Первый слайд презентации: 8. CYBERSECURITY
D. Serikbayev East Kazakhstan State Technical University ICT Spring 2018 ‹#›
Слайд 2: Copyright Notice
‹#› This presentation is presented as is. This presentation was assembled using information from various websites or sources across the web. This presentation uses Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0). © 2019 BilimEdtech
Слайд 3: 8.1: Cybercrime
8.2: Cybersecurity 8.3: Common Threats 8.1: Cybercrime ‹#›
Слайд 4: Learning Objectives
‹#› Know the definitions of cybercrime and cybersecurity Describe cybercriminals List four categories of computer crimes Explain why you should care about cybercriminal Describe the difference between Computer as a Tool and Computer as a Target
Слайд 5: Terminology
‹#› Cyber : Relating to the culture of computers, information technology, and virtual reality Cyberspace : The online world of computer networks
Слайд 6: Terminology (2)
‹#› Cybercrime : Criminal activities carried out using computers or the internet
Слайд 7: Terminology (3)
‹#› Cybersecurity, computer security, or IT security: Measures taken to protect a computer against unauthorized access or attack
Слайд 8: Do I need to worry about cybersecurity?
‹#› Hackers are getting more sophisticated… and more effective! Hackers run successful international enterprises Hackers hack for a living That what they do, and they’re very good at it!
Слайд 9: Cybercrime is not New
‹#› Computers have been hacked since their inception The first spam email took place in 1978 when it was sent out over ARPANET The first virus was installed on an Apple computer by a high school student 1981
Слайд 10: Cybercriminals – No Rules!
‹#› Steady increase in cybercrime Many nations refuse to investigate and prosecute Hackers and governments can access your unprotected data Ransomware is increasing – because it works!
Слайд 11: What do cybercriminals do?
Apply all sorts of techniques to steal personal or financial data Work silently in the background They are stealthy Use stolen data for their gain ‹#›
Слайд 12: Who are the cybercriminals?
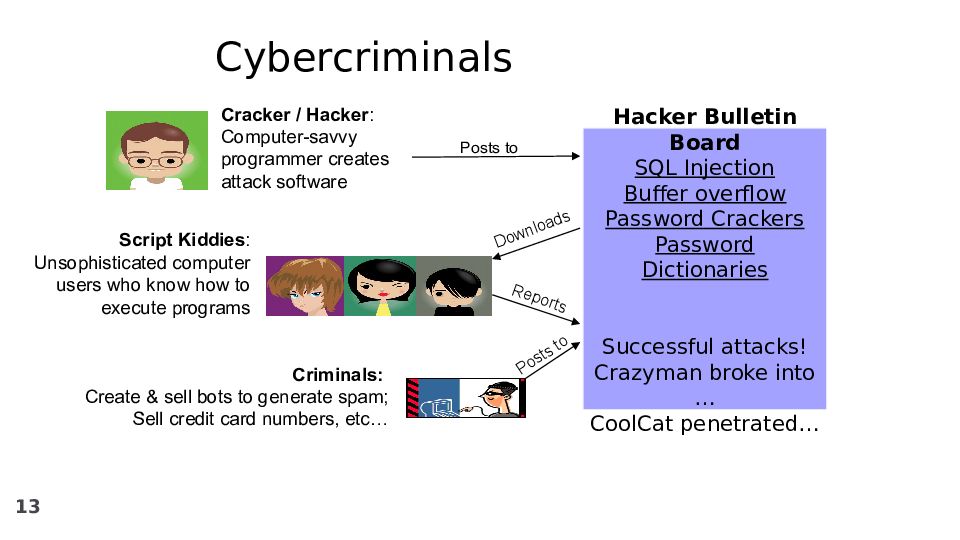
‹#› Crackers and Hackers Computer-savvy programmer who create attack software Script Kiddies Unsophisticated computer users who know how to execute programs created by the crackers Criminals Create & sell bots to generate spam Sell credit card numbers, etc…
Слайд 13
‹#› Cybercriminals Cracker / Hacker : Computer-savvy programmer creates attack software Script Kiddies : Unsophisticated computer users who know how to execute programs Hacker Bulletin Board SQL Injection Buffer overflow Password Crackers Password Dictionaries Successful attacks! Crazyman broke into … CoolCat penetrated… Criminals: Create & sell bots to generate spam; Sell credit card numbers, etc… Posts to Downloads Posts to Reports
Слайд 14: What do cybercriminals want?
Make their living through cybercrimes Money Information Notoriety Status, fame ‹#›
Слайд 15: Categories of Computer Crimes
‹#› Computer as a Tool Computer as the Target Selling Illicit Goods Offensive content or Harassment
Слайд 16: Computer as a Tool
‹#› Using a computer to target an individual Spam, phishing scams, cyber theft, fraud (deception), identity theft, etc. These cyberthieves are scammers, not technical experts
Слайд 17: Computer as a Target
‹#› Targeting a computer or system to commit a crime Viruses or malware Destruction or theft of information Unauthorized access of a computer or account A select group of people with technical knowledge commit these crimes
Слайд 18: Selling Illicit Goods
‹#› Using a computer to sell illicit goods Drugs trafficking Counterfeit products Stolen items Weapons Organized crime groups commit these crimes
Слайд 19: Offensive Content or harassment
‹#› The content of online information may be distasteful, obscene or offensive for a variety of reasons Hate speech Against a group based race, religion, ethnic origin, disability, etc. Harassing someone through cyberspace Stalking, threats of violence, cyberbullying
Слайд 20: Common Types of Cybercrime
Phishing : Using fake email messages to get personal information from internet users Identity theft (misusing personal information) Illegal pornography Hacking : Shutting down or misusing websites or computer networks Spreading hate and inciting terrorism; Grooming : making sexual advances to minors. ‹#›
Слайд 21: Cybercrime Legislation Worldwide
‹#› A worldwide fight against cybercrimes 138 countries have created laws to fight cybercriminals However, 20% of countries do not have any legislation
Слайд 22: Cybercrime Summary
‹#› Cybercrime is any criminal activity carried out using computers or the internet Cybersecurity is taking measures to protect a computer from unauthorized access Cybercriminals exploit others for their personal gain Cybercrime categories: Computer as a tool, as the target, selling illicit goods, offensive content and harassment Computer as a tool : When an individual is a primary target Computer as a target : When a computer is a target
Слайд 23: 8.2: Cybersecurity
8.1: Cybercrime 8.2: Cybersecurity 8.3: Common Threats 8.2: Cybersecurity ‹#›
Слайд 24: Learning Objectives
‹#› Define the goal of cybersecurity Describe easy targets Explain general guidelines of protection against cyber threats Describe why pirated software is not safe State why software updates are important Describe the difference between a password and a passphrase
Слайд 25: Cybersecurity Goal
‹#› Your goal is to make it as difficult as possible to dissuade a hacker from getting your data or from being a victim of cybercrime Cybercriminals go after easy targets unless the victim has something of great value
Слайд 26: Good Line of Defense
‹#› Can you prevent from being a victim of cybercrime? If a professional hacker or government surveillance wants your information, they will get it. Make them work them for it ! In doing so, they might give up and move on to an easier target Minimizes the chances of being a victim
Слайд 27: Password Cracking Example
‹#› Hackers use “Brute-Force” Password Crackers One group cracked 2700 “bad” passwords in 30 seconds The crack program ran for 48 hours more and did not crack the 250 remaining “good” passwords Do the hackers keep trying to get the remaining 250 passwords? Or do they find easier targets? Your goal : Be one of the 250
Слайд 28: Are you a target?
‹#› Most victims are not specifically targeted They are bystanders or part of a larger cybercrime operation A lot of information is out of your control Logins from a website you use is hacked and your password was leaked Control what you can control
Слайд 29: Who are the easy targets?
Easy Targets Use weak passwords Reuse passwords Respond to spam Click links in emails Visit shady internet sites Run pirated software Difficult Targets Security conscious Understand the dangers and risks Use encryption Use Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) ‹#›
Слайд 30: Why do Breaches Happen?
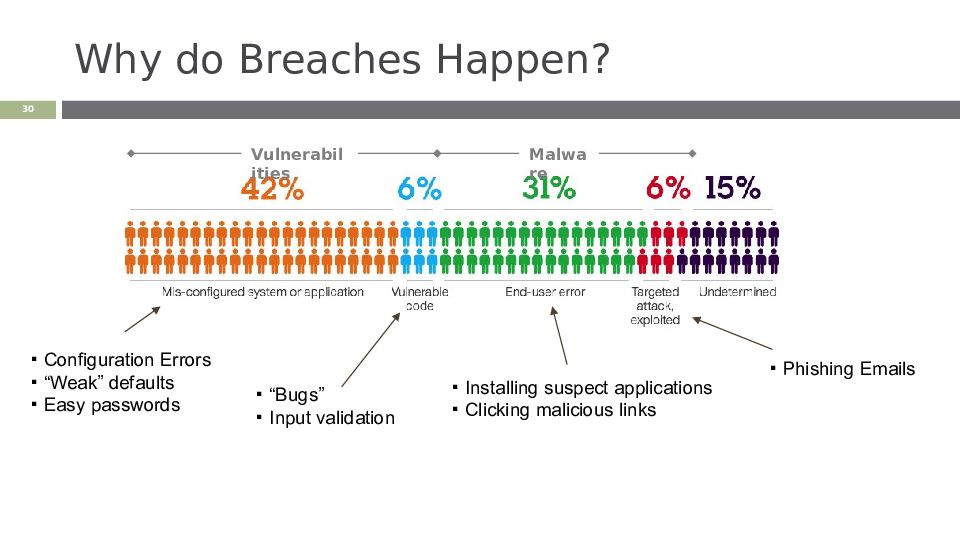
‹#› Configuration Errors “Weak” defaults Easy passwords “Bugs” Input validation Installing suspect applications Clicking malicious links Phishing Emails Malware Vulnerabilities
Слайд 31: General Protection Guidelines
‹#› Use official software (not pirated) Do not visit shady websites Update software regularly Use a reputable antivirus program Use strong passwords Do not reuse passwords
Слайд 32: Pirated Software
‹#› Pirated software is software that has been copied or distributed for free against the wishes of the creator Popular choices Windows 7/10 Microsoft Office Kaspersky Lab Adobe products
Слайд 33: Pirated Software (2): Created by Criminals
‹#› Crackers hack software for a living They do not do it for the goodwill of the community They are not Robin Hood If they crack software, they do so to help their criminal enterprise They can control the computers of those who install it
Слайд 34: Pirated Software (3): Risks
‹#› Pirated software contains backdoors Cybercriminals use your computer in many ways Mine for Bitcoins or cryptocurrencies Send spam Launch cyber attacks Monitor communications for financial information
Слайд 35: Pirated Software (4): Assumptions
‹#› All pirated software is compromised All cracking software used to hack official versions contains malware
Слайд 36: Pirated Software (5): Assumptions
‹#› Free download sites can be dangerous, even for free software, such as Adobe PDF Could contain unofficial versions of the software with malware
Слайд 37: Pirated Software (6): Food for Thought
Would you install a free lock on your door from a mafia street vendor? What are the risks? Similarly, why would you trust a hacker with your computer and data? ‹#›
Слайд 38: Pirated Software (7): Alternatives
‹#› Only download software from official sources microsoft.com; adobe.com; google.com; mozilla.org; Do not use cracking software to unlock software Use free alternatives GIMP - GNU Image Manipulation Program Linux FreeOffice Google Drive
Слайд 39: Software Updates: Are they important?
‹#› Crackers find new exploits all the time Write software to exploit these Script kiddies and cybercriminals purchase the hacker’s software to use the exploits Running up-to-date software patches these vulnerabilities
Слайд 40: Passwords
‹#› Bad passwords easily guessed by a computer program Qwerty; 123456; password; superman; p@ssword Good passwords are long and have special characters and numbers. They do not make sense, such as: KN%6hGYgEqdVvAt7#W!cVk31
Слайд 41: Passwords (2): Passphrase
‹#› Use a passphrase if you need to memorize your password Strong passwords require a password safe Memorize a passphrase (can use special letters) Positive message: I want 2 smile more :) Random words: Yellow-green pancakes 4bfast Some phrase: Te@ is better with milk A memory: Remember Turkey 2017?
Слайд 42: Final point to ponder
Someone will always have your data You give them permission to read the emails and your documents by using the service Do you trust them? Who do you trust more not to abuse your data? mail.ru/.kz Gmail.com yandex.ru/.kz any-email-address /.com/.ru/.cn/.eu/.abc
Слайд 43: Cybersecurity Summary
‹#› Goal : Be a difficult target Easy targets : People with a low awareness of cybersecurity; don’t take measures to protect themselves online Protection guidelines : U se official software that automatically updates, do not visit shady websites, and choose strong passwords Pirated software : Are tools of hackers Software updates : Fix recent exploits in software Password : UecX6JxZJ^cJ$; Passphrase : I like d33p blue!
Слайд 44: 8.3: Common Threats
8.1: Cybercrime 8.2: Cybersecurity 8.3: Common Threats 8.3: Common Threats ‹#›
Слайд 45: Learning Objectives
‹#› Describe the common cyber threats Understand how malware works List the ways that malware infects computers Describe how to protect against data leaks Explain the dangers links in unsolicited email Describe security risks when using public WiFi
Слайд 46: Common Cyber Threats
Malware Data Leaks Unsolicited Email Open WiFi Networks ‹#›
Слайд 47: Malware
‹#› The word "malware" comes from the term " MAL icious soft WARE." Malware is any software that infects and damages a computer system without the owner's knowledge or permission
Слайд 48: Malware (2): How Malware Operates
‹#› The malicious code attaches itself to a program, file, or disk When the program executes, the virus activates and replicates itself The virus works in background, often without knowledge of the user
Слайд 49: Malware (3): Infection Methods
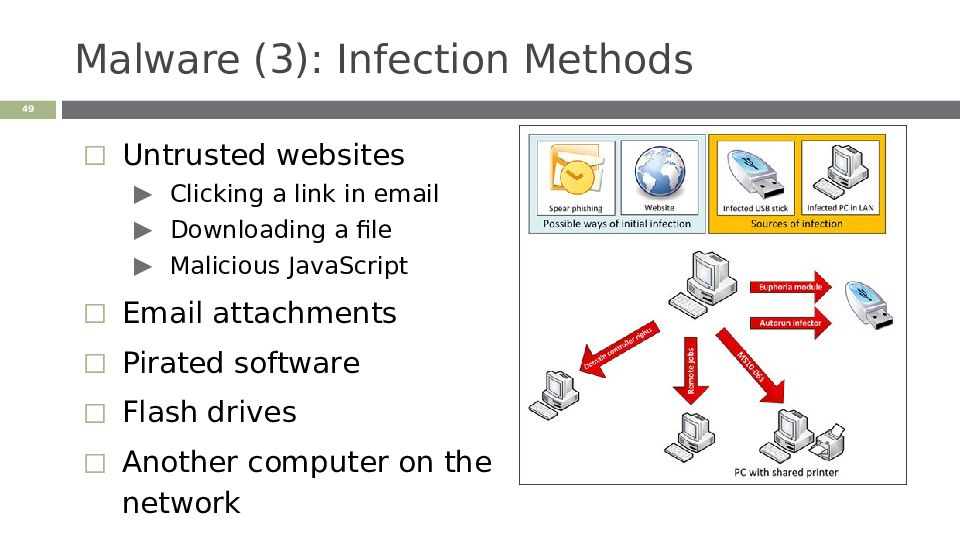
Untrusted websites Clicking a link in email Downloading a file Malicious JavaScript Email attachments Pirated software Flash drives Another computer on the network ‹#›
Слайд 50: Malware (4): What They Do
‹#› Worms self-replicate but do not cause harm Viruses can cause the computer crashes, loss of data, Trojan horses steal data and provide a backdoor for the cybercriminal Spyware collects data from the infected machine Keyloggers record all of a user’s keystrokes Fake antivirus software allows malware to remain undetected This is true for pirated/hacked antivirus software
Слайд 51: Malware (5): Ransomware
Encrypts your entire computer Only way to get access to your files is to pay the cybercriminal ‹#›
Слайд 52: Malware (6): Infected Computers
Antivirus software can clean some malware, but not all Might require the user to reinstall the operating system User’s data may or may not be salvaged ‹#›
Слайд 53: Malware (7): Protect Against
‹#› Use a reputable antivirus program Keep your computer up to date Do not visit untrusted websites Do not click unknown links in an email Do not download files from unknown sources Do not use pirated software Most pirated software contains malware
Слайд 54: Data Leaks
Release of secure information to an untrusted environment Cybercriminals frequently post hacked usernames and passwords from websites One online hacker’s database has 1.4 billion usernames and passwords ‹#›
Слайд 56: Data Leaks (3)
You cannot prevent data leaks Instead, plan for your username, password, and other sensitive data to be leaked online ‹#›
Слайд 57: Data Leaks (4)
Cybercriminal plan on users using the same username and password for multiple accounts ‹#›
Слайд 58: Data Leaks (5): How to Plan
‹#› Use a unique username and password combination for each account Use a password manager LastPass 1Password KeePass Use two-factor authentication
Слайд 59: Data Leaks (6): Encryption
‹#› Encrypt sensitive data Secure Folder (Samsung) BitLocker (Windows 7/10 Pro ) VeraCrypt (Windows) 7zip encrypts compressed files (Any) The easiest to use You will learn how to use 7zip in a lab
Слайд 60: Unsolicited Email
Unsolicited email is a favorite way for cybercriminal to get access to a computer or an account Phishing : Tricking the user to giving account information Click Here : The link takes a user to a malicious website ‹#›
Слайд 61: Unsolicited Email (2)
Infected attachments : A doc, pdf, or another file that contain malicious software Self-replicating : Once you are infected, the malware uses your account to send the infected email to everyone in your address book ‹#›
Слайд 62: Unsolicited Email (2): Click Here
‹#› If you click a malicious link or fall for a phishing scam, it might be too late… Drive-by downloads : Malicious software can install just by visiting a website (virus, ransomware, keylogger) Ransomware : 93% of all phishing emails are now ransomware
Слайд 63: Unsolicited Email (3): Protection
‹#› In addition to the malware protection guidelines: Know how to identify fake email or spam Never click a link in an email, not even from a friend, unless you know it is safe Never click a password reset link. Instead, go to the website directly Mouse over a link to verify the URL
Слайд 64: Open WiFi Access Points
‹#› Any data transmitted through an unsecured WiFi connection can be easily collected Intercepting login credentials Only use SSL/HTTPS when logging into your sites Understand the risks and use with care Virus threat from infected users Better to use mobile data through your phone
Последний слайд презентации: 8. CYBERSECURITY: Common Threats Summary
‹#› Common cyber threats malware, data leaks, unsolicited email, and public WiFi Malware is malicious software that runs the background From: untrusted websites, email attachments, pirated software, infected flash drives, or infected computers on a network Data leaks publish private data online Harmful websites automatically install malware when visited Public WiFi expose unencrypted data, such as passwords