Первый слайд презентации: Competency-based education: Teaching and Learning in the 21 st century
Bernadette L. Dean Naryn Campus December 2018/January 2019
Слайд 2
In the last few years we have heard much talk of “21st century skills” but little about why skill demands are actually changing. Will students really need better or different skills to succeed in life and work in the 21st century? What trends are behind such changes? What specific kinds of knowledge and skills will be most important? University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Social Economic Political Technological Environment Workplace Health Education: Teaching and Learning University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 4: How is our world different today? (participants views)
University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 5: Why competency-based education?
Globalization: increased competition for fewer jobs therefore high levels of creativity and innovation in order to stay competitive. Information and Communication revolution: rapid technological advances and unprecedented access to information Advances in brain science providing new insights into how people learn University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 6
Corporate change. Because of technology, globalization, competitive forces, how work gets done is radically different. Work more collaborative, self-managing work teams responsible for tackling major projects, often global in nature. Jobs have become less predictable and stable requiring employees to adapt to new challenges and demands. Automation: Computers good at doing ‘routine jobs’ therefore replacing humans University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 7
‘... schools have to prepare students for jobs that have not yet been created, technologies that have not yet been invented and problems that we don't yet know will arise.’ Andreas Schleicher, OECD Education Directorate, 2010 University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 8
If our world is different today and we do not know what our world will be like tomorrow, should the education we provide our young people be like yesterday? University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 9: What does the research suggest?
Students who obtain more education (higher, skill training) will be at a great advantage to secure a middle-class lifestyle. The need for knowledge and skills in languages, mathematics, science and technology is necessary; in fact, students who master these skills will have a distinct advantage over their peers. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 10
For success on the job, in their personal lives, and in society students must be able to “apply” what they learn rather than simply “reproduce” the information on tests. Students who develop in-demand cross-curricula competencies—the ability to think critically, communicate and collaborate, create new products, and adapt to change—will be at an even greater advantage in work and life. Applied skills and competencies can best be taught in the context of the academic curriculum. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 11
“Education should develop each child’s personality, talents and abilities to the fullest” UN Convention on the Rights of the Child, Article 29a University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 12
Shift in pedagogy from teaching to learning Formative assessment is important to promote learning Create teaching and learning environments to intellectually engage students University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
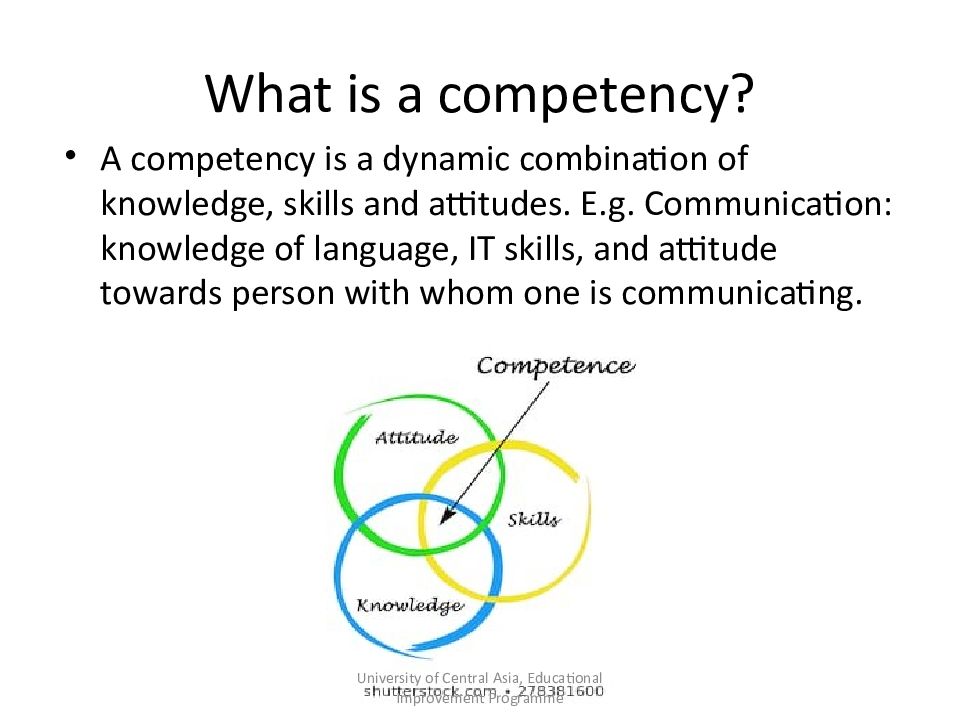
Слайд 13: What is a competency?
A competency is a dynamic combination of knowledge, skills and attitudes. E.g. Communication: knowledge of language, IT skills, and attitude towards person with whom one is communicating. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 15: Characteristics of a competency
1. Dynamic combination of knowledge, skills and attitudes whose mastery enables its attainment. 2. Linked to all three of the domains of performance that can be assessed: knowledge, skills and attitude. 3. As a performance, it is observable. 4. Since observable, also measurable. 5. Are transferable across the curricula. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 16: Learning Outcomes
Learning outcomes are statements that describe the learning students will achieve at the end of lesson, unit or course of study. E.g. Students will be able to read the given text correctly. Learning Outcome statements have three main components: an action word that identifies the performance to be demonstrated; a learning statement that specifies what learning will be demonstrated in the performance; and a broad statement of the criterion or standard for acceptable performance. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 17: Activity
Write three learning outcomes. Share them with your partner and together check that they have an action word, a learning statement and a criterion of acceptable performance. Share one learning outcome with the class. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 18: Foundational Knowledge and Skills
Students will still need to be competent in the disciplines traditionally taught in the school curriculum, especially strong language, math, science and technology skills and the ability to apply their learning to meet real-world challenges to succeed in higher education, work and life. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 19: Language(s)
The ability to express and interpret thoughts, feelings and facts in both oral and written form in the full range of societal and cultural contexts — work, education and training, home and leisure — in one’s first language, in the language(s) of instruction at school and other languages of one’s choice. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 20: Language(s): Rationale
Countries have been and are becoming more multicultural. The internet facilitates communication beyond national borders. Being multilingual is a requirement of the 21 st century. Being multilingual allows us to participate in a range of societal and cultural contexts. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 21: Language(s): Learning outcomes
Students will be able to: use the article ‘the’ correctly in spoken interaction and in their writing read and understand the given texts as evidenced in their answers to the given questions. speak confidently in public. show sensitivity to cultural difference and positive attitude to other cultures in their communications. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 22: Mathematical literacy: Definition
At a basic level, mathematical literacy includes the use of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, percentages and ratios in mental and written computation for problem-solving purposes. Further development involves, as appropriate to the context, the ability and willingness to use mathematical modes of thought (logical and spatial thinking) and presentation (formulas, models, constructs, graphs/charts) which have universal application in explaining and describing reality. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 23: Mathematical Literacy: Rationale
Mathematics is used in every facet of life, from buying something in a store to use of technology. Mathematics is a critical component of success in jobs of the future. Mathematics is not as a solitary subject, but must be integrated with other subjects. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 24: Mathematical Literacy: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: make mathematical presentation in the form of graphs, formulas and statistics from the given data explain their thinking and reasoning in solving problems on….. develop a respect for truth as the basis of mathematical thinking University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 25: Science and Technology: Definition
Scientific competence is the ability and willingness to use the body of knowledge and the methodology employed in the field of science to explain the natural world. Competence in technology is viewed as the application of that knowledge in order to modify the natural environment in response to perceived human wants or needs. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 26: Science and technology: Rationale
Science and technology are fundamentally altering the way we live, connect, communicate and transact, with profound effects on social and economic development. All young people must acquire scientific knowledge and skills, seek careers in the fields of science and technology and be ready to make decisions around issues of science and technology as citizens. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 27: Science and technology: Learning outcomes
Students will be able to: describe the structure, composition and functions of proteins use and manipulate technological tools to create a rocket that can reach a height of 10 meters practice general and experiment specific safety and security measures when working in the lab be aware of and practice ethical behaviour when using social media University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 28
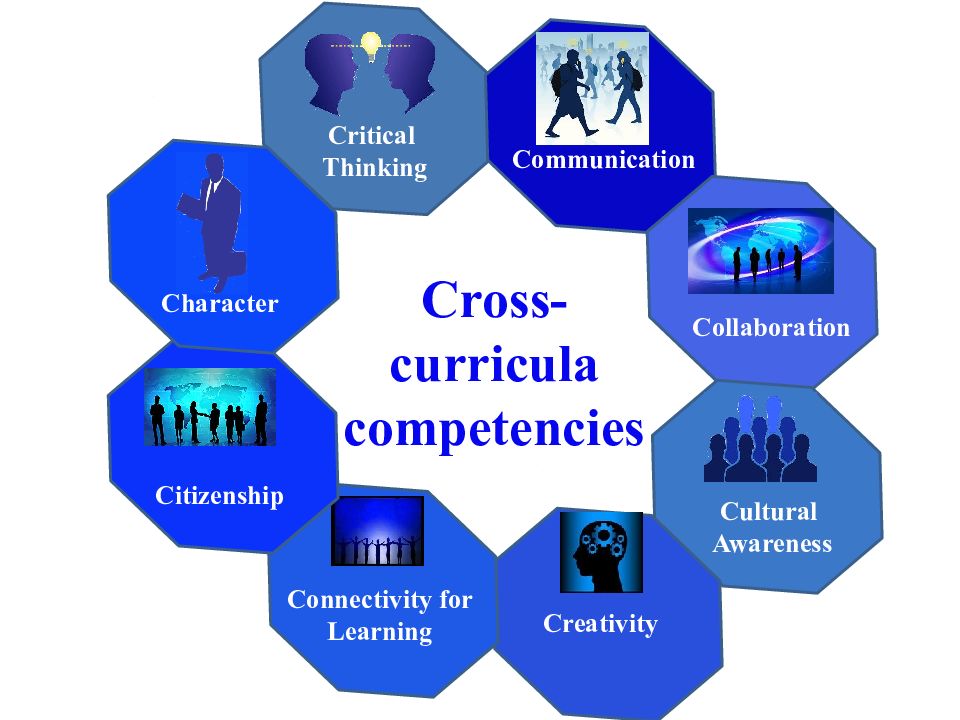
Critical Thinking Communication Collaboration Cultural Awareness Creativity Connectivity for Learning Citizenship Character Cross-curricula competencies
Слайд 29: Activity: Jigsaw cross-curricula competencies
Read the given text and prepare to teach: Critical thinking and citizenship Communication and connectivity for learning Collaboration and character qualities Creativity and cultural awareness Teach and check for understanding Provide definition, rationale and two learning outcomes for each competency Do all the above in a respectful manner. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 30: Creativity, Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Definition
Creativity incorporates curiosity and innovation to generate new or original thoughts, interpretations, products, works, or techniques. An entrepreneurial mindset is the ability to recognize and act on opportunities and the willingness to embrace risk and responsibility. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 31: Creativity and Innovation : Rationale
Today’s challenges are increasingly complex and require creative and innovative thinking to identify and solve problems and create new products. For success in school, work and life, young people must be able to generate new ideas, theories, products and knowledge. Creative ideas are required for countries to succeed economically. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 32: Creativity and Innovation: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: make discoveries through inquiry and research. elaborate, refine, analyze, and evaluate original ideas to improve and maximize creative efforts apply new knowledge in innovative ways to create new products or solve complex problems. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 33: Critical Thinking: Definition
The ability to access, analyse and synthesize information presented in a multitude of forms from a variety of media to answer questions, make informed decisions and develop solutions to complex problems. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 34: Critical Thinking: Rationale
The knowledge and digital era demands people with the: ability to think logically and rationally ability to solve problems by identifying and describing the problem, critically analyzing the information available, framing and testing various hypotheses, formulating creative solutions, and taking action. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 35: Critical Thinking: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: clearly define problems acquire, process, interpret, and critically analyze information to answer a question/ make an informed decision/take timely action. use various types of reasoning (e.g. inductive, deductive) to solve a problem University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 36: Collaboration: Definition
Collaboration is forming and working in groups or teams as a means to learn with and from others as well as conduct and facilitate business. Collaboration includes teamwork, leadership and assistance that serves to benefit the whole. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 37: Collaboration: Rationale
In today’s globalized world working with others requires interpersonal capabilities and skills than were not required when we were not so interconnected and when our work was focused on production of goods. Social media has seriously impacted the collaboration dynamic which occurs outside schools. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 38: Collaboration: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: interact positively and respectfully with others in creating new ideas and developing products. work in teams with other people in varying contexts, managing and resolving conflicts. show sensitivity to the issues and processes associated with collaborating across cultures. collaborate across networks, using various information and communication technologies. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 39: Communication: Definition
Communication provides the means by which the individual can present information in a multitude of means through a variety of media. Information must be clear and concise, effective and engaging, and presented in a way that is meaningful to the individual and the audience. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 40: Communication: Rationale
Today, communication is more complex and sophisticated than ever before especially with work often occurring with peers located half-way around the world. The science of learning encourages constructivist models of developing understanding and meaning making from human interactions. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 41: Communication: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: communicate effectively in their mother tongue, the official language and at least one foreign language. communicate using a variety of media and technologies. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 42: Citizenship: Definition
The ability to know how to exercise the rights and responsibilities of citizenship at the local, national and global levels; developing the motivation, disposition and skills for civic participation; and understanding the local and global implications of civic issues (P21, 2007a, 2013). It also includes knowing how to participate productively, responsibly and ethically in virtual communities (P21, 2013), that is, exercising digital citizenship. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 43: Citizenship: Rationale
Education for citizenship is exciting and relevant to children, and gives learning meaning. Citizenship acknowledges that as individuals we have power to change things by the choices we make and the way we behave/act. Global citizenship enables the challenging of misinformation and stereotyped views about countries, and allows children to counter ignorance and intolerance. In our interdependent world, global citizenship encourages us to recognize our responsibilities towards each other. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 44: Citizenship: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: comprehend the local and national political, social, economic and financial systems in a global context. explain key ideas and concepts related to democracy, social justice and human rights. use their knowledge, skills and attitudes to take actions to solve problems. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 45: Character Qualities: Definition
Character is the particular combination of qualities in a person that makes them different from other people. Character qualities are the social and emotional skills needed to achieve goals, live and work with others and manage emotions. They include perseverance, adaptability/flexibility, empathy or perspective taking, open-mindedness, ethics, courage, accountability and responsibility. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 46: Character Qualities: Rationale
The knowledge economy and social environment is highly complex, fast paced and multi-cultural, demanding people with highly developed interpersonal traits and strength of character. Learning requires social and emotional skills including self- awareness, social awareness, personal and relationship skills University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 47: Character Qualities: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: complete given tasks despite their difficulty respond and adjust to new tasks, roles and situations respect and appreciate diversity inspire others to do their best Identify goals, plan and work towards achieving them University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 48: Cultural awareness: Definition
The ability to live and work together in culturally diverse societies and organizations. It includes the ability to understand and communicate with people from other cultures, to work effectively in diverse teams (e.g. respecting cultural differences and collaborating with people from a wide range of social and cultural backgrounds), be open-minded to different ideas and values, and use social and cultural differences to generate ideas, innovate and produce quality work (Scott, 2015) University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 49: Cultural Awareness: Rationale
We all value our own history and culture. The increasingly global nature of life and work means increasing cross-cultural interactions, creating both opportunities and challenges that require unique competencies and skill sets. While valuing one’s own history and culture, one must demonstrate respect for diverse identities and cultures. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 50: Cultural Diversity: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: welcome, seek out and engage the talents and ideas of diverse people (Scott, 2015) work respectfully and cooperatively in interdisciplinary and intercultural teams leverage social and cultural differences to create new ideas and increase both innovation and quality of work University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 51: Connectivity for learning: Definition
Effective students, workers and citizens of the 21st century must be able to exhibit a range of functional (e.g. access, manage, integrate) and critical thinking skills (e.g. evaluate) related to information, media and technology. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 52: Connectivity for Learning: Rationale
We live in an information, media and technology infused environment, characterised by access to an abundance of information, rapid changes in technology tools, and the ability to make individual and collaborate contributions. Information, media and ICT literacy is an essential competency for both students and teachers. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 53: Connectivity for Learning: Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to: use computers and digital resources to access information create knowledge, solutions, products and services. identify how media messages are constructed and for what purposes use social media for learning. University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 54
Critical Thinking Communication Collaboration Cultural Diversity Creativity & Innovation Connectivity for Learning Citizenship Character 8 C’s of Education for the Future
Слайд 55
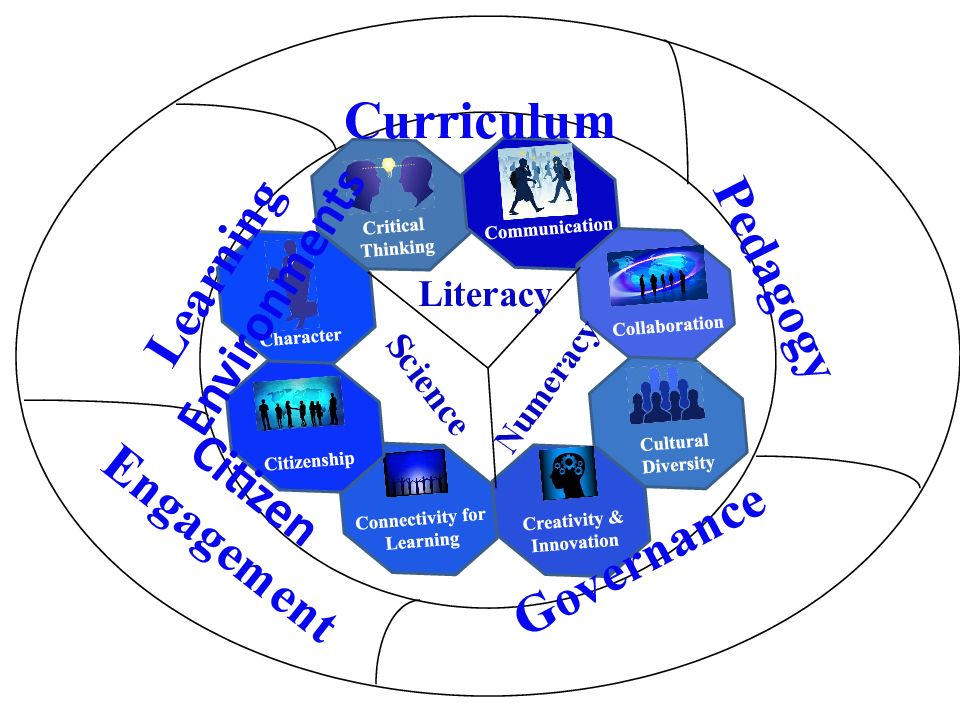
Critical Thinking Communication Collaboration Cultural Diversity Creativity & Innovation Connectivity for Learning Citizenship Character Curriculum Pedagogy Governance Citizen Engagement Learning Environments Literacy Numeracy Science
Слайд 56: System change is required but how?
System Change 5 Key actions Curriculum Infuse the 8Cs across the curriculum, ensuring relationship but no repetition Pedagogy Facilitate teachers to ensure they are fluent users of technology so that they can engage and support student learning Assessment Increase the range of assessment strategies so as to better assess the 8Cs learning outcomes Learning Environments Make learning spaces more flexible so as to promote independent and collaborative learning Governance Leadership must be a shared responsibility using the process of collaboration and communication Community Engagement Engage the community in providing authentic learning opportunities to students beyond the school and classroom University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme
Слайд 57
What will the people involved have to do? The Principal (e.g. design a education improvement plan to promote 21 st Century learning) The Teachers (e.g. use 21 st century activities and pedagogies, use formative and performance assessment, create a safe and engaging environment to ensure all children learn) The Parents (e.g. support the school in implementing the plan for promoting 21 st Century learning) Other stakeholders (e.g. provide authentic learning opportunities for students outside the school and classroom) University of Central Asia, Educational Improvement Programme