Первый слайд презентации: Viruses as agents of foodborne illness
Слайд 2: What is a virus ?
Viruses are very small infectious microorganisms composed of a DNA or RNA genome enclosed within a protein coat. Unlike bacteria, viruses can only multiply inside living cells of other organisms.
Слайд 3: What viruses commonly cause foodborne illness?
The majority of viral foodborne illnesses are caused by a few types of viruses including: Norovirus (most common viral foodborne illness, which causes gastroenteritis, a medical condition characterised by diarrhoea, vomiting and abdominal pain)
Слайд 6: How are foodborne viruses spread?
The origin of all foodborne viruses are the intestines of humans and animals. As such viruses are often shed in faeces or other body fluids. As viruses do not replicate in foods, foodborne transmission of viruses occurs through:
Слайд 7: How are foodborne viruses spread?
1) Contamination of food by infected food handlers due to poor hygienic practices 2) Contact of food with animal waste, human sewage or sewage-polluted water. 3) Consumption of products of animal origin contaminated with viruses (e.g. meat, fish etc.)
Слайд 8: The main foods associated with viral foodborne illnesses
Shellfish (e.g. Oysters, mussels), crustaceans and their products which are farmed and/or harvested in waters near human sewage outlets (e.g. waste-water treatment plants)
Слайд 9: The main foods associated with viral foodborne illnesses
Fruit/vegetables grown on land fertilised with animal waste or irrigated with contaminated water. Undercooked meats such as pork.
Слайд 10: O utbreaks of viral foodborne illness
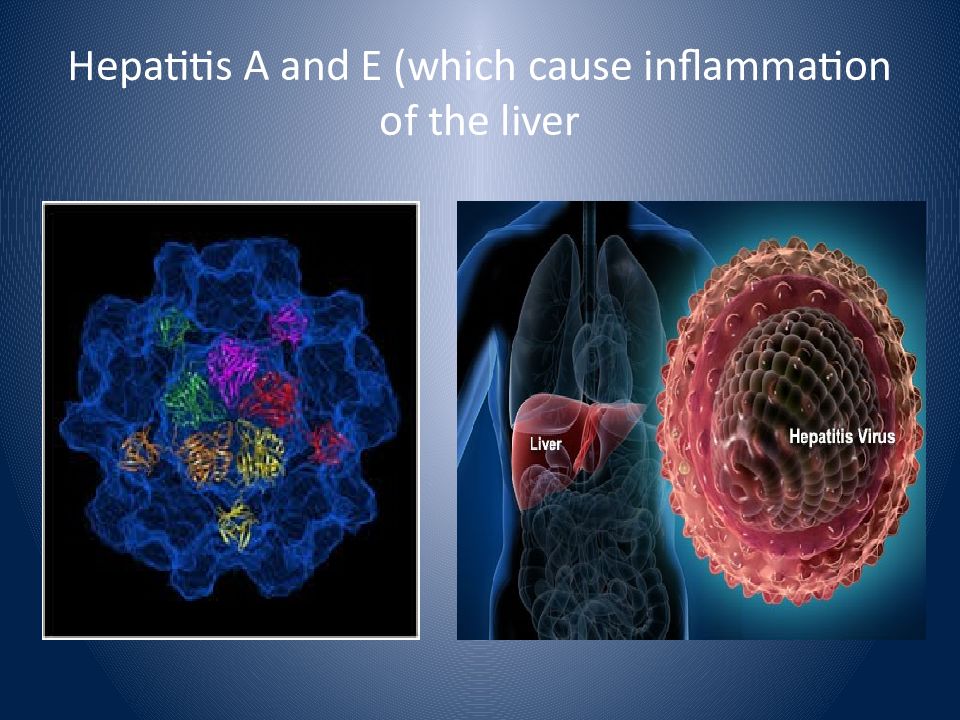
In 1988, clams harvested from polluted waters in China were eaten raw and caused 300,000 cases of hepatitis. In the EU, in 2008, crustaceans, shellfish and associated products were most frequently implicated in outbreaks of foodborne viral illness I n 2013 one of the most notable issues was foodborne outbreaks due to the presence of hepatitis A virus found in berry mixes and strawberries which affected 315 people across 11 European countries.
Слайд 11: How are viruses in food detected?
Detection of foodborne viruses is difficult and requires a different approach to the detection of most foodborne bacteria. As viruses cannot be cultured in the laboratory like bacteria, their detection often requires molecular techniques with various steps to extract, purify and identify. It is thought that the majority of foodborne viral illness is under diagnosed and unreported.1,2 This is often because people do not go to a doctor when they have mild gastroenteritis, which can be associated with some foodborne viral illness.
Слайд 12: How can foodborne viral illnesses be prevented and controlled?
1) Training and awareness in good hygiene practices (e.g. hand washing, washing and proper handling of fruits and vegetables, adequate storage of food in the refrigerator, thorough cooking of pork meat). 2) Employees suffering from illness should be restricted from food service work. 3) Use of clean water to irrigate crops, particularly ready to eat crops 4) Avoiding the use of animal manures on crops, particularly ready to eat crops, 5)Farming of shellfish in clean seawater protected from sewage contamination.
Последний слайд презентации: Viruses as agents of foodborne illness: Conclusion
While a number of viruses are associated with foodborne illness and its transmission, norovirus and hepatitis viruses are of primary concern. Increased awareness of the importance of good food hygiene practice and training in the production and handling of foods is necessary to minimise the transmission of foodborne viral illnesses. Improving the methods of detection of viruses will allow for better monitoring of viruses in food and help improve the safety of those foods commonly associated with foodborne viral illnesses.