Слайд 2
1. PSp in the system of the language. 2. General characteristics of PSp. 3. The history of development of the PSp classifications. 4. Different approaches to the PSp classification in English. 5. Notional and functional words. 6. Disputable points in the PSp classification. 7. The field (prototypical) structure of PSp. Interaction between PSp. 8. Syntactic transposition as a means of parts-of-speech interaction in English. 4
Language is a huge, but structured system of signs. It consists of many subsystems. ↓ One of the most important subsystems in any language is the system of parts of speech. 4
It goes first among all the subsystems and reflects the categorization of words into grammatically relevant sets or classes. ↓ Their number is minimum and limited. 4
Parts of speech occupy the central position in the language system as they present the meeting point of the two main domains of the language: its lexicon, its grammar. 4
Слайд 6: Parts of Speech in the System of the Language
Therefore, they are indispensable for both the theory of the language and the language acquisition. ↓ 4
Слайд 7: Parts of Speech in the System of the Language
It is impossible: to present a word in a dictionary without placing it into a certain part of speech; to explain the meaning of a word in the process of teaching a foreign language without identifying its part-of-speech belonging. 4
Слайд 8: 2. General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
PSp are lexico-grammatical word-classes that bear a general abstract grammatical meaning, expressed in certain grammatical markers. ↓↓ 4
Слайд 9: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
PSp present a mixed lexical and grammatical phenomenon : 1) words are characterized by a certain lexical meaning; 2) each generalized word-class possesses a unifying general abstract meaning. 4
Слайд 10: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
Usually PSp are considered in grammars as isolated groups, each with their own grammatical meaning and material shape. ↓ 4
Слайд 11: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
However, in a system of language they are interdependent. E.g. There was much snow last winter. Let’s make a snow ball. 4
Слайд 12: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
English has over a dozen parts of speech. The precise number varies according to the analysis. 4
Слайд 13: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
What meaning (lexical or grammatical) helps to define a part of speech belonging? 4
Слайд 14: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
The lexical meaning of the word is an unreliable guide to its part of speech. 4
Слайд 15: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
What is the role of grammatical meaning? 4
Слайд 16: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
Membership is, as a rule, determined by grammatical criteria. 4
Слайд 17: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
A feature of English is that a word can belong to two or more different classes without changing its form. 4
Слайд 18: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
Examples : 1) a nice shade of brown (a noun), a brown ( an adjective ) skirt, Please, brown (a verb) the meat. 4
Слайд 19: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
2) Schumacher accelerated down the straight (a noun), a straight ( an adjective) line, She hit the ball straight (an adverb). 4
Слайд 20: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
Note : a word can only belong to one part of speech at a time. 4
Слайд 21: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
The words in a single class do not allow absolutely identical behavoiur. Instead, they are further divided into several subclasses, which show somewhat different behaviour. ↓ This is subcategorization. 4
Слайд 22: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
Examples: The nouns are subcategorized into: - proper ( John, Brown, Washington ) - common ( boy, board, pond, mushroom ), - animate ( man, bird, cat ) - inanimate ( toy, lake, grass ), - countable ( pen(s), door(s), hand(s) ) - uncountable ( news, money, furniture), - concrete ( book, towel, phone ) - abstract ( hatred, danger, happiness, love ). 4
Слайд 23: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
How are verbs subcategorized? 4
Слайд 24: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
Verbs are subcategorized into: - fully predicative ( walk, sail, prepare, shine, blow ) - partially predicative ( can, may, shall, be, become ), - transitive ( take, put, speak, listen, see, give ) - intransitive ( live, float, stay, ache, ripen ), - actional ( write, play, strike, boil, receive, ride ) - statal ( exist, sleep, rest, suffer ), factive ( roll, tire, begin, ensnare, build, tremble ) - evaluative ( consider, approve, mind, desire, hate, incline ). 4
Слайд 25: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
How are adjectives subcategorized? 4
Слайд 26: General Characteristics of the Parts of Speech
Adjectives are subcategorized into: - qualitative ( long, red, lovely, noble, comfortable ) - relative ( wooden, rural, daily, subterranean, orthographical ), - factive ( tall, heavy, smooth, mental, native ) - evaluative ( kind, brave, wonderful, wise, stupid ). 4
Слайд 27: 3. The History of Development of the Parts of Speech Classifications
The first classification of vocabulary into groups, or classes was made in ancient Greece (Aristotle). ↓ The Greek term "parts of speech" ("parts orationis") came to stay in linguistics. 4
Слайд 28: The History of Development of the Parts of Speech Classifications
Conception: There exists a basic correlation between the way the world is organized and the way language is organized. The world consists of two basic parts: things and processes (what these things do). ↓ ↓ 4
Слайд 29: The History of Development of the Parts of Speech Classifications
This relationship was reflected in the two main parts of speech: the Name, the Verb (to which Aristotle later added the Adjective and the Adverb). 4
Слайд 30: The History of Development of the Parts of Speech Classifications
The grammatical teaching of Ancient Greece (“traditional” grammar ) was completed in Alexandria (the 2 nd century B.C. - 2 nd century A.D.). ↓↓ 4
Слайд 31: The History of Development of the Parts of Speech Classifications
The words were grouped into eight PSp : inflected (name, verb, participle, article, pronoun); uninfected (preposition, adverb, conjunction). 4
Слайд 32: The History of Development of the Parts of Speech Classifications
The Romans constructed their grammar on the Greek model with some modifications. Traditional grammar (linguistic achievements of the Greek) was introduced to Europe due to Roman sources. 4
Слайд 33: The History of Development of the Parts of Speech Classifications
The philosophers of the Middle Ages made some further important observations. Their conception : all languages had essentially the same basic structure as Latin. Main achievement : They defined nouns and adjectives as different parts of speech within the class of names. 4
Слайд 34: The History of Development of the Parts of Speech Classifications
The present day linguistics is more focused not on the world outside us, i.e. the physical environment, but rather on the world inside us, i.e. the reflection of this world in the human mind (the picture of the world), the conceptualization and categorization of the world by the human mind. 4
Слайд 35: 4. Different Approaches to he Parts of Speech Classification n English
Classifications: based upon one criterion ( monodifferential approach ) ; based upon several criteria ( polydifferential approach ) ↓ 4
Слайд 36: 4. Different Approaches to he Parts of Speech Classification n English
The first one is presented by classical, functional, distributional approaches, the other one – by a complex approach. 4
Слайд 37: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The classical (morphological, formal) parts of speech theory of the English language is based on Latin grammar: declinable PSp (nouns, pronouns, verbs and participles); indeclinable PSp (adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections). 4
Слайд 38: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
But: the inflectional classification is quite successful for synthetic languages (with developed morphology). It cannot be applied to analytical languages. 4
Слайд 39: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Henry Sweet realized the inadequacy of the morphological criterion alone. So, he completed his classification by adding the syntactic criterion to it. 4
Слайд 40: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
But: he failed to break the tradition and classified words into declinable (having morphological forms) and indeclinable (lacking morphological forms). 4
Слайд 41: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
O. Jespersen’s approach was functional (theory of "The Three Ranks”). He gave the traditional list of parts of speech "for the dictionary“ and differentiated them in speech on the basis of mutual relations of words in a sentence. 4
Слайд 42: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Illustration: an extremely hot weather / a furiously barking dog weather, dog are primary words, hot, barking are secondary words, extremely, furiously are tertiary words. 4
Слайд 43: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
However: the theory did not cover the relations of all the main word classes. It left out the most important word-class — the verb. 4
Слайд 44: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Charles Fries, an American linguist, suggested a distributional approach. On the basis of syntactic criterion he introduced 4 major classes of words and 15 form-classes. ↓↓ 4
Слайд 45: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
He used the following three sentences (minimum free utterance test frames) with most typical syntactic structures: Frame A The concert was good (always); Frame B The clerk remembered the tax (suddenly); Frame C The team went there. 4
Слайд 46: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
With the help of substitution test Ch. Fries divided all the notional words into four classes: Class I : concert, clerk, team, tax, etc. Class II : remembered, went, etc. Class III : good, etc. Class IV : there, always, suddenly, etc. 4
Слайд 47: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The remaining words were referred to function words (15 subclasses). 4
Слайд 48: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Achievements of Charles Fries : 1) He was the first linguist to pay attention to some of the peculiarities of function words (“form-classes”). 2) His classification appears to be very simple, workable, convenient for practical purposes. 4
Слайд 49: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
But: The classification ignores one very important aspect of the parts-of-speech phenomenon - the dynamic character of the parts-of-speech system, i.e. the ability of parts of speech for interaction, for an exchange of their syntactic functions in the process of speech production. 4
Слайд 50: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Example : The concert was a treat (the function of an adjective) 4
Слайд 51: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
In modem linguistics PSp are discriminated on the basis of three criteria: semantic, formal, functional. ↓ 4
Слайд 52: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
This approach is complex, polydifferential. 4
Слайд 53: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
When characterizing any part of speech we are to describe: its semantics (the grammatical meaning of the whole class of words, general grammatical meaning); its morphological features, its syntactic peculiarities. 4
Слайд 54: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
A generalized abstract meaning is a common categorial meaning. 4
Слайд 59
substance, or thingness for nouns, action for verbs, property for adjectives, property of property for adverbs. 4
Слайд 60: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
These generalized grammatical meanings present lingual representations of the most important concepts (units of the mental world). 4
Слайд 61: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The human mind has an ability to conceptualize reality in a variety of ways. 4
Слайд 62: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Examples: A noun can name: a thing ( a book), an action (a ride), a property ( kindness), a relation (friendship), etc. 4
Слайд 63: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
A verb can name: an action (do), a state (sleep), a property (widen), a display of emotion (admire). 4
Слайд 64: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Therefore linguists differentiate between: ontological objects ; gnosiological objects. 4
Слайд 65: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Ontological objects correspond to real objects of the physical world. 4
Слайд 66: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Gnoseological objects are other phenomena of reality conceptualized as objects, "objects in the mind", i.e. in the conceptual picture of the world. 4
Слайд 67: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The absence of one-to-one correlation between reality, its conceptualization by the human mind and its representation in the system of parts of speech actually determines the structure of parts of speech. ↓ 4
Слайд 68: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
There exist: central (prototypical), peripheral units (less prototypical units). 4
Слайд 69: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The interaction between parts of speech is obligatory. 4
Слайд 70: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
General grammatical meanings find their manifestation in the formal (morphological) properties. ↓ Words belonging to one part of speech possess common derivational affixes and common grammatical categories. 4
Слайд 71: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Examples : deforestation is a noun, upped (The government upped the customs tax) is a verb. 4
Слайд 72: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The semantic properties of words are projected into their functional (syntactic) properties. ↓ 4
Слайд 73: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Primary syntactic functions are: subject, object and predicative for nouns, predicate for verbs, attribute and predicative for adjectives, adverbial modifier for adverbs. 4
Слайд 74: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Realizing their secondary syntactic functions words function on the syntactic territory of other parts of speech. ↓ It makes the borderlines between different parts of speech not closed. 4
Слайд 75: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The features of the noun: the categorial meaning of substance ("thingness"); - the changeable forms of number and case; - the specific suffixal forms of derivation; 3) - the substantive functions in the sentence (subject, object, predicative); - prepositional connections; - modification by an adjective. 4
Слайд 76: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The features of the adjective: the categorial meaning of property (qualitative and relative); - the forms of the degrees of comparison (for qualitative adjectives); - the specific suffixal forms of derivation; 3) adjectival functions in the sentence (attribute to a noun, adjectival predicative). 4
Слайд 77: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The features of the numeral: the categorial meaning of number (cardinal and ordinal); - the narrow set of simple numerals; - the specific forms of composition for compound numerals; - the specific suffixal forms of derivation for ordinal numerals; 3) the functions of numerical attribute and numerical substantive. 4
Слайд 78: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The features of the pronoun: the categorial meaning of indication ( deixis ); the narrow sets of various status with the corresponding formal properties of categorial changeability and word-building; the substantival and adjectival functions for different sets. 4
Слайд 79: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The features of the verb : the categorial meaning of process (finite process and non-finite process); - the forms of the verbal categories of person, number, tense, aspect, voice, mood; - the opposition of the finite and non-finite forms; 3) the function of the finite predicate for the finite verb; the mixed verbal — other than verbal functions for the non-finite verb. 4
Слайд 80: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The features of the adverb : the categorial meaning of the secondary property; - the forms of the degrees of comparison for qualitative adverbs; - the specific suffixal forms of derivation; 3) the functions of various adverbial modifiers. 4
Слайд 81: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The role of these three criteria varies: for different parts of speech within one language E.g.: for adverbs in English the morphological criterion is not so important 4
Слайд 82: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
across languages E.g.: for highly inflectional languages (Russian, German) the morphological criterion plays a more important role than for isolating languages (Chinese, Vietnamese). In the latter the parts of speech are differentiated mostly on the basis of their syntactic positions. 4
Слайд 83: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The status of the word with clear morphological part-of-speech markers can be identified on their basis. E.g.: a runn er, beauti ful, to identi fy, etc. 4
Слайд 84: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
The words with a simple morphological structure are easily converted from one part of speech into another. E.g.: a mother - to mother; to say - a say, etc. ↓ 4
Слайд 85: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Their part-of-speech status is identified only on the basis of the syntactic position in the sentence. E.g.: "eyes” Her eyes are so beautiful! She always eyes strangers suspiciously. 4
Слайд 86: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
From the cognitive point of view parts of speech are considered to be the main vectors through which the humans perceive, cognize and verbalize the world. ↓ ↓ 4
Слайд 87: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Parts of speech represent the main concepts (components of the mental world): the concept of an object → the form of a noun, the concept of an action → a verb, the concept of a property → an adjective. 4
Слайд 88: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Yet the parts-of-speech structure is very complex. 4
Слайд 89: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
It is the result of a human’s mind to represent as nouns not only objects but other phenomena of the world: actions (a race), qualities ( kindness, forgetfulness), states ( delirium), ↓ 4
Слайд 90: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Verbs denote not only actions but: both actions and their participants ( to kidnap ), actions and their characteristics ( to shuffle ). 4
Слайд 91: Different Approaches to the Parts of Speech Classification in English
Thus, one and the same part of speech may unite words representing various concepts; the same concept may be represented by different parts of speech. 4
Слайд 92: 5. Notional and Functional Words
The first stage of classifying the vocabulary into parts of speech is the division of words into: a) notional words ; b) function words. 4
Слайд 93: Notional and Functional Words
Notional words: have a full nominative value (name things, objects, actions, qualities, peculiar to the real world); 4
Слайд 95: Notional and Functional Words
constitute the bulk of the existing word stock; 4
Слайд 98: Notional and Functional Words
- each class of notional words is primarily designed for a certain syntactic position in the sentence which becomes its primary syntactic function. 4
Слайд 99: Notional and Functional Words
Function ( or grammatical ) words: have no references of their own in the objective reality; 4
Слайд 100: Notional and Functional Words
express relations between objects and actions (relationship words), attitudes and thus have a partial nominative value; 4
Слайд 101: Notional and Functional Words
they are very close to grammatical affixes E.g.: написано Байроном - written by Byron. 4
Слайд 102: Notional and Functional Words
- the grammatical meaning dominates over the lexical one; 4
Слайд 103: Notional and Functional Words
their number is small, limited (about 50 in Modern English); 4
Слайд 105: Notional and Functional Words
they are the most frequently used units; 4
Слайд 107: Notional and Functional Words
have no syntactic functions of their own. 4
Слайд 108: Notional and Functional Words
They: accompany notional words and are used in the syntactic positions together with them (articles and prepositions), 4
Слайд 109: Notional and Functional Words
2) accentuate certain parts of the sentence (particles), 4
Слайд 110: Notional and Functional Words
3) connect parts of the sentence and/or sentences (conjunctions), 4
Слайд 111: Notional and Functional Words
4) stand outside the sentence structure and form a kind of projection on the information presented in the sentence expressing the speaker’s emotional or judgmental attitude to this information (interjections, particles and modal words). 4
Слайд 112: Notional and Functional Words
NB: Significance of functional words vary across languages. E.g.: Russian, German and Greek are the so-called "particle" languages " Приехать - то я вряд - ли приеду, а уж написать - то напишу ”. 4
Слайд 113: Notional and Functional Words
2) In highly inflectional languages functional words have a less significant value. In analytical languages the role of functional words, especially prepositions, is very significant. They often manifest the syntactic and the semantic role of a word in the sentence. 4
Слайд 114: Notional and Functional Words
However, in actual speech the border line between notional and function words is not always clear. ↓ ↓ 4
Слайд 115: Notional and Functional Words
- Some notional words develop the meanings peculiar to function words (e.g. semi-notional words — to turn, to get, etc.). 4
Слайд 116: Notional and Functional Words
- Some functional words were derived from the forms of notional words E.g.: the conjunction provided ← Participle II, the preposition notwithstanding ← Participle I. 4
Слайд 117: Notional and Functional Words
- Notional words are used as functional ones: E.g.: adverbs in the function of conjunctions ( Once you said it you are committed), modal words in the function of parentheses ( Luckily, he escaped). 4
Слайд 118: Notional and Functional Words
- Function words are occasionally converted into notional ( E.g.: But me no buts ! There is a big if to it), - or serve as the basis for deriving new notional words (E.g.: The question is very iffy ). 4
Слайд 119: Notional and Functional Words
Traditional parts-of-speech classification: Notional words in English are nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, numerals and pronouns. Functional words are articles, prepositions, conjunctions, particles, modal words and interjections. 4
Слайд 120: Notional and Functional Words
But: - Prof. Ilyish considers the so called statives ( a sleep, a wake, a blaze, etc.) as a separate class of notional words. 4
Слайд 121: Notional and Functional Words
But: - Prof. Blokh refers pronouns to functional words. 4
Слайд 122: 6. Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
Some words cannot find their proper place in the system of lexico-grammatical classes. 4
Слайд 123: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
The class of adverbs comprises the words that cannot find their place anywhere else Cf : perfectly (She speaks English perfectly) and again (He is here again); 4
Слайд 124: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
a t the same time, there are no grounds for grouping them together either Cf : already, yet, still ( non-nominative units with a temporal meaning) ; 4
Слайд 125: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
moreover, these words are devoid of nominative power, and they have no direct equivalents in other languages Cf : after all, anyway, actually, in fact ( don’t belong anywhere). 4
Слайд 126: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
2. The class of pronouns does not name objects or properties but just point to something already named. 4
Слайд 127: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
their categorial semantics is closer to the semantics of functional words. 4
Слайд 128: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
Their morphological properties (the categories of person, number and case in personal pronouns, the number in demonstrative and reflexive pronouns) and their syntactic features (the ability to function as parts of the sentence) make them close to notional words E.g.: The pleasure is mine. 4
Слайд 129: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
3. The class of numerals does not name objects but just add a quantitative characteristic to the class of nouns. 4
Слайд 130: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
this class is comparatively closed, which is not characteristic of notional classes. 4
Слайд 131: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
it has no grammatical categories of its own, it has no syntactic positions of its own (except cases like Two and two makes four). 4
Слайд 132: Disputable Points in the Parts-of-Speech Classification
- Functionally this class is characterized as pro adjectives. 4
Слайд 133: 7. The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
The parts of speech are characterized by a field, or a prototypical structure : categories are not closed but open; they have fuzzy boundaries; there exist the centre and a periphery within a category. 4
Слайд 134: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
The central units ( prototypes, or prototypical members of the category ) possess the maximum number of categorial features. 4
Слайд 135: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
The peripheral units may lack some features of the given category and have, at the same time, some features of other, intersecting categories. 4
Слайд 136: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
The central position in the system of parts of speech is taken by the four parts of speech: the noun, the verb, the adjective, the adverb. ↓ ↓ 4
Слайд 137: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
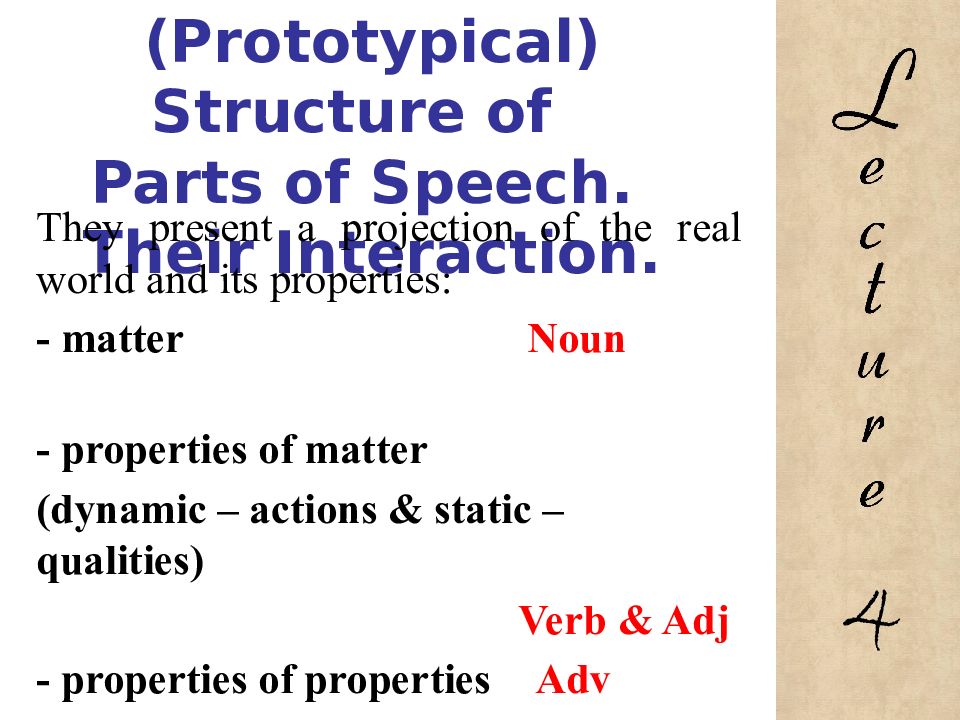
They present a projection of the real world and its properties: - matter Noun - properties of matter (dynamic – actions & static – qualities) Verb & Adj - properties of properties Adv 4
Слайд 138: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
1. These four parts of speech "cover" the positions of all parts of the sentence: the subject, the predicate, the object, the attribute, the adverbial modifier. 4
Слайд 139: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
2. They can form a four-member paradigmatic set of nominal, verbal, adjectival and adverbial representation of the same stem E.g. silence - to silence - silent - silently. 4
Слайд 140: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
Numerals and pronouns form the transitional zone between the notional and functional classes. 4
Слайд 141: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
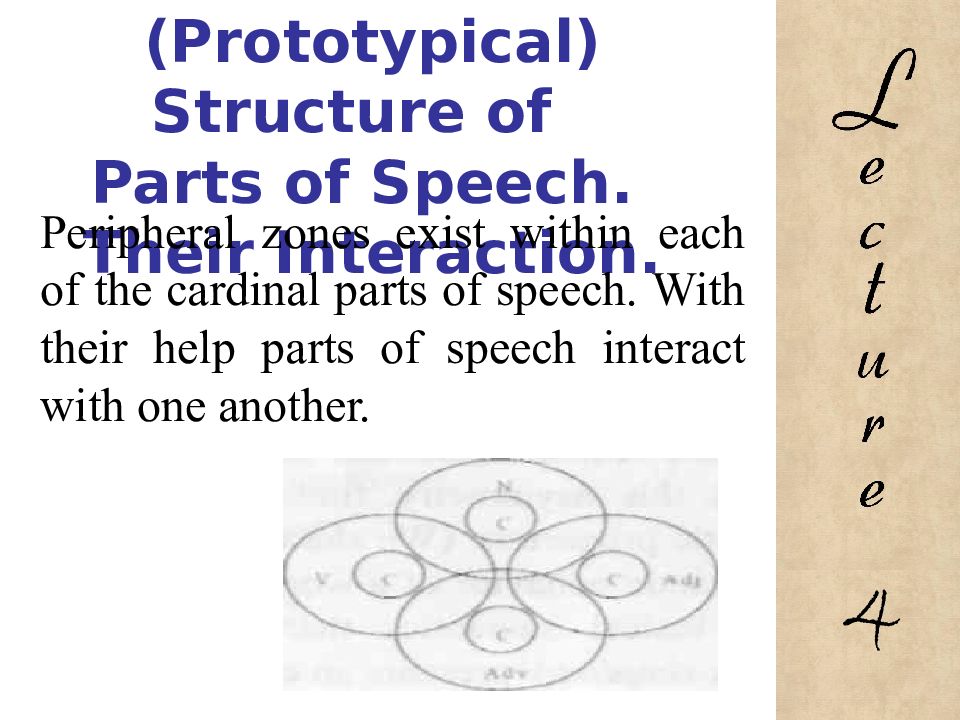
Central and peripheral units also exist within each notional part of speech. ↓ ↓ 4
Слайд 142: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
The central units are characterized by the presence of all the features of their class. 4
Слайд 143: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
E.g.: the noun man denotes a living thing, has the grammatical categories of number and case, is primarily used in the syntactic positions of subject, object and predicative (in its classifying function). 4
Слайд 144: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
Peripheral units include words of the so-called mixed categorial semantics. 4
Слайд 145: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
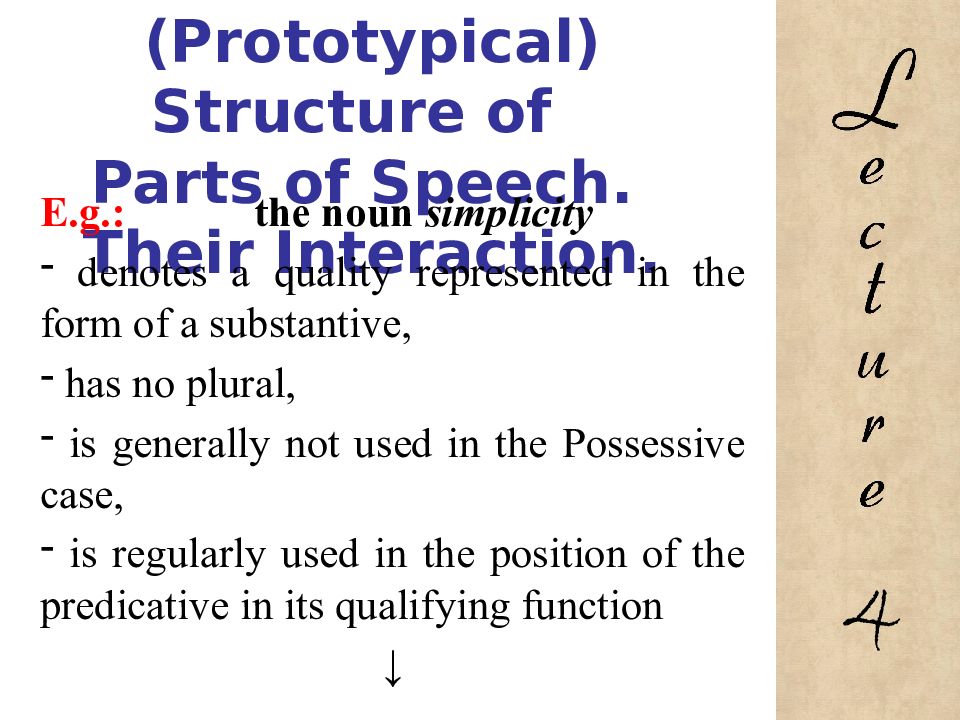
E.g.: the noun simplicity denotes a quality represented in the form of a substantive, has no plural, is generally not used in the Possessive case, is regularly used in the position of the predicative in its qualifying function ↓ 4
Слайд 146: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
Her one evening dress, reluctantly packed at Annette's half scornful insistence, was simplicity itself ( Ch. Lamb ) 4
Слайд 147: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
Examples of peripheral nouns: names of qualities (simplicity) intersect with the class of adjectives; 4
Слайд 148: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
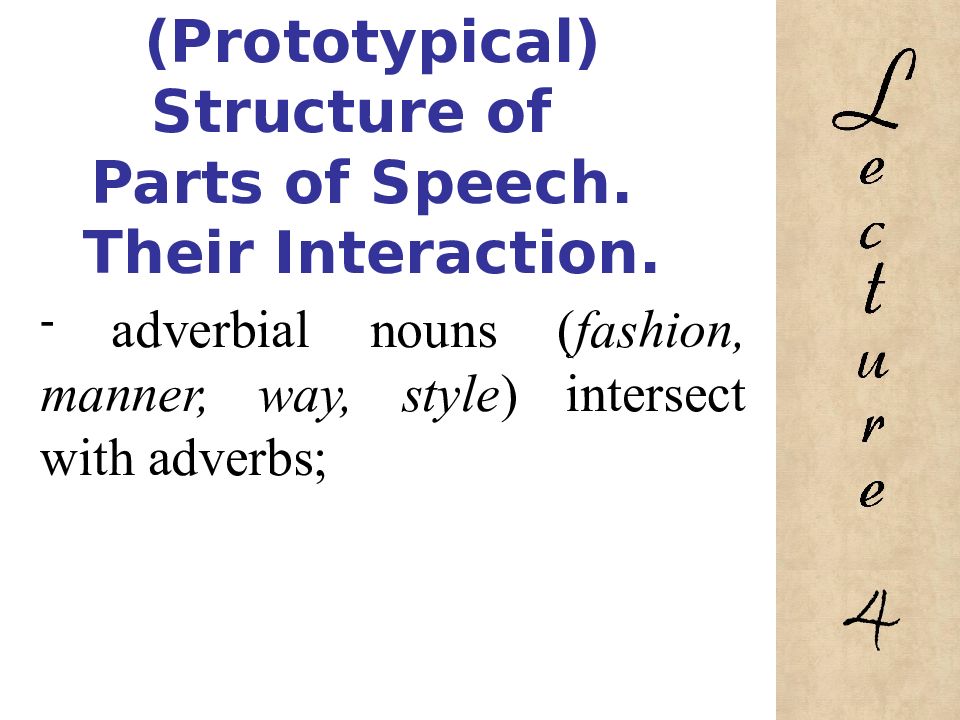
adverbial nouns ( fashion, manner, way, style ) intersect with adverbs; 4
Слайд 149: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
verbal nouns, i.e. nouns denoting actions, intersect with verbs Then, a short, quick run forward, a fault, a check, a try back, and then a slow, steady, confident advance K. Grahame 4
Слайд 150: The Field (Prototypical) Structure of Parts of Speech. Their Interaction
Peripheral zones exist within each of the cardinal parts of speech. With their help parts of speech interact with one another. 4
Слайд 151: 8. Syntactic Transposition
Syntactic (or functional) transposition is the most common way of functional interaction between parts of speech. 4
Слайд 152: Syntactic Transposition
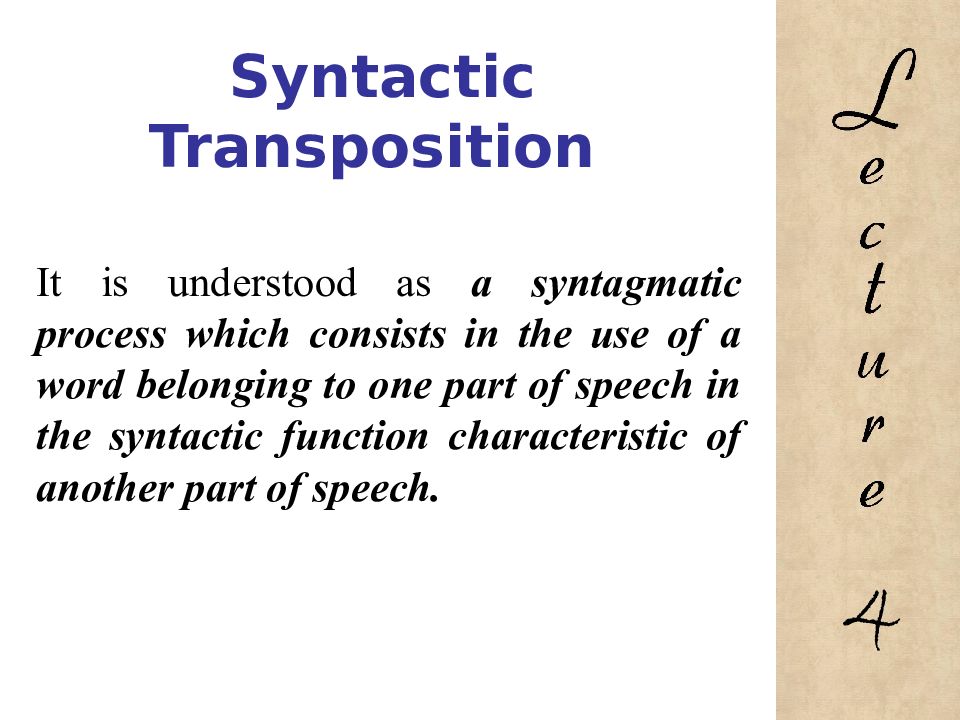
It is understood as a syntagmatic process which consists in the use of a word belonging to one part of speech in the syntactic function characteristic of another part of speech. 4
Слайд 153: Syntactic Transposition
Examples: She sings it very Dixieland ( J. Salinger ) – N adv 4
Слайд 154: Syntactic Transposition
2) “You look very tired. - A hard day?” – “A nothing day, Herr Ritter " ( J. Carrol ) - Prn Adj 4
Слайд 155: Syntactic Transposition
3) At last he turned and started walking slowly down the now deserted corridor ( E. Segal) – Adv Adj 4
Слайд 156: Syntactic Transposition
4) There is a round table... and various other pieces of furniture including a grandfather clock (D. Smith)- N Adj 4
Слайд 157: Syntactic Transposition
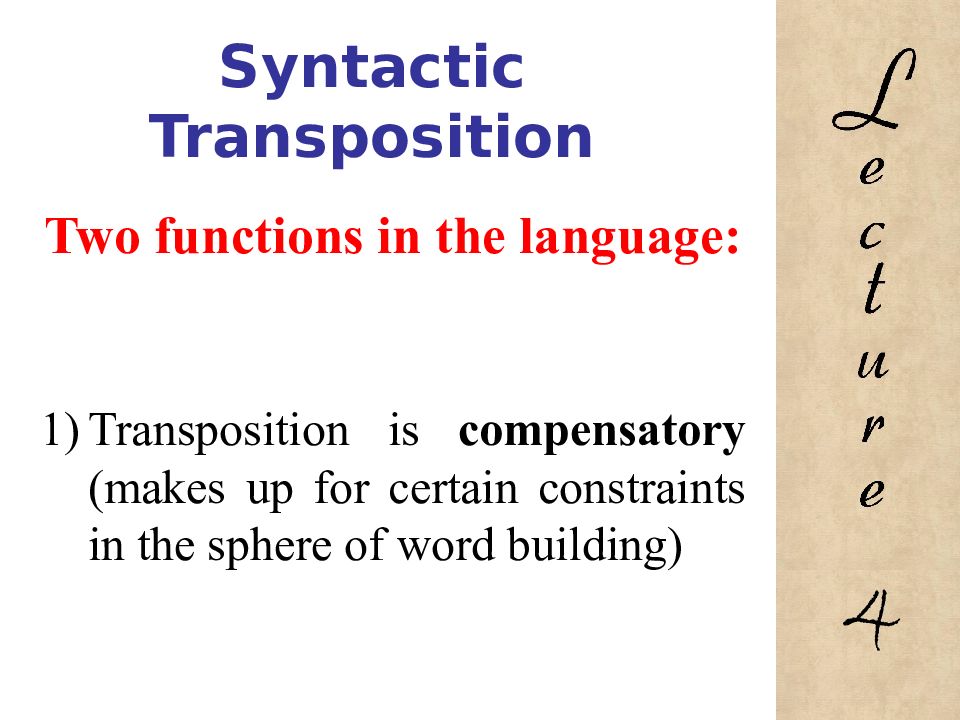
Two functions in the language: Transposition is compensatory (makes up for certain constraints in the sphere of word building) 4
Слайд 158: Syntactic Transposition
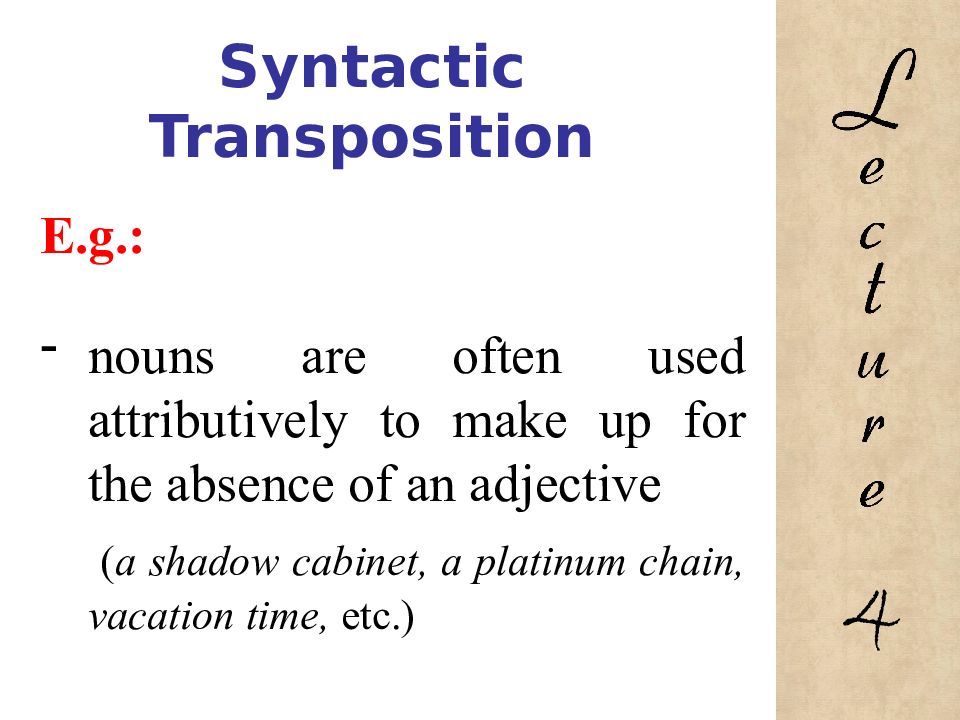
E.g.: nouns are often used attributively to make up for the absence of an adjective ( a shadow cabinet, a platinum chain, vacation time, etc.) 4
Слайд 159: Syntactic Transposition
the adverbial nouns way and manner are often transposed into adverbial sphere to make up for the absence of a corresponding adverb After a week we all served ourselves Chinese style, standing and stretching across the table one after another (L. Hobbs ) 4
Слайд 160: Syntactic Transposition
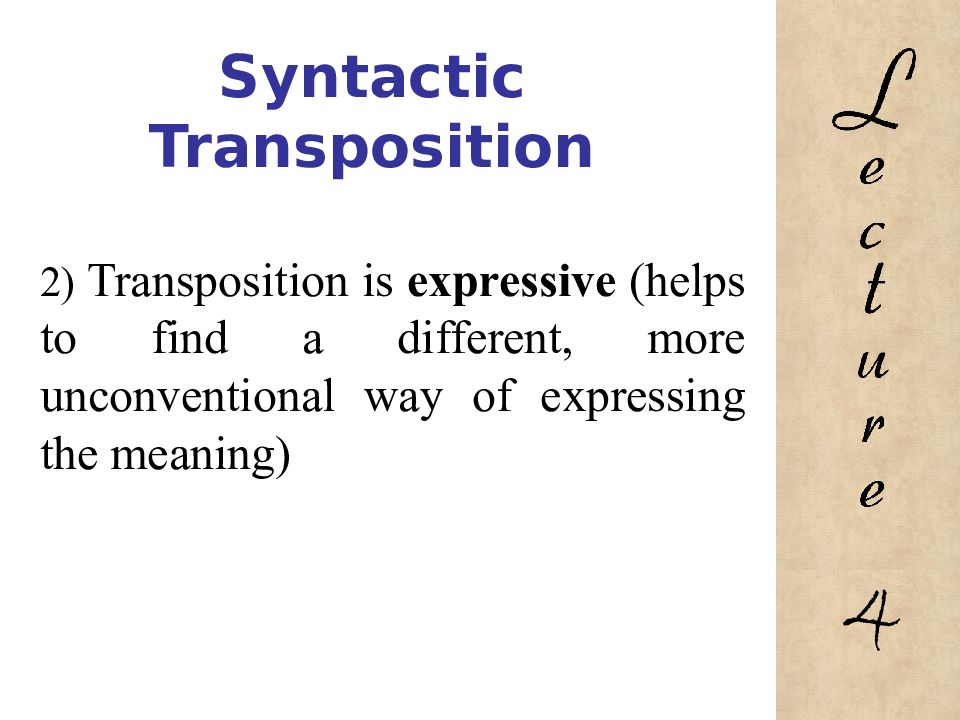
2) Transposition is expressive (helps to find a different, more unconventional way of expressing the meaning) 4
Слайд 161: Syntactic Transposition
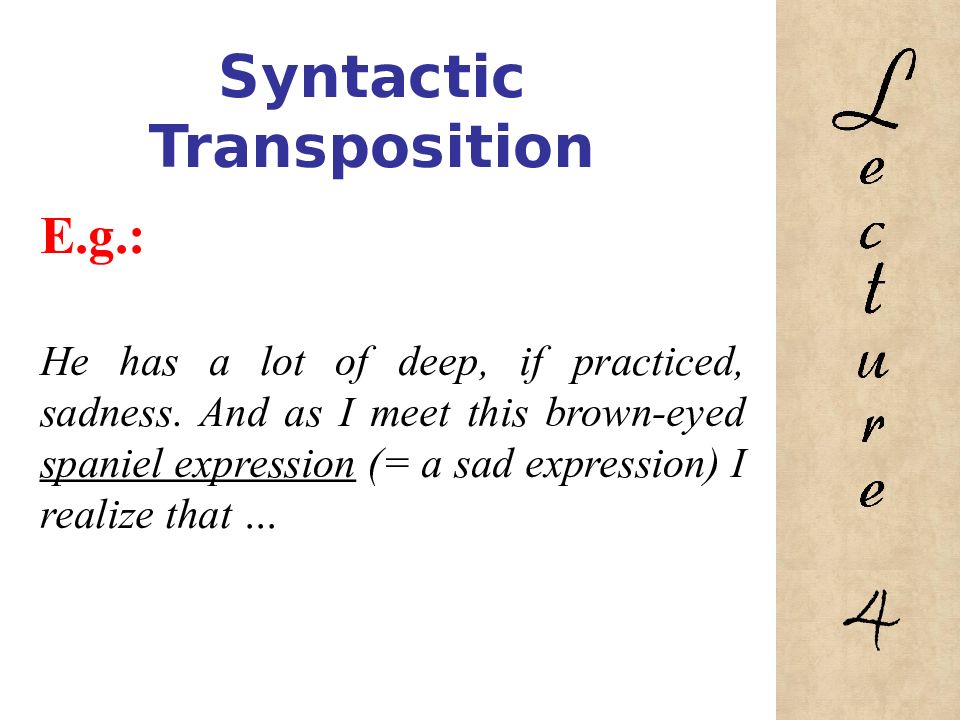
E.g.: He has a lot of deep, if practiced, sadness. And as I meet this brown-eyed spaniel expression (= a sad expression) I realize that … 4
Слайд 162: Syntactic Transposition
So, syntactic transposition reveals: the dynamic and creative potential of the language, its ability to satisfy the communicative and expressive needs of the speakers. 4
Слайд 163: Syntactic Transposition
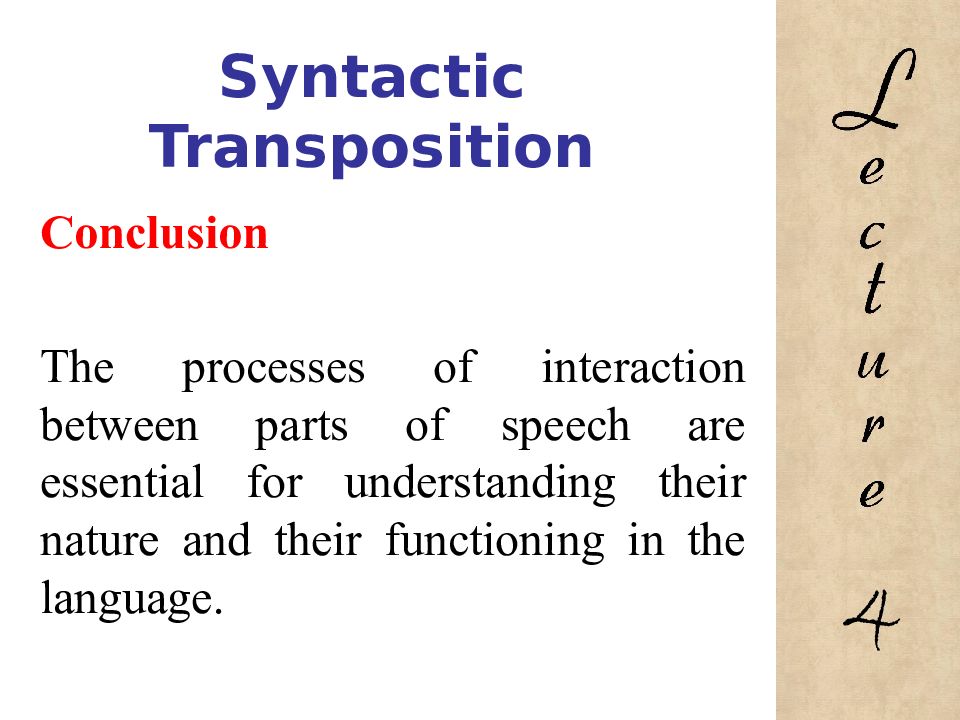
Conclusion The processes of interaction between parts of speech are essential for understanding their nature and their functioning in the language. 4