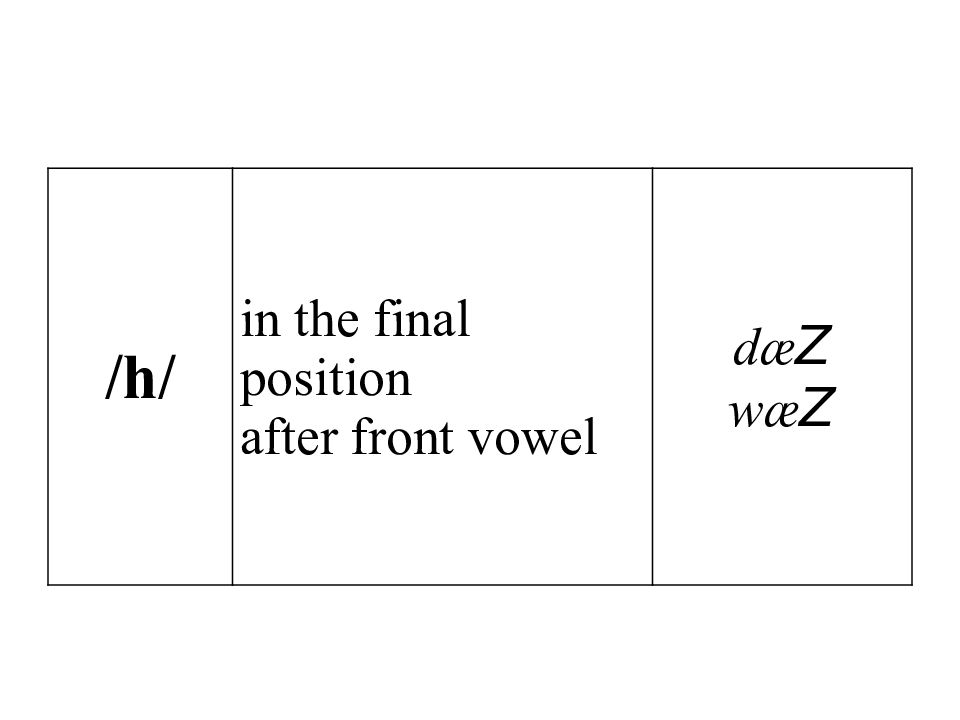
/g/ after l after r in the middle of the word between back vowels fol Z ian sor Z dra Z an
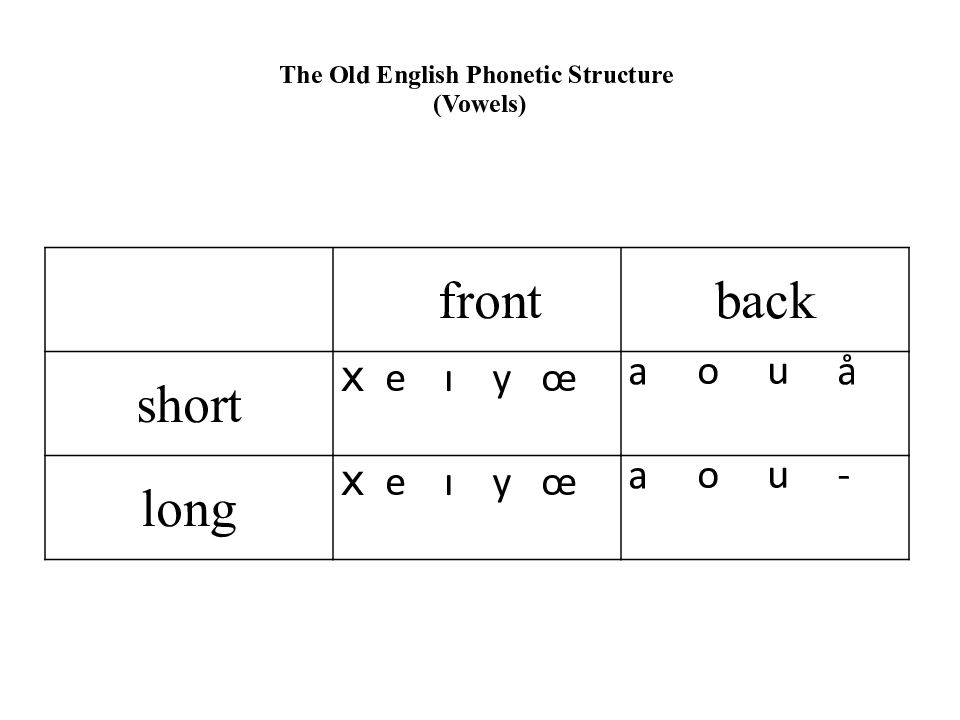
front back short x e ı y œ a o u å long x e ı y œ a o u -
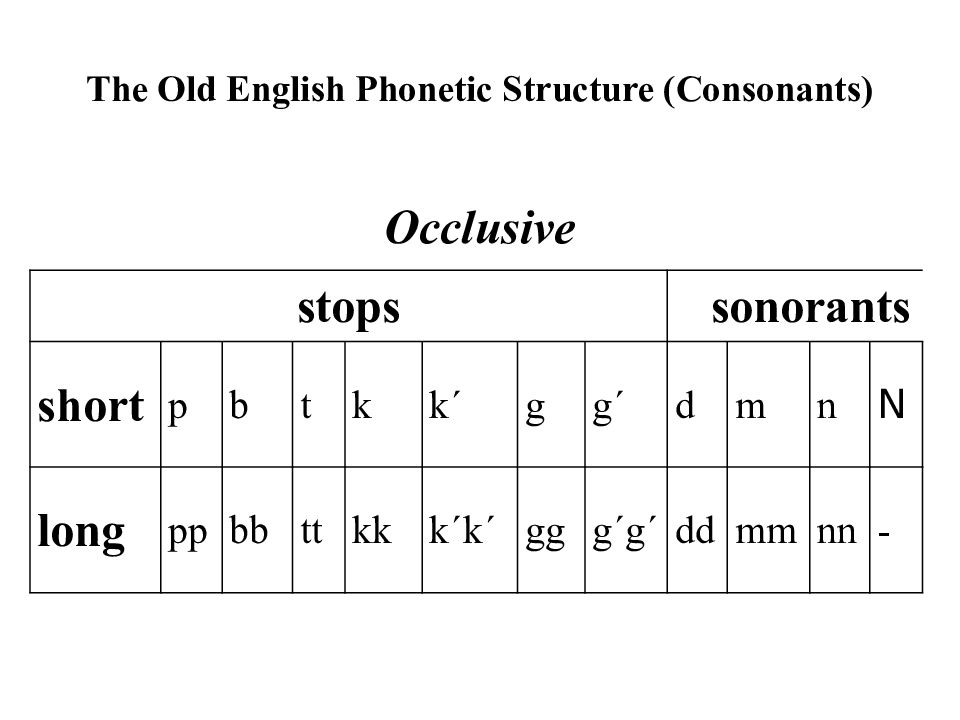
Occlusive stops sonorants short p b t k k´ g g´ d m n N long pp bb tt kk k´k ´ gg g´g ´ dd mm nn -
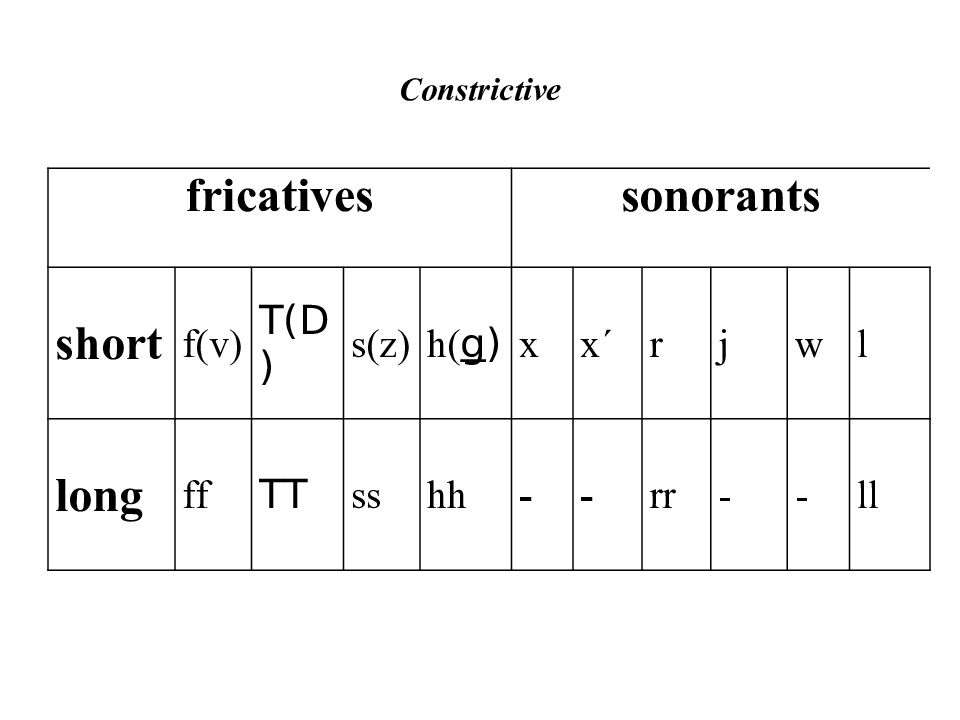
Слайд 13: Constrictive
fricatives sonorants short f(v ) T(D) s(z) h( g ) x x´ r j w l long ff TT ss hh - - rr - - ll
Слайд 14: Breaking
x > ea e > eo if they were followed by i > io r, l, h + consonant or single h e.g. x rms > ea rm c x lds > c ea ld w e rc > w eo rc l i rnen > l io rnen
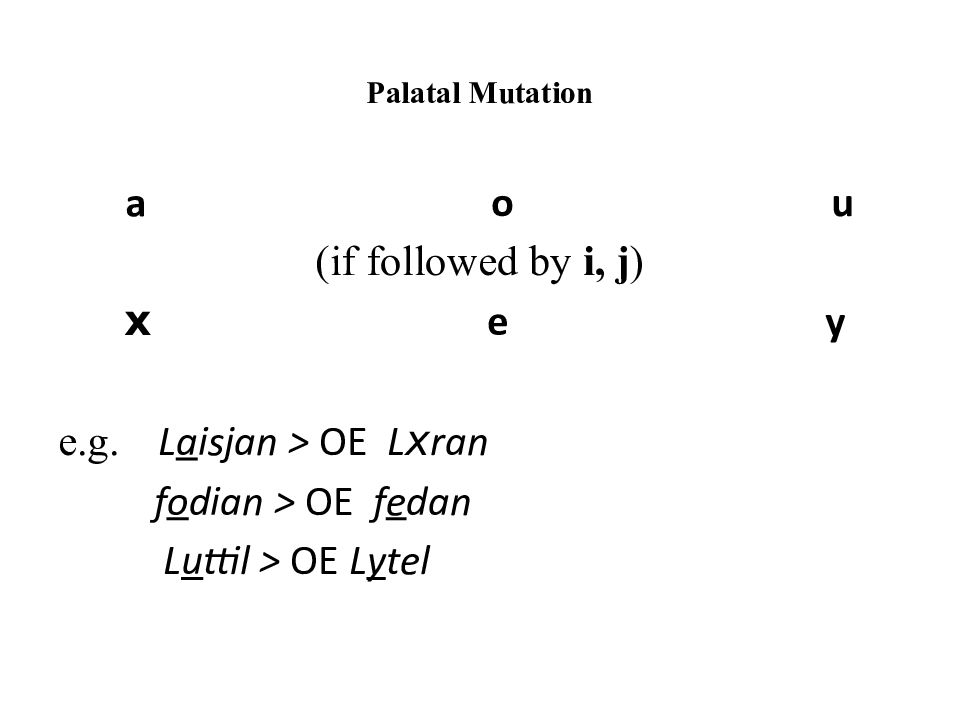
Слайд 15: Palatal Mutation
a o u (if followed by i, j ) x e y e.g. L a isjan > OE L x ran f o dian > OE f e dan L u ttil > OE L y tel
Слайд 16: Exceptions from Palatal Mutation
Palatal mutation didn’t take place: 1) due to the failure of chronological coincidence e.g. folcisc (folk) 2) if sound i was stressed e.g. an'lic (only) 3) due to the restoration of unmutated vowels from cognate words e.g. mod, n modiZ, adj
Слайд 17: Double Mutation
In words consisting of three syllables a, o, u / u / i the vowels of the first two syllables became front: e.g. OS arundi – OE ærende OS saturni-dæ Z – OE sæterndæ Z
Слайд 18: Traces of Palatal Mutation in Modern English
1. In some plurals of nouns e.g. man – men 2. In some abstract nouns formed from adjectives e.g. strong – strength
Слайд 19
3. In some verbs formed from nouns e.g. food – feed 4. In some verbs formed from adjectives e.g. full – fill 5. In some comparatives e.g. old – elder – eldest
Слайд 20: Back Umlaut
Front vowels x, e, I turned into diphthongs if the following syllable contained a back vowel – a, o, u e.g. x > ea c x ru > c ea ru e > eo h e fon > h eo fon i > io s i lufr > s io lufr
Слайд 21: Lengthening of Vowels
1. The rejection of nasals before fricatives: OHG Z ans – OE Z os sinþs – siþ, uns - us
Слайд 24: Consonantal Changes Palatalisation of Initial Consonants
1. Initial consonants [ k, g, g ] were palatalized and turned into [ k', g', g' ] e.g. ceap, sen Z ian, Z ear 2. Combination sc was always palatal e.g. scip
Слайд 25
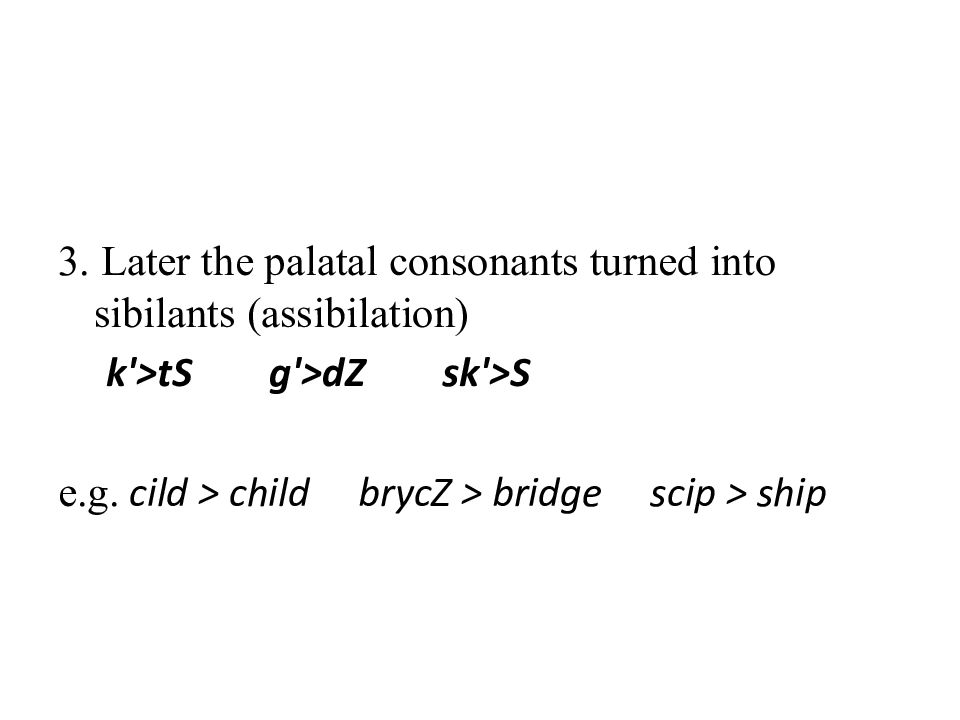
3. Later the palatal consonants turned into sibilants (assibilation) k'> tS g'> dZ sk '>S e.g. cild > child brycZ > bridge scip > ship
Слайд 26
If the vowel was not original, assibilation didn’t take place. Goth. kunin Z > cynin Z > kin Z
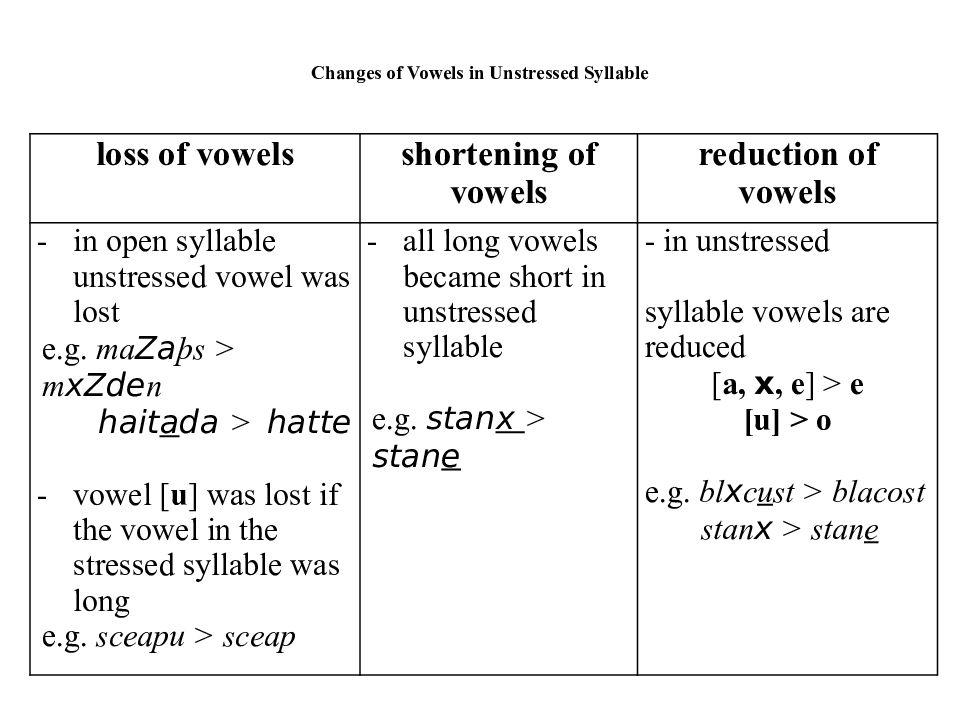
Последний слайд презентации: OLD ENGLISH ALPHABET AND PRONUNCIATION: Changes of Vowels in Unstressed Syllable
loss of vowels shortening of vowels reduction of vowels in open syllable unstressed vowel was lost e.g. ma Za þs > m xZde n hait a da > hatte vowel [ u ] was lost if the vowel in the stressed syllable was long e.g. sceapu > sceap all long vowels became short in unstressed syllable e.g. stan x > stan e - in unstressed syllable vowels are reduced [ a, x, e ] > e [u] > o e.g. bl x c u st > blacost stan x > stan e