Первый слайд презентации: PEDAGOGY / Education
Слайд 2: What is it?
The word comes from the Greek (paidag ōgeō ); in which means "child" and ( ágō ) means "lead"; so it literally means "to lead the child". Teaching or the activity of educating or instructing and the methods used to instruct.
Слайд 3: What is it?
Pedagogy is defined as many different types and variations of teaching. There are many different ways in which students learn and teachers teach. Some of these ways are: discovery learning, group learning, distance learning, and independent study. S imply - it’s about teaching.
Слайд 4: What is it?
Another way to explain it is by referring to: the art of teaching - the responsive, creative, intuitive part; the craft of teaching - skills and practice; the science of teaching - research-informed decision making and the theoretical underpinning.
Education and psychology are interdependent ; Psychology gives education the theory of individual differences that every person has different mental ability and learns with different pace; Psychology is the study of human behaviour while Education is the process of modifying human behaviour SO both deal with human behaviour in different ways; Problem solving.
Psychology suggests use of different methods in teaching learning process to achieve better result; Psychology emphasis on Motivation and readiness in classroom; Psychology introduces new theories of learning in education; Psychology emphasis on activity base teaching learning process; Psychology emphasis on use of Visual Aid in teaching learning process etc.
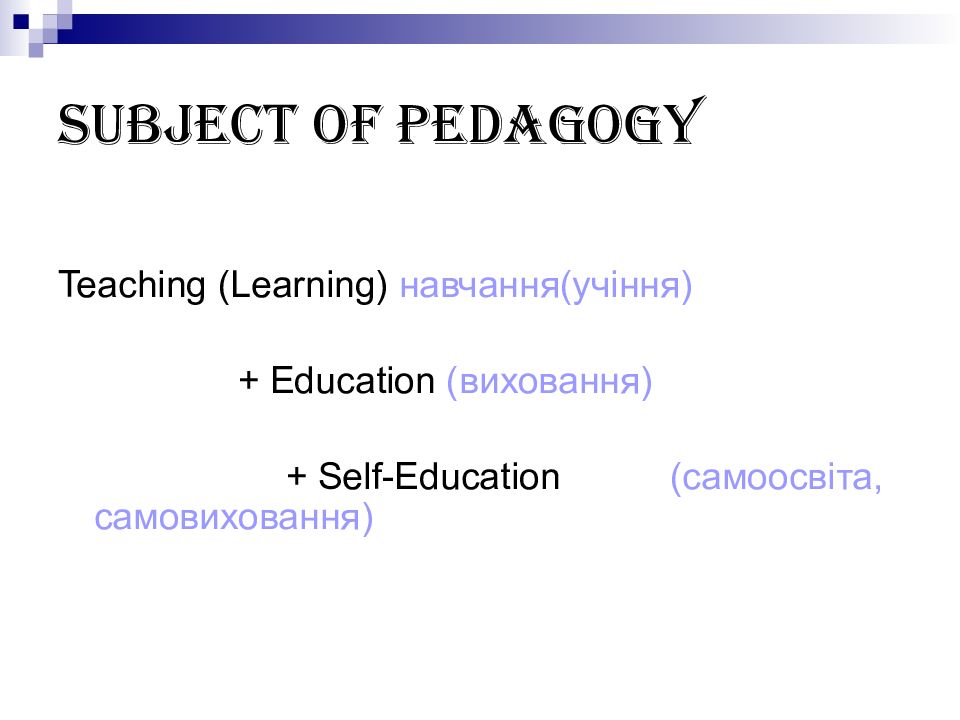
Слайд 7: Subject of pedagogy
Teaching (Learning) навчання(учіння) + Education (виховання) + Self-Education (самоосвіта, самовиховання)
Слайд 8: Teaching methods in Education
Lecture; Case study; Socratic; Group; Problem; Seminar; Tutorial, individual presentations, role play etc.
Слайд 9: Lecture Method
Merits: Best method for large number of students. Demerits: Students remain passive; Lecture seldom receives feedback; One way process of communication; Virtually no scope for students to think.
Слайд 10: Case study method
It is a description of an actual situation, commonly involving a decision, a challenge, an opportunity, a problem or an issue faced by a person or persons in an organization; It is active learning and creative thinking.
Слайд 11: Socratic method
Pioneered by Socrates; Students come prepared by reading; Teacher asks a series of questions to students; Questions stimulating rational thinking; There may be more than one correct answer; Students come to legal principals by there own;
Слайд 12: Group discussion
Group of 5-10 students; Teacher’s role - peripheral; Group leader’s role - important. Merits: Interactive method promoting active learning; Lots of ideas and experiences from a group. Demerits: Transmission of information is slow.
Слайд 13: Problem method
Students are given practical problems; It provides stimulus to students’ interest; Students have to apply their mind.
Слайд 14: Seminar methods
Students to prepare a brief paper; Paper presentation before classmates followed by discussion; Students’ capacity for research and creative thinking developed; Teacher's role is that of the guide; Student based method.
Слайд 15: Tutorial method
Intensive tuition given by tutor to small number of students; Interactive method of teaching; 8-12 students; Informal atmosphere; Free and frank exchange between students and teacher; Individual attention to the students.
Слайд 16: Effective teaching
How do people learn? Information processing, cognitive psychology, learning theory: pay attention to information; new information related to prior knowledge; new information is stored; knowledge is retrieved at appropriate time.
Слайд 17: Effective teaching
A new information should be conveyed in such a way that the students grasp the knowledge efficiently and can apply it correctly in new situations.
Слайд 18: What can make teaching non-effective?
Problems in transmission/ techniques/ strategies Classroom management/ administration Personal issues Instructor<-->student Student<-->student Solution Being proactive
Слайд 19: Effective learning is promoted through:
active Learning; collaborative Learning; responsibility in Learning; Learning cycle: DO – REVIEW – LEARN – APPLY…………
Слайд 20: Effective learning
Learning from others - explanatory instruction; Learning by discovery - guided inquiry instruction; Learning by doing - activities for applying-and-exploring.
Слайд 21: Methods of education
They are interdependent: Belief; Sample; Stimulation; Forcing; Competition; Exercise / Practice.
Слайд 22: The main methods of self-education
Self-obligation; Self-affirmation; Self-organization; Self-control; Self-report; Relation to him/herself; Imitation of the example; Self-stimulation; Self-forcing; Auto-training. Including: Favorable conditions; Psychological condition.
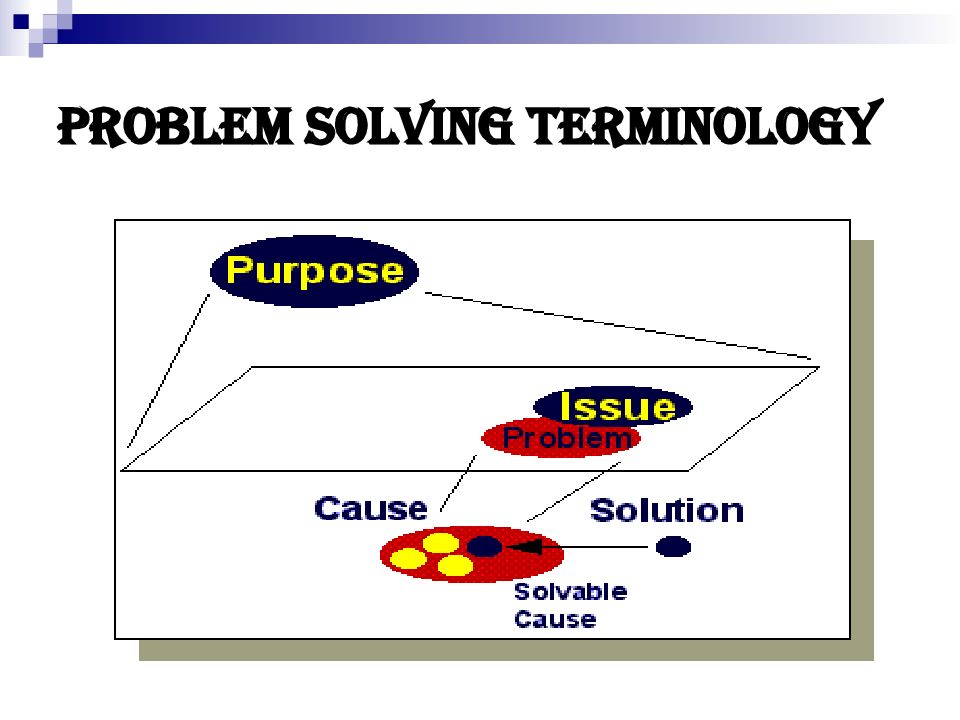
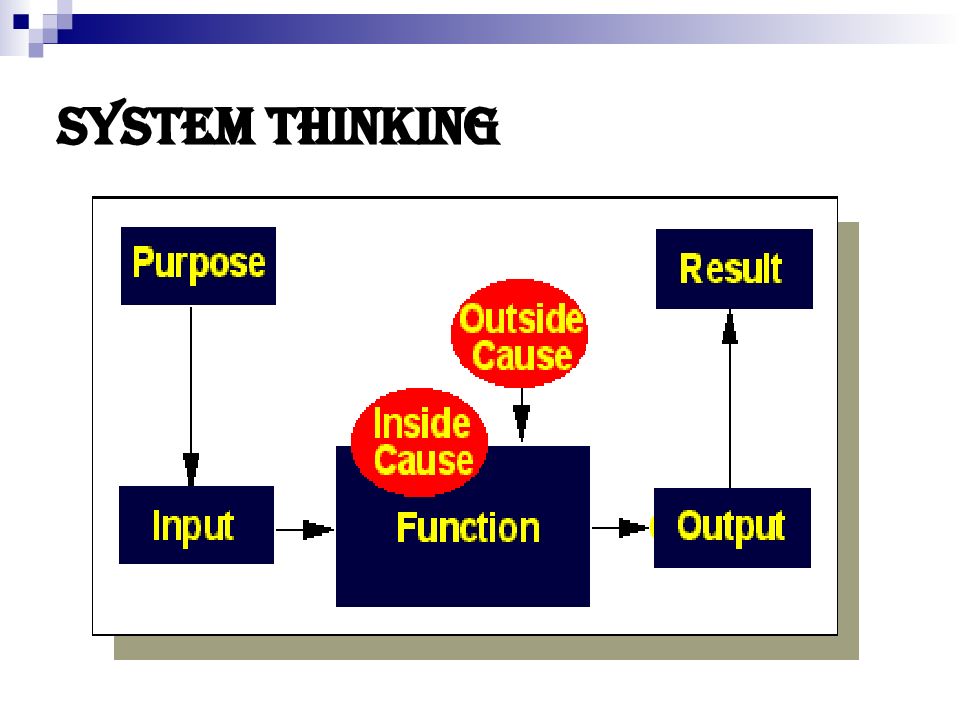
Слайд 24: Problem-Solving Skills in Education and Life
In common language, a problem is an unpleasant situation, a difficulty. In education - a question raised for inquiry, consideration, or solution. "A solution, to be a solution, must share some of the problems characteristics." Richard L Kempe
Слайд 25: Problem-Solving Skills in Education and Life
Here is one of many possible models of problem solving: Problem identification - What is my concern? Goal definition - What do I want to achieve or change? Brainstorming - What can I do? Consequences - What might happen? Decision - How should I do it? Implementation - Do it! Evaluation - Did it work?
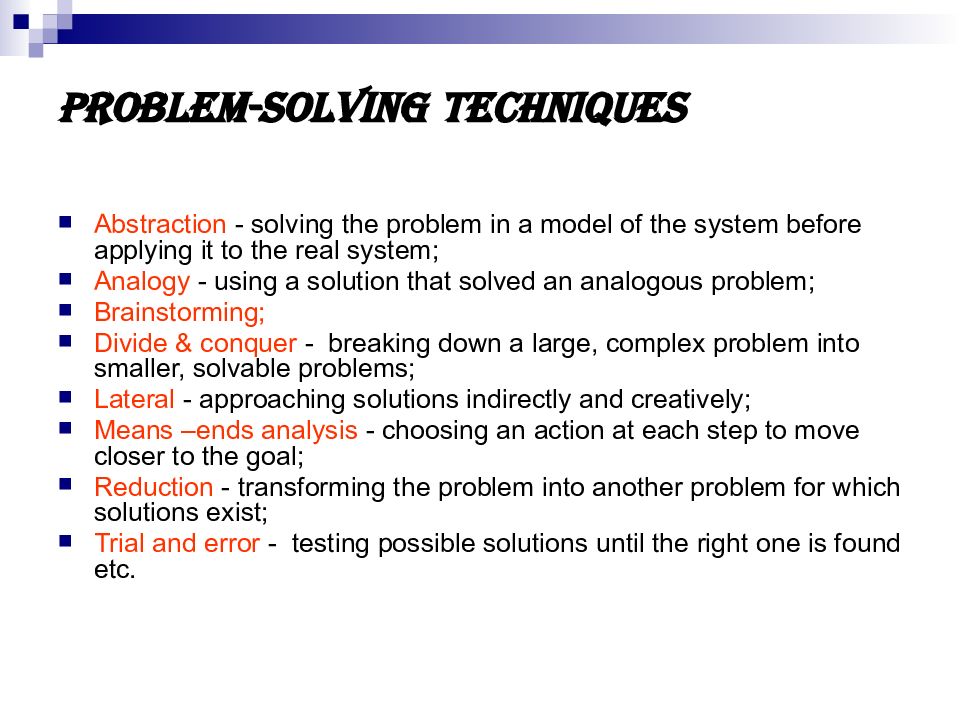
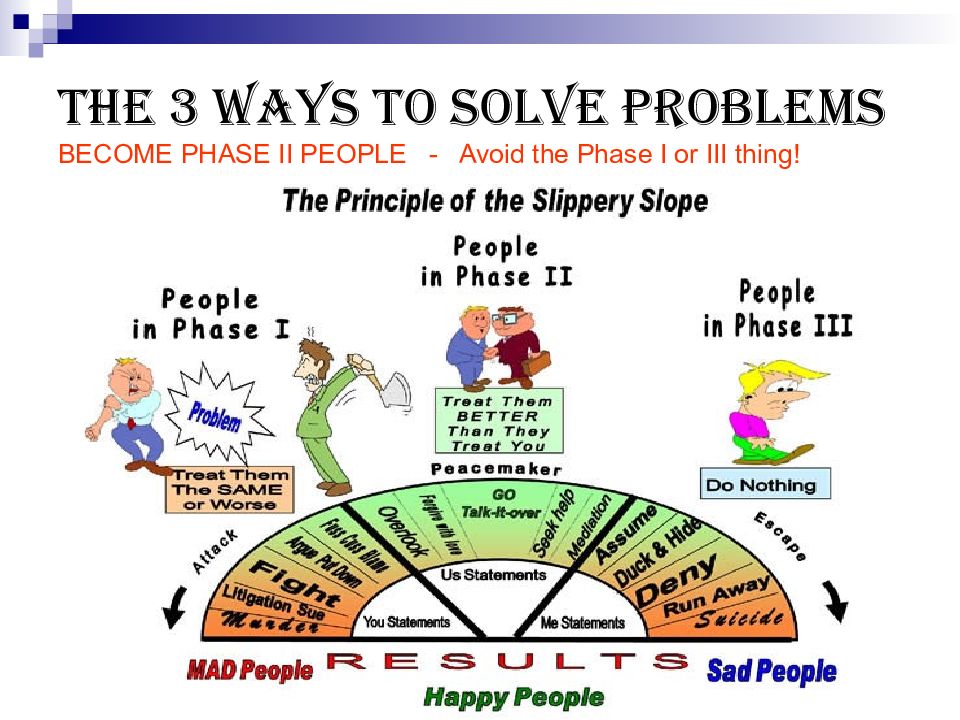
Слайд 26: Problem-solving techniques
Abstraction - solving the problem in a model of the system before applying it to the real system; Analogy - using a solution that solved an analogous problem; Brainstorming; Divide & conquer - breaking down a large, complex problem into smaller, solvable problems; Lateral - approaching solutions indirectly and creatively; Means –ends analysis - choosing an action at each step to move closer to the goal; Reduction - transforming the problem into another problem for which solutions exist; Trial and error - testing possible solutions until the right one is found etc.
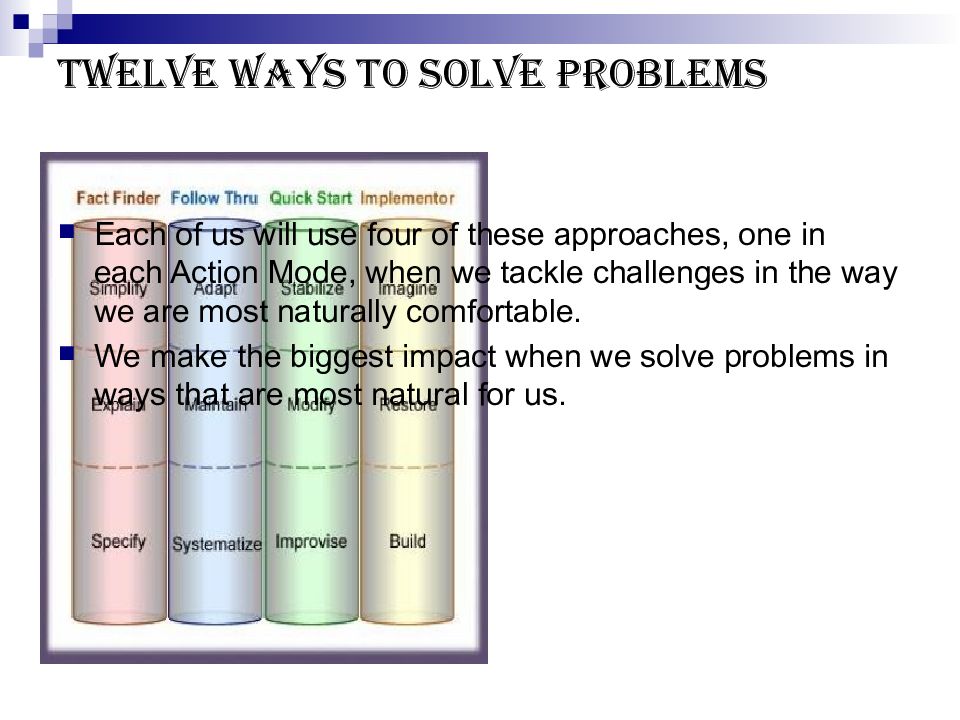
Слайд 29: Twelve Ways to Solve Problems
Each of us will use four of these approaches, one in each Action Mode, when we tackle challenges in the way we are most naturally comfortable. We make the biggest impact when we solve problems in ways that are most natural for us.