Первый слайд презентации: creators: Bokayeva M.S. Tyulyugenova L
Theme: DATA ANALYSIS Innovative University of Eurasia Subject : Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) creators: Bokayeva M.S. Tyulyugenova L.
Слайд 2: OVERVIEW
Qualitative and quantitative Simple quantitative analysis Simple qualitative analysis Tools to support data analysis Theoretical frameworks: grounded theory, distributed cognition, activity theory Presenting the findings: rigorous notations, stories, summaries
Слайд 3: SCALES OF MEASUREMENT
into a no n - Many people are confused about what type of analysis to use on a set of data and the relevant forms of pictorial presentation or data display. The decision is based on the scale of measurement of the data. These scales are nominal, ordinal and numerical. Nominal scale A nominal scale is where: the data can be classified numerical or named categories, and the order in which these categories can be written or asked is arbitrary. Ordinal scale An ordinal scale is where: the data can be classified into non-numerical or named categories an inherent order exists among the response categories. Ordinal scales are seen in questions that call for ratings of quality (for example, very good, good, fair, poor, very poor) and agreement (for example, strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree). Numerical scale A numerical scale is: where numbers represent the possible response categories there is a natural ranking of the categories zero on the scale has meaning there is a quantifiable difference within categories and between consecutive categories.
Слайд 4
When using a quantitative methodology, you are normally testing theory through the testing of a hypothesis. In qualitative research, you are either exploring the application of a theory or model in a different context or are hoping for a theory or a model to emerge from the data. In other words, although you may have some ideas about your topic, you are also looking for ideas, concepts and attitudes often from experts or practitioners in the field.
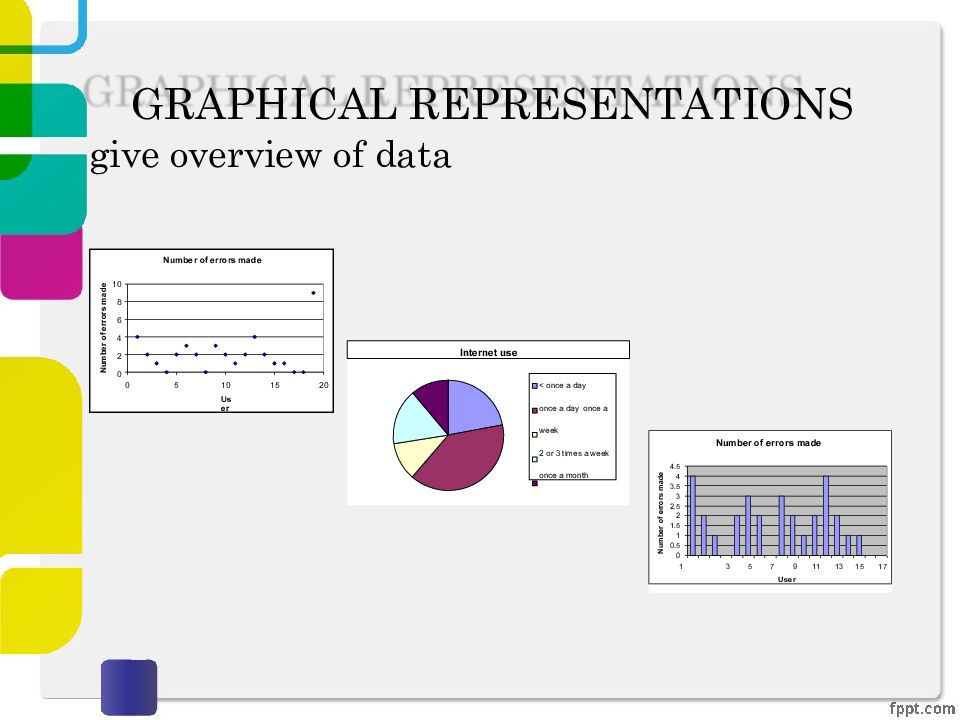
Слайд 13: GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATIONS
give overview of data Number of errors made 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 User N u m b er o f e rr o r s m a d e Internet use < once a day once a day once a week 2 or 3 times a week once a month Number of errors made 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 5 15 20 10 U s e r N u m b e r o f e rr o r s ma d e
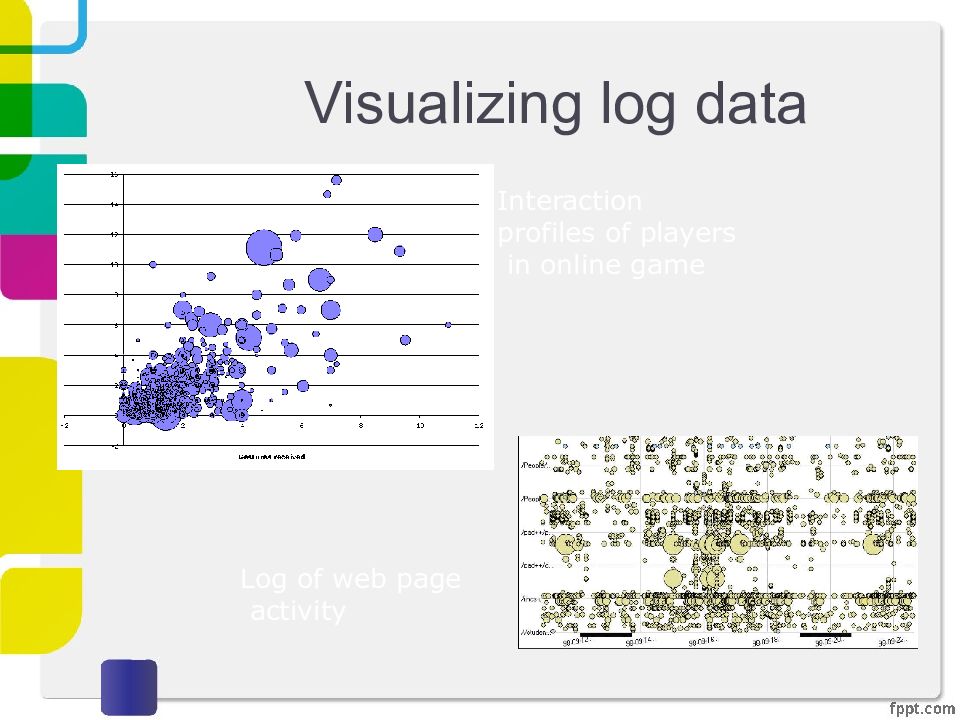
Слайд 14: Visualizing log data
Interaction profiles of players in online game Log of web page activity
Слайд 15: QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
"Data analysis is the process of bringing order, structure and meaning to the mass of collected data. It is a messy, ambiguous, time- consuming, creative, and fascinating process. It does not proceed in a linear fashion; it is not neat. Qualitative data analysis is a search for general statements about relationships among categories of data." Marshall and Rossman, 1990:111 Hitchcock and Hughes take this one step further: "…the ways in which the researcher moves from a description of what is the case to an explanation of why what is the case is the case." Hitchcock and Hughes 1995:295
Слайд 16: Simple qualitative analysis
Unstructured - are not directed by a script. Rich but not replicable. Structured - are tightly scripted, often like a questionnaire. Replicable but may lack richness. Semi-structured - guided by a script but interesting issues can be explored in more depth. Can provide a good balance between richness and replicability.
Слайд 17: Simple qualitative analysis
Recurring patterns or themes Emergent from data, dependent on observation framework if used Categorizing data Categorization scheme may be emergent or pre-specified Looking for critical incidents Helps to focus in on key events
Слайд 18: TOOLS TO SUPPORT DATA ANALYSIS
Spreadsheet – simple to use, basic graphs Statistical packages, e.g. SPSS Qualitative data analysis tools Categorization and theme-based analysis, e.g. N6 Quantitative analysis of text-based data
Слайд 19: Theoretical frameworks for qualitative analysis
Basing data analysis around theoretical frameworks provides further insight Three such frameworks are: Grounded Theory Distributed Cognition Activity Theory
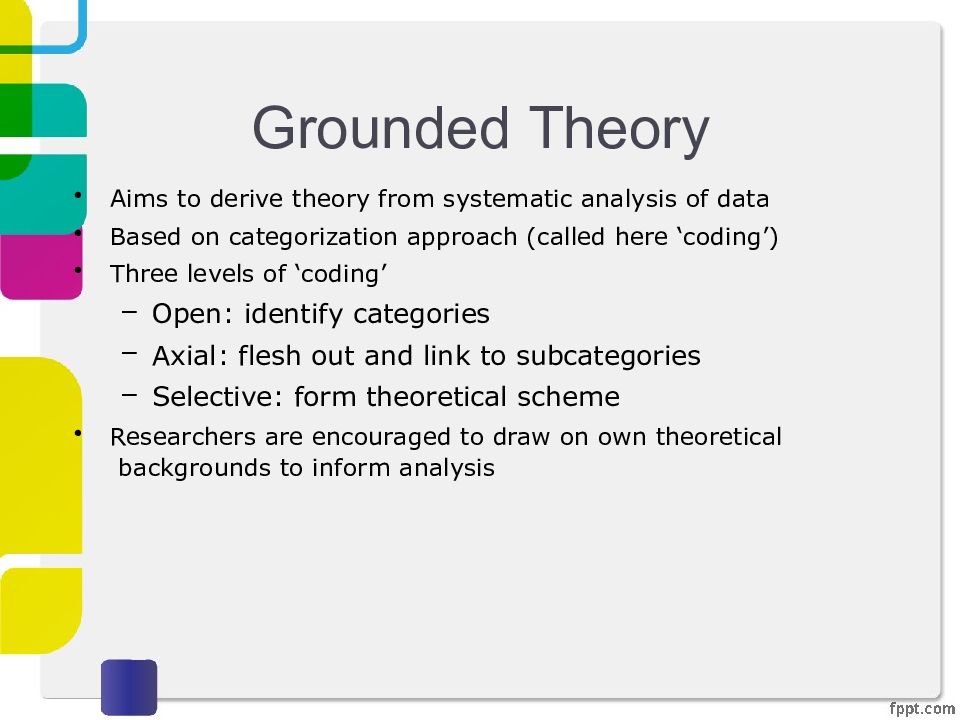
Слайд 20: Grounded Theory
Aims to derive theory from systematic analysis of data Based on categorization approach (called here ‘coding’) Three levels of ‘coding’ Open: identify categories Axial: flesh out and link to subcategories Selective: form theoretical scheme Researchers are encouraged to draw on own theoretical backgrounds to inform analysis
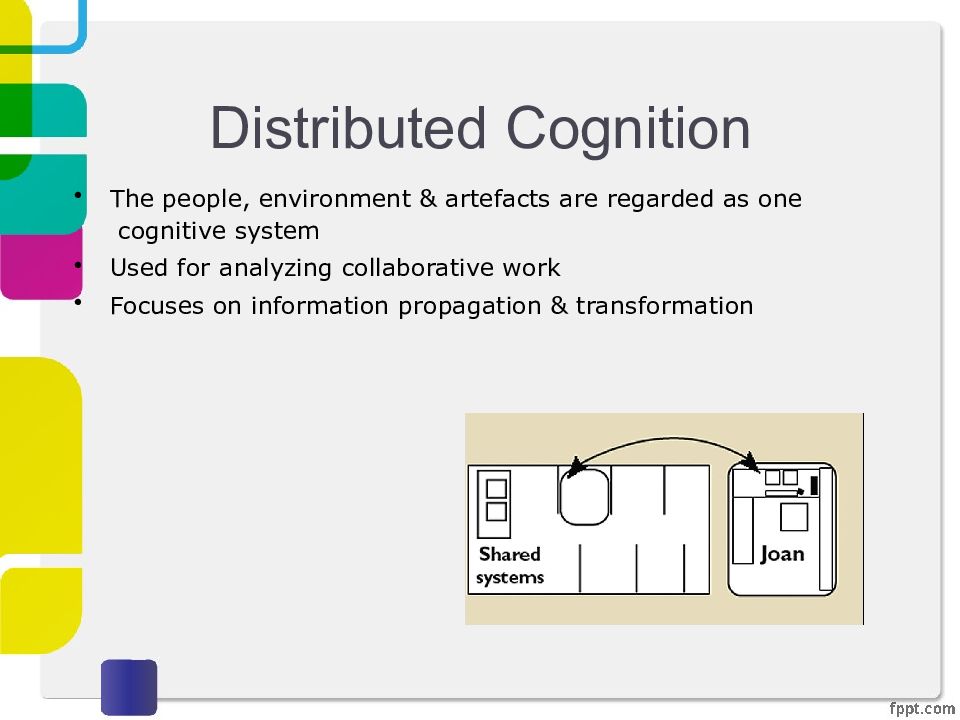
Слайд 21: Distributed Cognition
The people, environment & artefacts are regarded as one cognitive system Used for analyzing collaborative work Focuses on information propagation & transformation
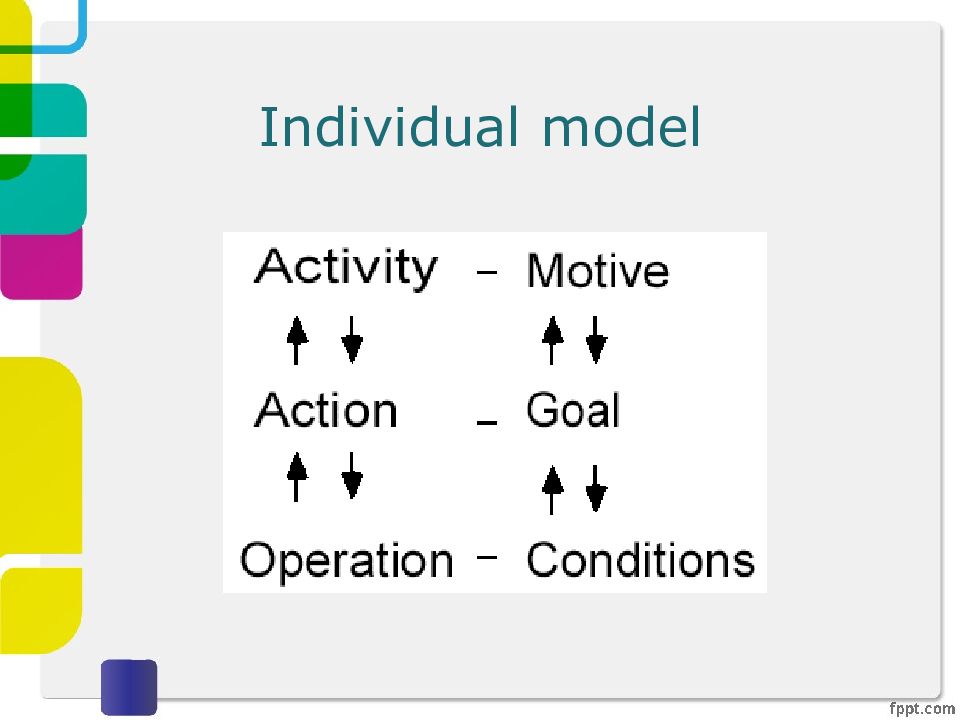
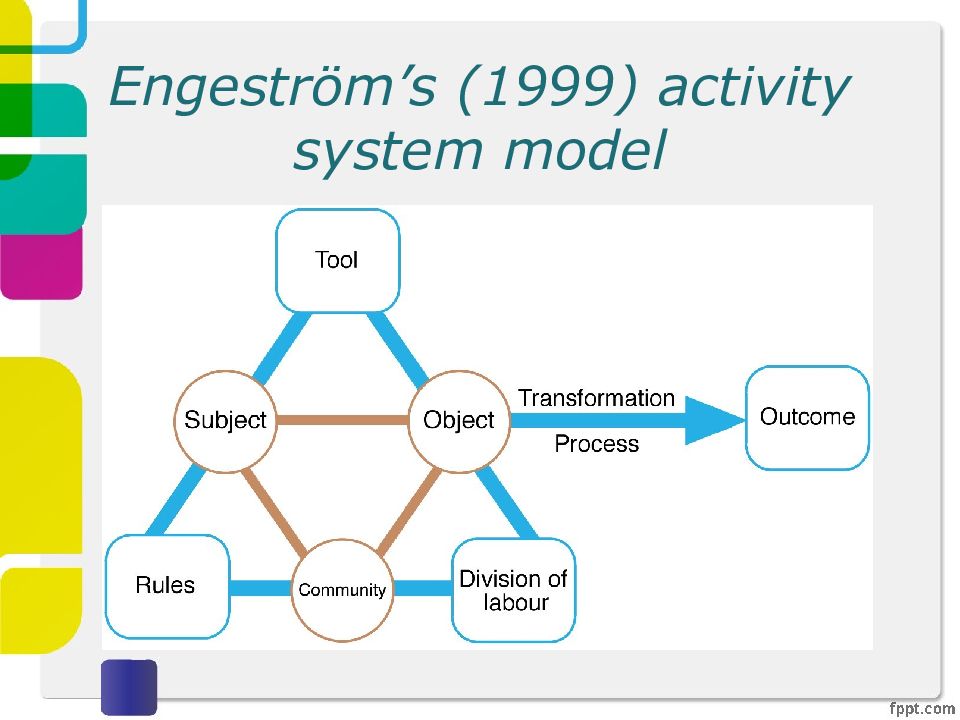
Слайд 22: Activity Theory
Explains human behavior in terms of our practical activity with the world Provides a framework that focuses analysis around the concept of an ‘activity’ and helps to identify tensions between the different elements of the system Two key models: one outlines what constitutes an ‘activity’; one models the mediating role of artifacts
Последний слайд презентации: creators: Bokayeva M.S. Tyulyugenova L: Presenting the findings
Only make claims that your data can support The best way to present your findings depends on the audience, the purpose, and the data gathering and analysis undertaken Graphical representations (as discussed above) may be appropriate for presentation Other techniques are: Rigorous notations, e.g. UML Using stories, e.g. to create scenarios Summarizing the findings