Первый слайд презентации: Update on Mumps and Current Status of Outbreak in NW Arkansas
Cat Waters, BSN Outbreak Response Section Chief Arkansas Department of Health 1
Слайд 2
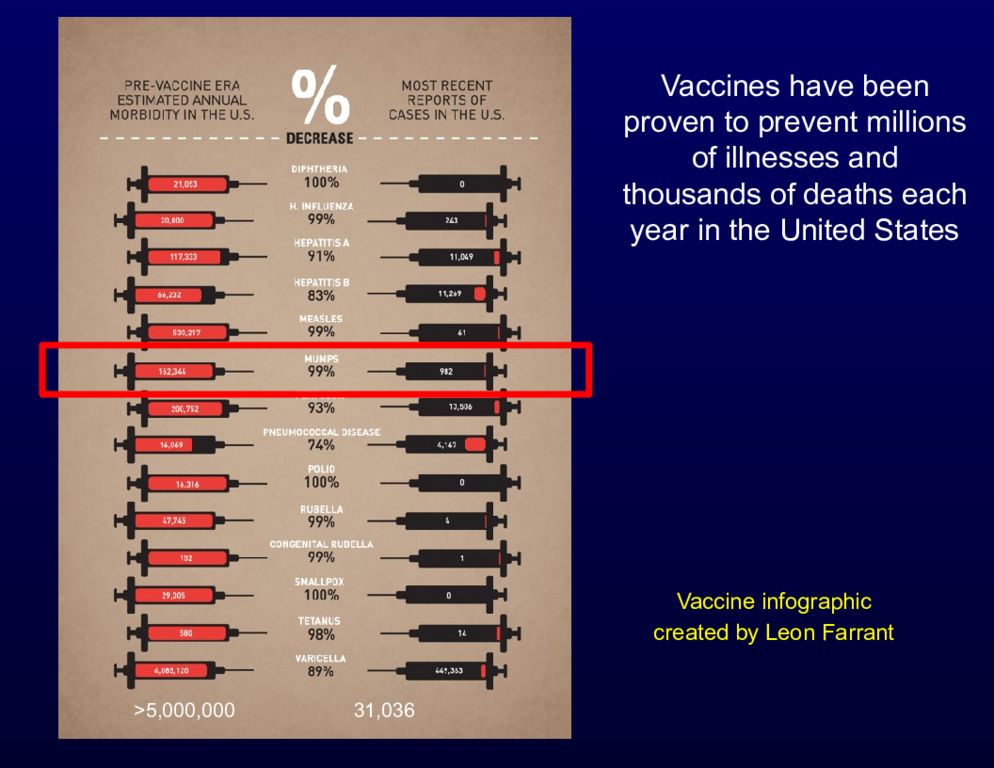
Vaccine infographic created by Leon Farrant Vaccines have been proven to prevent millions of illnesses and thousands of deaths each year in the United States >5,000,000 31,036
Слайд 3: Mumps
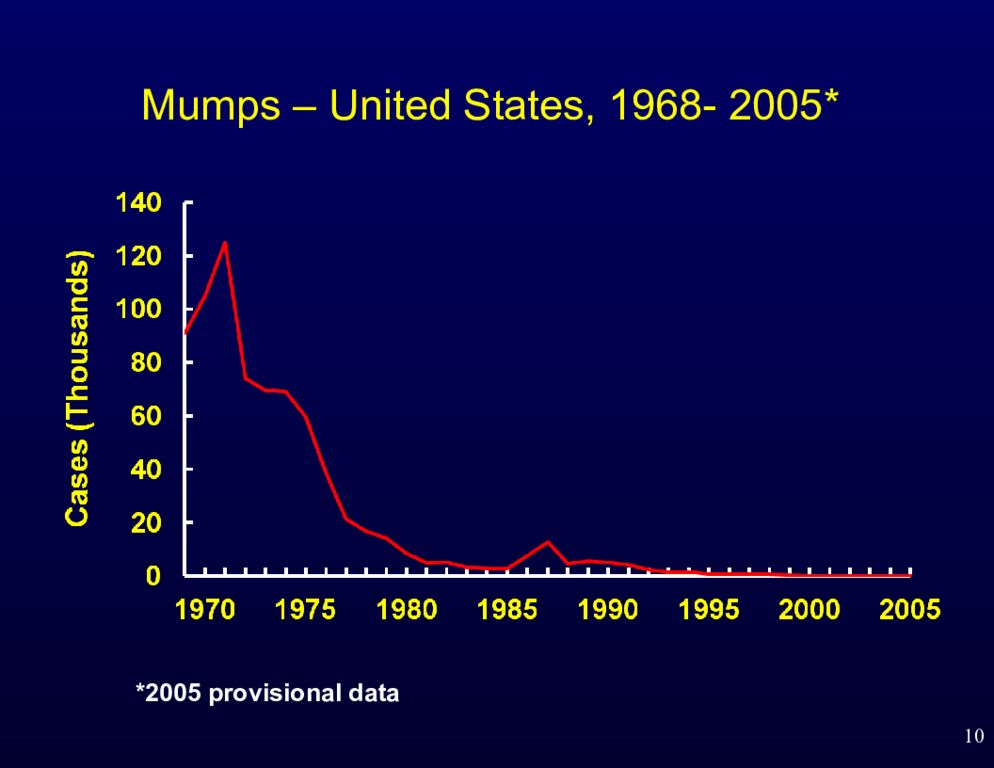
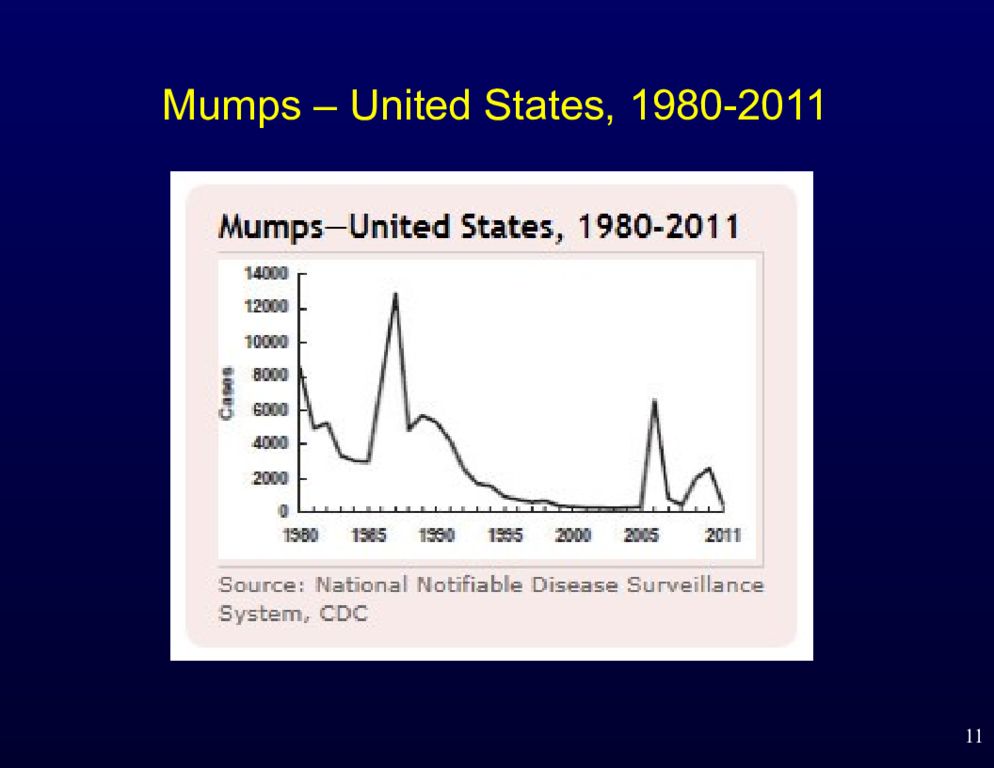
3 Mumps Major cause of outbreaks in pre-vaccine era Vaccination has reduced mumps by 99% in the US Recently, a few outbreaks have centered around colleges and schools Particularly in dormitory settings and dense housing Also in the National Hockey League
Слайд 4: Mumps Virus
4 Mumps Virus Paramyxovirus Enveloped RNA virus One antigenic type Rapidly inactivated by UV light, heat, and various chemical agents
Слайд 5: Mumps Laboratory Diagnosis
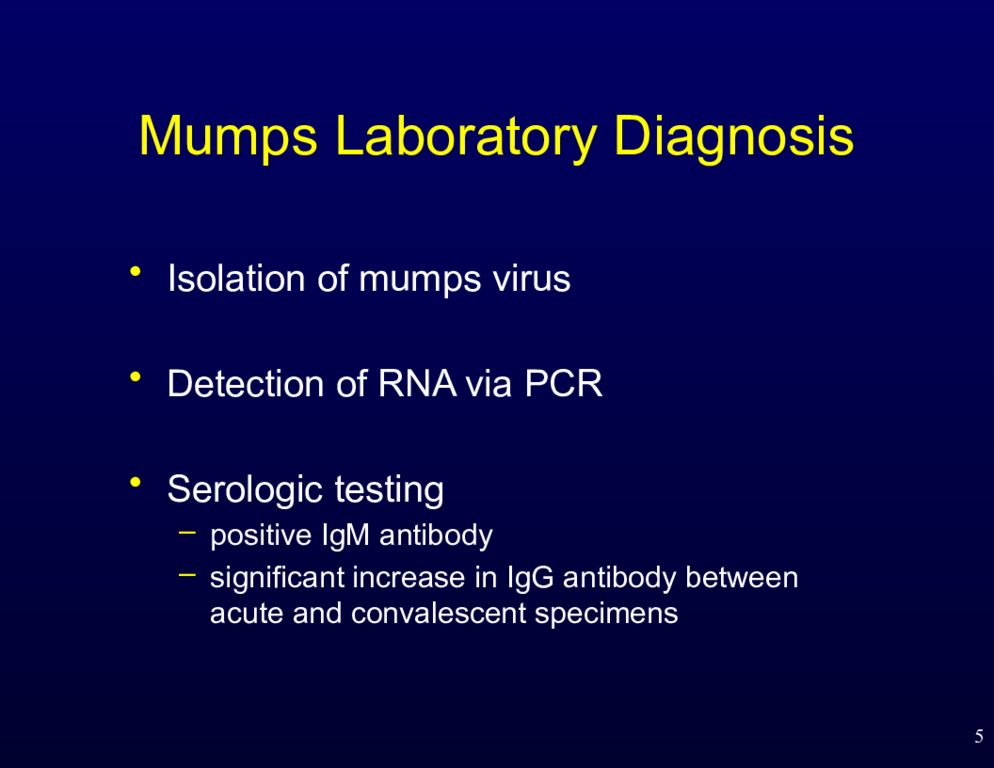
5 Mumps Laboratory Diagnosis Isolation of mumps virus Detection of RNA via PCR Serologic testing positive IgM antibody significant increase in IgG antibody between acute and convalescent specimens
Слайд 7: Mumps Pathogenesis
7 Mumps Pathogenesis Respiratory transmission of virus (droplet nuclei) Subclinical infections may transmit Replication in nasopharynx and regional lymph nodes Viremia 12-25 days after exposure with spread to tissues Infective dose – medium. Typical 2 o attack rate of 31%
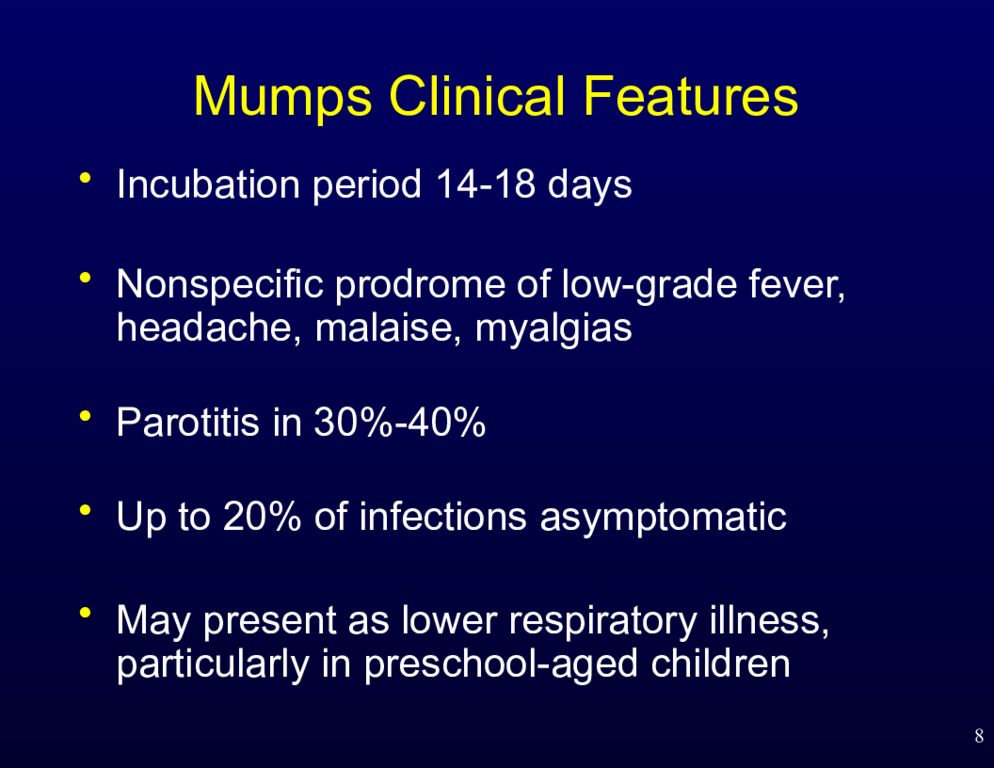
Слайд 8: Mumps Clinical Features
8 Mumps Clinical Features Incubation period 14-18 days Nonspecific prodrome of low-grade fever, headache, malaise, myalgias Parotitis in 30%-40% Up to 20% of infections asymptomatic May present as lower respiratory illness, particularly in preschool-aged children
Слайд 9: Mumps Epidemiology
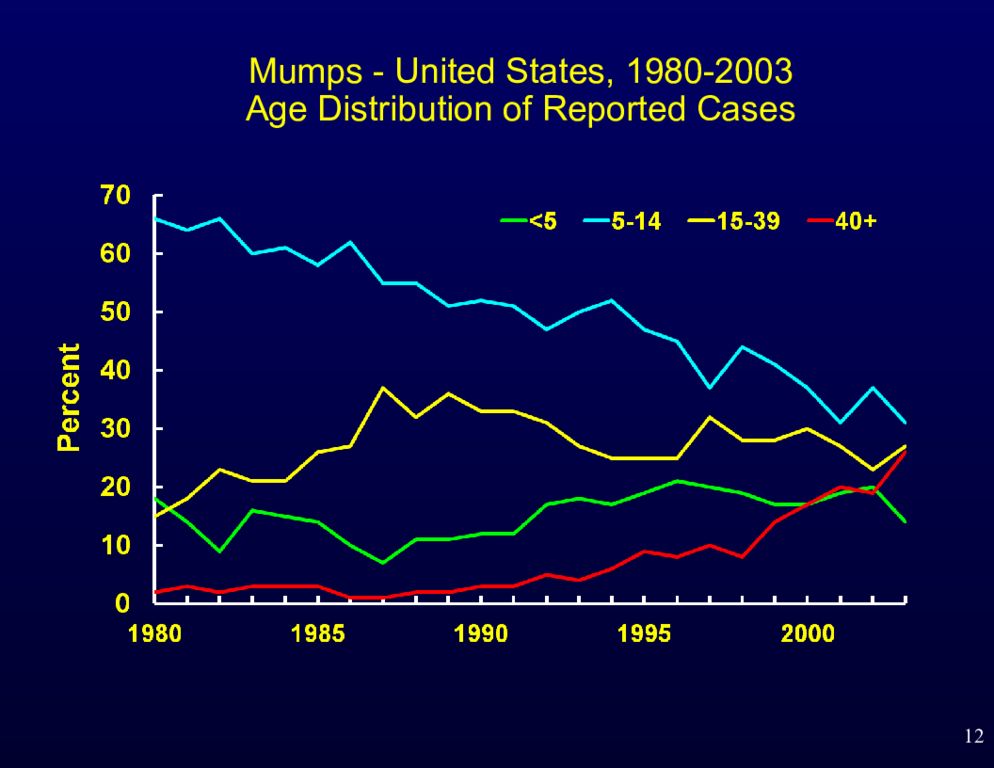
9 Mumps Epidemiology Reservoir Human Temporal pattern Peak in late winter and spring Communicability Three days before to four days after onset of active disease
Слайд 13: Mumps Immunity
13 Mumps Immunity Born before 1957 Documentation of physician- diagnosed mumps Serologic evidence of mumps immunity Documentation of adequate vaccination
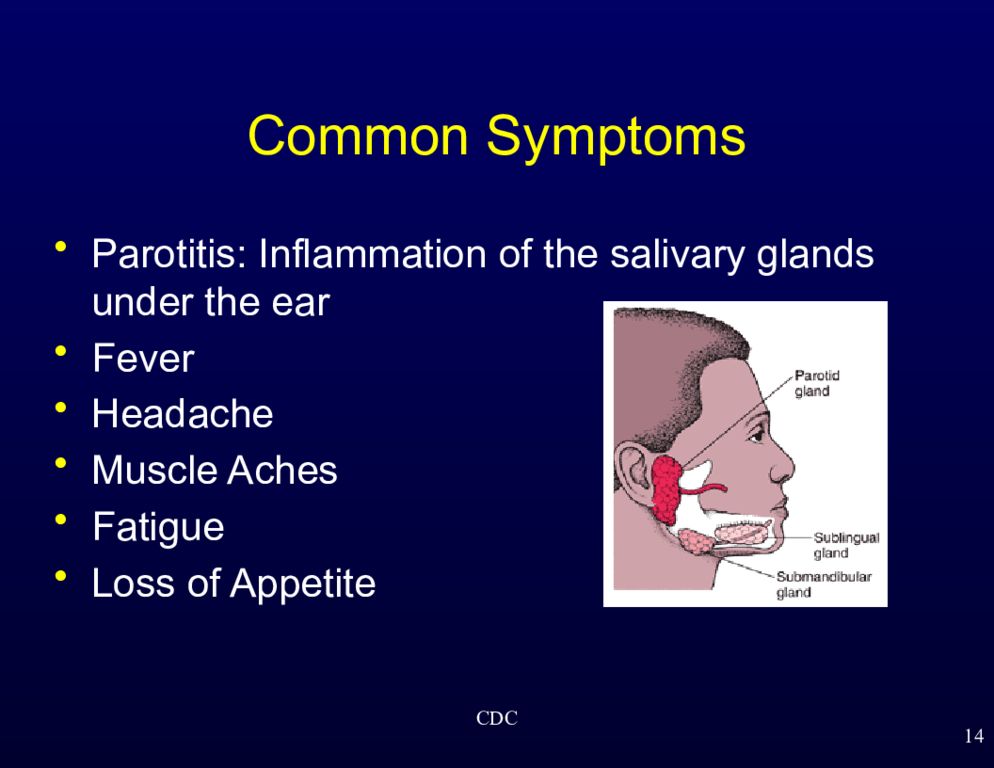
Слайд 14: Common Symptoms
Parotitis: Inflammation of the salivary glands under the ear Fever Headache Muscle Aches Fatigue Loss of Appetite 14 CDC
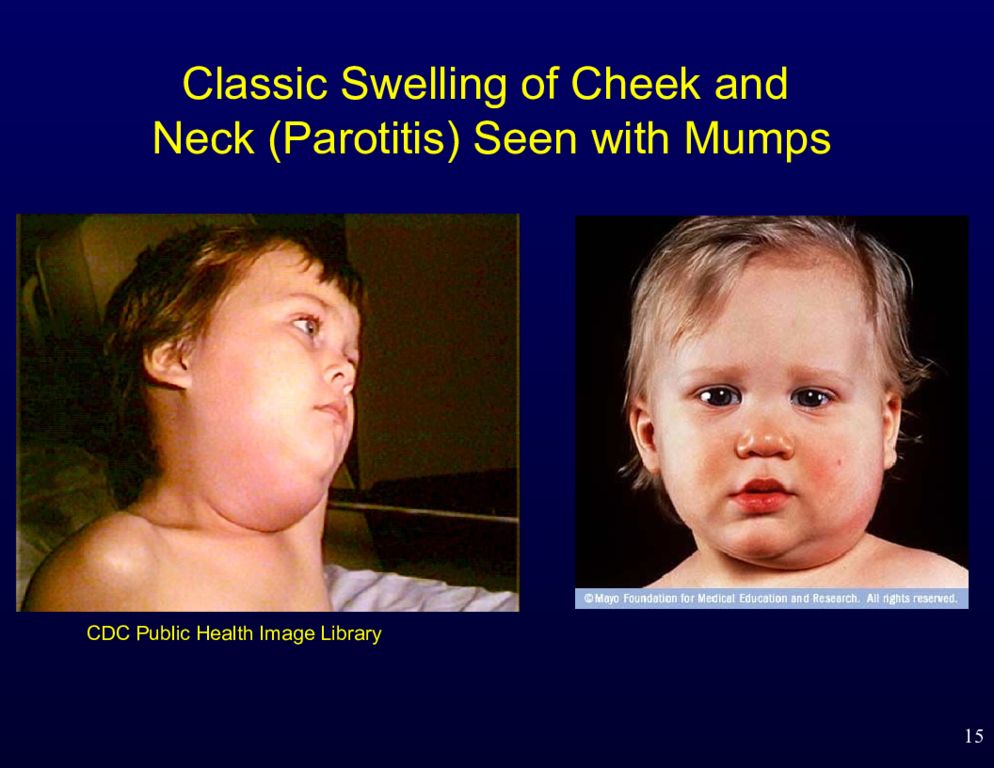
Слайд 15: Classic Swelling of Cheek and Neck (Parotitis) Seen with Mumps
15 Classic Swelling of Cheek and Neck (Parotitis) Seen with Mumps CDC Public Health Image Library
Слайд 16: Rare but Serious Complications
Inflammation of the: Testicles Pancreas Ovaries Breast Encephalitis or Meningitis Deafness Male infertility 16 CDC
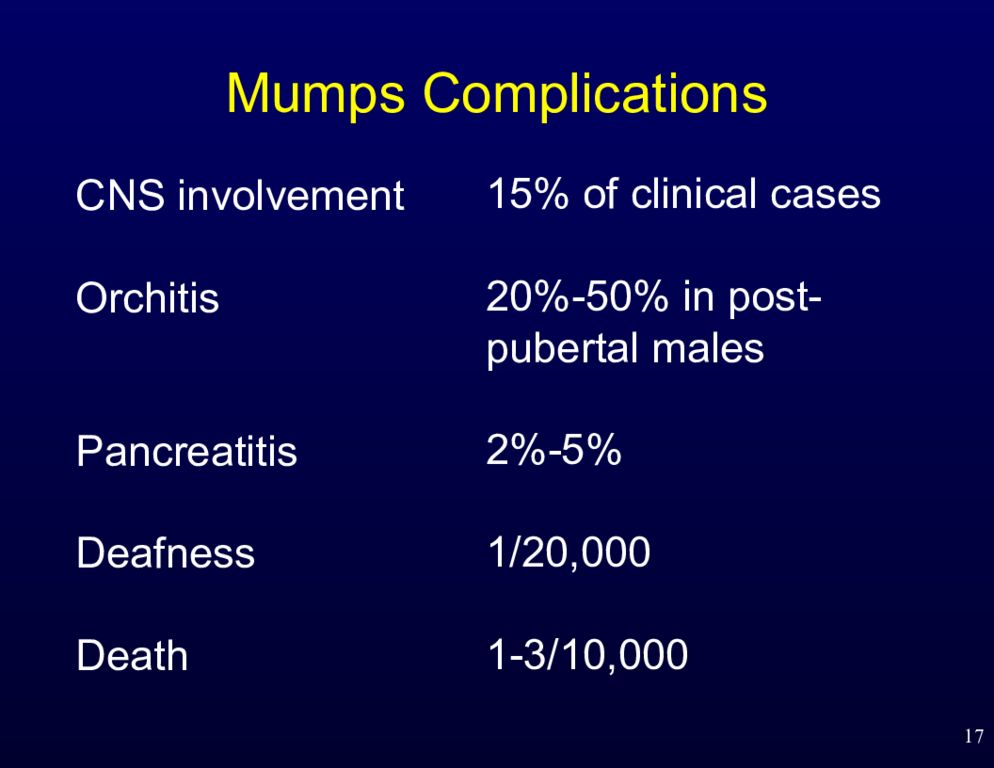
Слайд 17: Mumps Complications
17 CNS involvement Orchitis Pancreatitis Deafness Death 15% of clinical cases 20%-50% in post- pubertal males 2%-5% 1/20,000 1-3/10,000 Mumps Complications
Слайд 18: Epidemiological Characteristics
Persistence in Environment: Readily inactivated by UV light, formalin, heat, acid High risk groups: Post pubertal males – orchitis, atrophy, cancer? Persons with diabetes Epidemic Potential: High – epidemic parotitis Challenges Imported cases immunity may not be lifelong
Слайд 19: Mumps Vaccine
19 Mumps Vaccine Effectiveness 88% after two doses Duration of Immunity Generally lifelong Schedule 1 st dose at 12-15 months, 2 nd after age 4 and for adults at higher risk Administered with measles and rubella (MMR) Developed from the Jeryl Lynn strain (genotype B)
Слайд 20: Vaccine Side Effects
Brief achy joints (up to 25% of women) Uncommon in children Uncommon symptoms (less than 1%) Fever Rash Itching Extremely rare events (less than 1/100,000) Brief orchitis Mild parotitis Encephalitis (~1 in 800,000 doses) 20
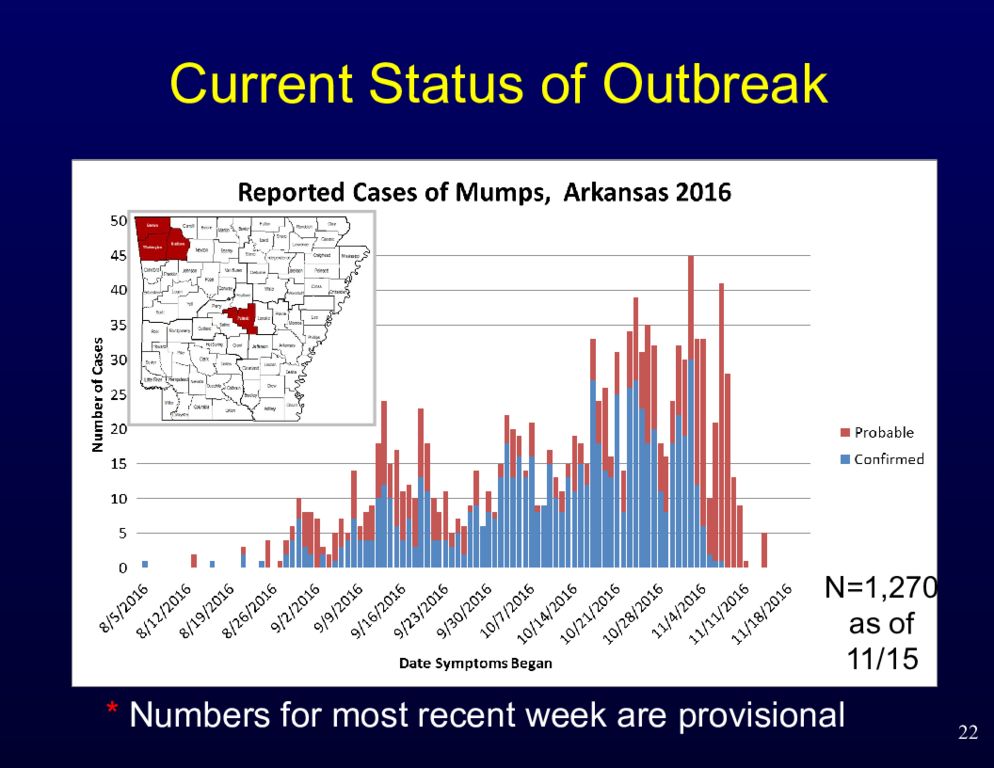
Слайд 22: Current Status of Outbreak
22 * Numbers for most recent week are provisional N=769 as of 10/26 N=1,270 as of 11/15
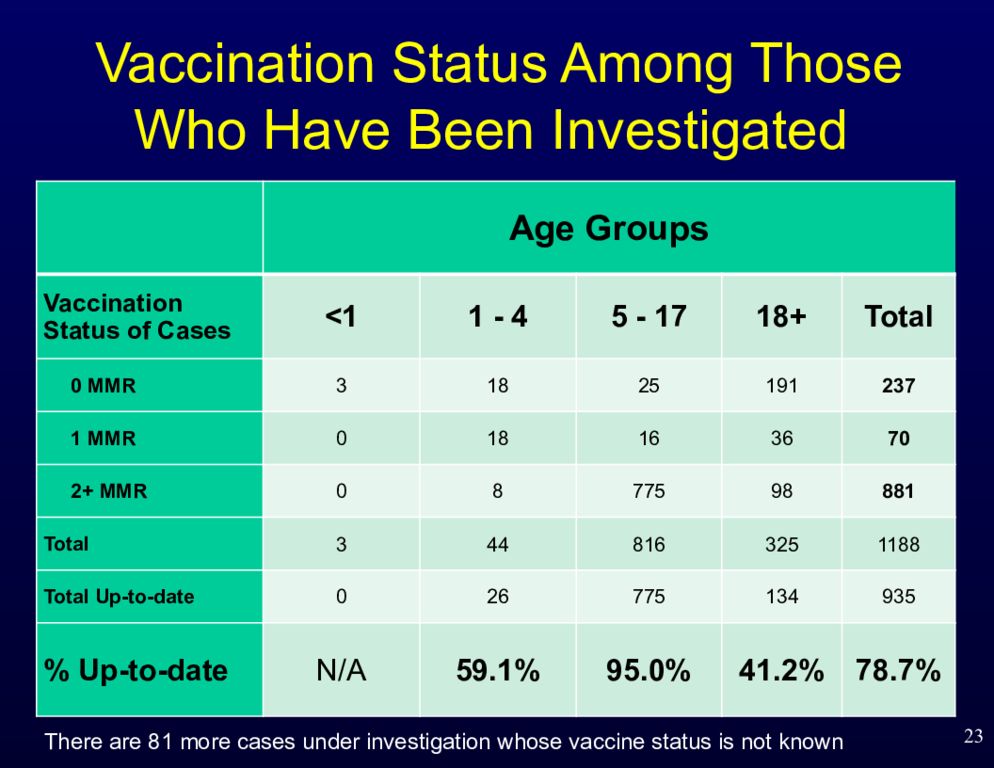
Слайд 23: Vaccination Status Among Those Who Have Been Investigated
Age Groups Vaccination Status of Cases <1 1 - 4 5 - 17 18+ Total 0 MMR 3 18 25 191 237 1 MMR 0 18 16 36 70 2 + MMR 0 8 775 98 881 Total 3 44 816 325 1188 Total Up-to-date 0 26 775 134 935 % Up-to-date N/A 59.1% 95.0% 41.2% 78.7% 23 There are 81 more cases under investigation whose vaccine status is not known
Слайд 24: Benefits of 2 nd (or 3 rd ) MMR shot
9 fold lower risk of illness Milder disease if you do get mumps Much less likely to transmit to others 24
Слайд 25: What is ADH Doing?
Using the best evidence to control the outbreak Interviewing all suspect cases and contacts Excluding under-vaccinated kids from school Performing vaccination clinics (65 complete, 4 others scheduled) 4,622 vaccines provided to date Providing advice to doctors and schools Communicating to many audiences 25
Слайд 27: Questions / Comments
Appreciation to those that have been involved in the outbreak response! 27
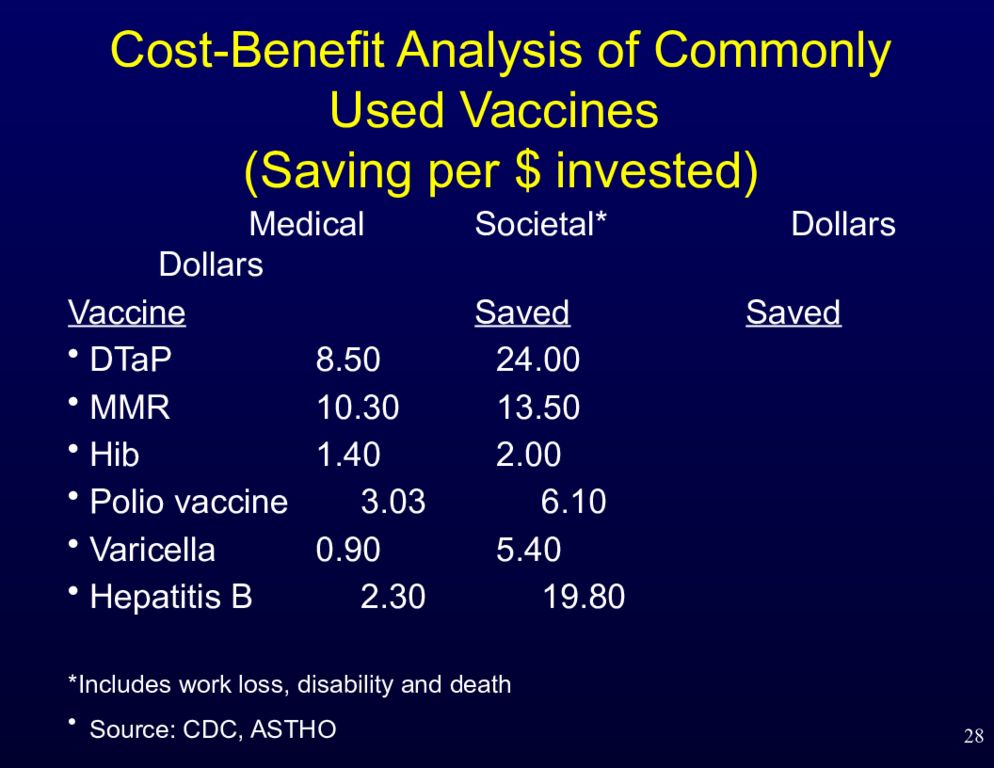
Слайд 28
28 Medical Societal* Dollars Dollars Vaccine Saved Saved DTaP 8.50 24.00 MMR 10.30 13.50 Hib 1.40 2.00 Polio vaccine 3.03 6.10 Varicella 0.90 5.40 Hepatitis B 2.30 19.80 *Includes work loss, disability and death Source: CDC, ASTHO Cost-Benefit Analysis of Commonly Used Vaccines (Saving per $ invested)
Последний слайд презентации: Update on Mumps and Current Status of Outbreak in NW Arkansas: Adult I mmunization Recommendations from ACIP
Generally recommended for all adults Influenza (every year) Tdap (once as adult then Td booster every ten years Chickenpox (AKA varicella) Need physician diagnosed illness, immunity, or 2 doses HPV (up to 26 years old, 3 doses) Shingles (AKA zoster) (once ≥ 60 years old) MMR (up to 59 years old) Immunity or 2 doses after 1967, unless born prior to 1957 Pneumococcal vaccine (two different vaccines ≥ 65 years old) Recommended for certain subgroups (see CDC website for detail) Hepatitis A (2 doses) Hepatitis B (3 doses) Pneumococcal vaccine (below age 65) Meningococcal vaccine (2 doses)